Moors murders
Ian Brady and Myra Hindley | |
|---|---|
 Brady and Hindley, October 1965 | |
| Born | Ian Duncan Stewart Myra Hindley Brady: 2 January 1938 Hindley: 23 July 1942 |
| Died | Hindley: 15 November 2002 (aged 60) Brady: 15 May 2017 (aged 79) |
| Cause of death | Hindley: Bronchial pneumonia Brady: Cor pulmonale caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Other names | The Moors Murderers |
| Conviction(s) | Murder |
| Criminal penalty | Life imprisonment (whole life tariff) |
| Details | |
| Victims | 5 |
Span of crimes | 12 July 1963 – 6 October 1965 |
| Country | United Kingdom |
Date apprehended | Brady: 7 October 1965 Hindley: 11 October 1965 |
The Moors murders were carried out by Ian Brady and Myra Hindley between July 1963 and October 1965, in and around Manchester, England. The victims were five children aged between 10 and 17—Pauline Reade, John Kilbride, Keith Bennett, Lesley Ann Downey and Edward Evans—at least four of whom were sexually assaulted. Two of the victims were discovered in graves dug on Saddleworth Moor; a third grave was discovered there in 1987, more than twenty years after Brady and Hindley's trial. The body of a fourth victim, Keith Bennett, is also suspected to be buried there, but despite repeated searches it remains undiscovered.
The police were initially aware of only three killings, those of Edward Evans, Lesley Ann Downey and John Kilbride. The investigation was reopened in 1985, after Brady was reported in the press as having confessed to the murders of Pauline Reade and Keith Bennett. Brady and Hindley were taken separately to Saddleworth Moor to assist the police in their search for the graves, both by then having confessed to the additional murders.
Characterised by the press as "the most evil woman in Britain",[1] Hindley made several appeals against her life sentence, claiming she was a reformed woman and no longer a danger to society, but was never released. She died in 2002, aged 60. Brady was declared criminally insane in 1985 and confined in the high-security Ashworth Hospital. He made it clear that he never wished to be released, and repeatedly asked to be allowed to die. He died in 2017, at Ashworth, aged 79.
The murders were the result of what Malcolm MacCulloch, professor of forensic psychiatry at Cardiff University, called a "concatenation of circumstances".[2] The trial judge, Mr Justice Fenton Atkinson, described Brady and Hindley in his closing remarks as "two sadistic killers of the utmost depravity".[3]
Victims

The full extent of Brady and Hindley's crimes did not come to light until their confessions in 1985, as both had until then maintained their innocence.[failed verification][4] Their first victim was 16-year-old Pauline Reade, a neighbour of Hindley's who disappeared on her way to a dance at the British Railways Club in Gorton, Manchester, on 12 July 1963.[5] That evening, Brady told Hindley that he wanted to "commit his perfect murder". He told her to drive her van around the local area while he followed behind on his motorcycle; when he spotted a likely victim he would flash his headlight, and Hindley was to stop and offer that person a lift. Brady and Hindley provided different accounts of the murder.[4]
Driving down Gorton Lane, Brady saw a young girl walking towards them, and signalled Hindley to stop, which she did not do until she had passed the girl. Brady drew up alongside on his motorbike, demanding to know why she had not offered the girl a lift, to which Hindley replied that she recognised her as Marie Ruck, a near neighbour of her mother.[failed verification] Shortly after 8:00 pm,[failed verification] continuing down Froxmer Street,[failed verification][6] Brady spotted a girl wearing a pale blue coat and white high-heeled shoes walking away from them, and once again signalled for the van to stop.[4] Hindley recognised the girl as Pauline Reade; a friend of her younger sister, Maureen.[failed verification][7] Reade got into the van with Hindley, who then asked if she would mind helping to search for an expensive glove she had lost on Saddleworth Moor. Reade said she was in no great hurry, and agreed. At 16, Pauline Reade was older than Marie Ruck, and Hindley believed that there would be less of an outcry over the disappearance of a teenager than there would over a child of seven or eight. When the van reached the moor, Hindley stopped and Brady arrived shortly afterwards on his motorcycle. She introduced him to Reade as her boyfriend, and said that he had also come to help find the missing glove. Hindley claimed Brady took Reade onto the moor while Hindley waited in the van. Brady returned alone after about 30 minutes, and took Hindley to the spot where Reade lay dying.[failed verification] Her throat had been cut twice with a large knife.[failed verification] The larger of these wounds was a four-inch incision across her voice box, and the collar of Reade's coat had been deliberately[failed verification] pushed into this wound.[8] He told her to stay with Reade while he fetched a spade he had hidden nearby on a previous visit to the moor, to bury the body. Hindley noticed that "Pauline's coat was undone and her clothes were in disarray ... She had guessed from the time he had taken that Brady had sexually assaulted her."[failed verification][4] Brady's account differed from Hindley's. He claimed that Hindley was not only there at the scene, but that she assisted him with the sexual assault on Pauline.[9] Returning home from the moor in the van—they had loaded the motorcycle into the back—Brady and Hindley passed Reade's mother, Joan, accompanied by her son, Paul, searching the streets for Pauline.[10]
Accompanied by Brady, Hindley approached 12-year-old John Kilbride in the early evening of 23 November 1963, at a market in Ashton-under-Lyne and offered him a lift home on the pretext that his parents would be worried about him being out so late. With the added inducement of a bottle of sherry,[failed verification] Kilbride readily agreed to get into the Ford Anglia car that Hindley had hired. Brady told Kilbride that the sherry was at their home, and they would have to make a detour to collect it. On the way he suggested that they take another detour, to search for a glove he said that Hindley had lost on the moor.[11] When they reached the moor Brady took Kilbride with him while Hindley waited in the car[failed verification]. Brady sexually assaulted Kilbride and attempted to slit his throat with a six-inch serrated blade before fatally strangling him with a piece of string, possibly a shoelace.[12]
Twelve-year-old Keith Bennett vanished on his way to his grandmother's house in Longsight, Manchester, early in the evening of 16 June 1964,[13] four days after his birthday[failed verification]. Hindley lured him into her Mini Pick-up—which Brady was sitting in the back of—by asking for the boy's help in loading some boxes, after which she said she would drive him home}}. She drove to a lay-by on Saddleworth Moor as she and Brady had previously arranged, and Brady went off with Bennett, supposedly looking for a lost glove. Hindley kept watch,[vague] and after about 30 minutes or so Brady reappeared, alone and carrying a spade that he had hidden there earlier. When Hindley asked how he had killed Bennett, Brady said that he had sexually assaulted the boy and strangled him with a piece of string.[14]
Brady and Hindley visited a fairground on 26 December 1964, in search of another victim, and noticed 10-year-old Lesley Ann Downey standing beside one of the rides. When it became apparent that she was on her own, they approached her and deliberately dropped some of the shopping[failed verification] they were carrying close to her, before asking for the girl's help to carry some of the packages to their car, and then to their home. Once inside the house Downey was undressed, gagged and forced to pose for photographs before being raped and killed, perhaps[failed verification] strangled with a piece of string. Hindley maintained[failed verification] that she went to fill a bath for Downey and found her dead (presumably killed by Brady) when she returned. In Chris Cowley's book Face to Face with Evil: Conversations with Ian Brady, Brady states that it was Hindley who killed Downey. The following morning Brady and Hindley drove with Downey's body to Saddleworth Moor,[15] where she was buried, naked with her clothes at her feet, in a shallow grave.[failed verification].[16]
On 6 October 1965, Brady met 17-year-old apprentice engineer Edward Evans at Manchester Central railway station and invited him to his home at 16 Wardle Brook Avenue in Hattersley, Cheshire, where Brady beat him with an axe and strangled him to death[failed verification].[17]
Murder of Edward Evans

The attack on Edward Evans was witnessed by[failed verification] Hindley's 17-year-old brother-in-law, David Smith, the husband of her younger sister Maureen. The Hindley family had not approved of Maureen's marriage to Smith,[failed verification] who had several criminal convictions, including actual bodily harm and housebreaking, the first of which, wounding with intent, occurred when he was 11.[18] Throughout the previous year Brady had been cultivating a friendship with Smith,[failed verification] who had become "in awe" of the older man, something that increasingly worried Hindley, as she felt it compromised their safety[failed verification].[19]
On the evening of 6 October 1965, Hindley drove Brady to Manchester Central railway station, where she waited outside in the car while he selected their victim. After a few minutes Brady reappeared in the company of Edward Evans, to whom he introduced Hindley as his sister. After they had driven back home and relaxed over a bottle of wine, Brady sent Hindley to fetch her brother-in-law. When they got back to the house Hindley told Smith to wait outside for her signal, a flashing light. When the signal came, Smith knocked on the door and was met by Brady, who asked if he had come for "the miniature wine bottles".[17] Brady led Smith into the kitchen and left him there, saying that he was going to collect the wine. A few minutes later, Smith heard a scream, followed by Hindley shouting loudly for him to come and help.[20] Smith entered the living room to find Brady repeatedly striking Evans with the flat of an axe, and watched as he then throttled Evans with a length of electrical cord.[21] Evans's body was too heavy for Smith to carry to the car on his own—Brady had sprained his ankle in the struggle—so they wrapped it in plastic sheeting and put it in the spare bedroom.[22]
Smith agreed to meet Brady the following evening to dispose of Evans's body.[22] But after he returned home and related to Maureen what he had seen, she insisted that he call the police, which they did from a nearby[failed verification] phone box (bringing a screwdriver and knife in case Brady should confront them)[failed verification].[23] Smith told the police that:
[Brady] opened the door and he said in a very loud voice for him ..."Do you want those miniatures?" I nodded my head to say yes and he led me into the kitchen ... and he gave me three miniature bottles of spirits and said: "Do you want the rest?" When I first walked into the house, the door to the living room ... was closed. ... Ian went into the living room and I waited in the kitchen. I waited about a minute or two then suddenly I heard a hell of a scream; it sounded like a woman, really high-pitched. Then the screams carried on, one after another really loud. Then I heard Myra shout, "Dave, help him," very loud. When I ran in I just stood inside the living room and I saw a young lad. He was lying with his head and shoulders on the couch and his legs were on the floor. He was facing upwards. Ian was standing over him, facing him, with his legs on either side of the young lad's legs. The lad was still screaming ... Ian had a hatchet in his hand ... he was holding it above his head and he hit the lad on the left side of his head with the hatchet. I heard the blow, it was a terrible hard blow, it sounded horrible.[24]
Arrest
Early on the morning of 7 October 1965, shortly after Smith's call, Superintendent Bob Talbot of the Cheshire Police[failed verification] arrived at the back door of 16 Wardle Brook Avenue, wearing a borrowed[failed verification] baker's overall to cover his uniform[failed verification]. Talbot identified himself to Hindley as a police officer when she opened the door, and told her that he wanted to speak to her boyfriend. Hindley led him into the living room, where Brady was sitting up in a divan[failed verification] text=writing a note to his employer explaining that he would not be able to get into work because of his ankle injury. Talbot explained that he was investigating "an act of violence involving guns" that was reported to have taken place the previous evening.[25]
Hindley denied there had been any violence, and allowed police to look around the house. When they came to the upstairs room in which Evans's body was stored the police found the door locked, and asked Brady for the key. Hindley claimed that the key was at work, but after the police offered to drive her to her employer's premises to retrieve it, Brady told her to hand the key over. When they returned to the living room, the police told Brady that they had discovered a trussed up body, and that he was being arrested on suspicion of murder.[25] As Brady was getting dressed, he said "Eddie and I had a row and the situation got out of hand."[26]
Hindley was not arrested with Brady, but she demanded to go with him to the police station, accompanied by her dog, Puppet, to which the police agreed.[27] Hindley was questioned about the events surrounding Evans's death, but she refused to make any statement beyond claiming that it had been an accident. As the police had no evidence that Hindley was involved in Evans's murder,[failed verification] she was allowed to go home, on the condition that she return the next day for further questioning. Hindley was at liberty for four days following Brady's arrest, during which time she went to her employer's premises and asked to be dismissed, so that she would be eligible for unemployment benefits. While in the office where Brady worked, she found some papers belonging to him in an envelope that she claimed she did not open, which she burned in an ashtray. She believed that they were plans for bank robberies, nothing to do with the murders. On 11 October, Hindley was charged as an accessory to the murder of Edward Evans and was remanded at Risley.[28]
Initial investigation
Brady admitted under police questioning that[failed verification] he and Evans had fought, but insisted[failed verification] that he and Smith had murdered Evans between them; Hindley, he said, had "only done what she had been told".[29] Smith told police that Brady had asked him to return anything incriminating, such as "dodgy books", which Brady then packed into suitcases. Smith had no idea what else the suitcases contained or where they might be, but he mentioned in passing that Brady "had a thing about railway stations". The police consequently requested a search of all Manchester's left-luggage offices for any suitcases belonging to Brady, and on 15 October British Transport Police found what they were looking for at Manchester Central railway station[30]—the left-luggage ticket was found several days later[failed verification] in the back of Hindley's prayer book.[31]
Inside one of the suitcases were nine pornographic photographs taken of a young girl, naked and with a scarf tied across her mouth[failed verification], and a 13-minute audiotape recording of her screaming and pleading for help.[32] Ann Downey, Lesley Ann Downey's mother, later listened to the tape after police had discovered the body of her missing 10-year-old daughter, and confirmed that it was a recording of her daughter's voice.[33]
Police searching the house at Wardle Brook Avenue found an old exercise book in which the name "John Kilbride" had been scribbled, which made them suspicious that Brady and Hindley might have been involved in the unsolved disappearances of other youngsters.[34] A large collection of photographs was discovered in the house, many of which seemed to have been taken on Saddleworth Moor. One hundred and fifty officers were drafted to search the moor, looking for locations that matched the photographs.[failed verification] Initially the search was concentrated along the A628 road near Woodhead, but a close[failed verification] neighbour, 11-year-old Pat Hodges, had on several occasions been taken to the moor by Brady and Hindley and she was able to point out their favourite sites[failed verification] along the A635 road.[35] On 16 October, police found an arm bone sticking out of the peat; officers presumed that they had found the body of John Kilbride, but soon discovered that it was that of Lesley Ann Downey. Her mother Ann West had been on the moor watching as the police conducted their search, but was not present when the body was found.[36] She was shown clothing recovered from the grave, and identified it as belonging to her missing daughter.[failed verification][37]
Detectives located another site on the opposite side of the A635 from where Lesley Ann Downey's body was discovered, and five days later[failed verification] they found the "badly decomposed" body of John Kilbride, which had to be identified by clothing.[38] That same day[failed verification], already being held for the murder of Evans, Brady and Hindley appeared at Hyde Magistrates' Court charged with Lesley Ann Downey's murder. Each was brought before the court separately and remanded into custody for a week.[39] They made a two-minute appearance on 28 October, and were again remanded into custody.[40]
The investigating officers suspected Brady and Hindley of murdering other missing children and teenagers who had disappeared from areas in and around Manchester over the previous few years,[failed verification] and the search for bodies continued after the discovery of John Kilbride's body, but with winter setting in it was called off in November.[38] Presented with the evidence of the tape recording,[failed verification] Brady admitted to taking the photographs of Lesley Ann Downey, but insisted that she had been brought to Wardle Brook Avenue by two men who had subsequently taken her away again, alive. By 2 December 1965, Brady had been charged with the murders of John Kilbride, Lesley Ann Downey and Edward Evans. Hindley had been charged with the murders of Lesley Ann Downey and Edward Evans, and being an accessory to the murder of John Kilbride.[41] At the committal hearing on 6 December, Brady was charged with the murders of Edward Evans, John Kilbride, and Lesley Ann Downey, and Hindley with the murders of Edward Evans and Lesley Ann Downey, as well as with harbouring Brady in the knowledge that he had killed John Kilbride. The prosecution's opening statement was held in camera rather than in open court,[42] and the defence asked for a similar stipulation but was refused.[43] The proceedings continued in front of three magistrates in Hyde over an 11-day period during December, at the end of which the pair were committed for trial at Chester Assizes.[44]
Many of the photographs taken by Brady and Hindley on the moor featured Hindley's dog Puppet, sometimes as a puppy. Detectives arranged for the animal to be examined by a veterinary surgeon to determine its age, from which they could date when the pictures were taken. The examination involved an analysis of the dog's teeth, which required a general anaesthetic from which Puppet did not recover, as he suffered from an undiagnosed kidney complaint. On hearing the news of her dog's death, Hindley became furious, and accused the police of murdering Puppet, one of the few occasions detectives witnessed any emotional response from her.[38] In a letter to her mother shortly afterwards, Hindley wrote:
I feel as though my heart's been torn to pieces. I don't think anything could hurt me more than this has. The only consolation is that some moron might have got hold of Puppet and hurt him.[45]
Trial
The trial was held over 14 days beginning on 19 April 1966, in front of Mr Justice Fenton Atkinson.[44] Such was the public interest that[failed verification] the courtroom was fitted with security screens to protect Brady and Hindley.[46] The pair were each charged with three murders, those of Evans, Downey and Kilbride, as it was considered that there was by then sufficient evidence to implicate Hindley in Kilbride's death. The attorney general, Sir Frederick Elwyn Jones, led the prosecution, assisted by William Mars-Jones.[44] Brady was defended by the Liberal Member of Parliament Emlyn Hooson,[47] and Hindley was defended by Godfrey Heilpern, recorder of Salford from 1964—both experienced Queen's Counsels (QCs).[48][49] David Smith was the chief prosecution witness, but during the trial it was revealed that he had entered into an agreement with a newspaper that he initially refused to name—even under intense questioning—guaranteeing him £1,000 (equivalent to about £20,000 in 2024) for the syndication rights to[failed verification] his story if Brady and Hindley were convicted,[contradictory] something the trial judge described as a "gross interference with the course of justice".[50][51] Smith finally admitted in court that the newspaper was the News of the World,[52] which had already paid for a holiday in France for him and his wife and was paying him a regular income of £20 per week,[failed verification] as well as accommodating him in a five-star hotel for the duration of the trial.[53]
Brady and Hindley pleaded not guilty to the charges against them;[failed verification] both were called to give evidence, Brady for over eight hours and Hindley for six.[54] Although Brady admitted to hitting Evans with an axe, he did not admit to killing him, arguing that the pathologist in his report had stated that Evans's death was "accelerated by strangulation". Under cross-examination by the prosecuting counsel,[failed verification] all Brady would admit was that "I hit Evans with the axe. If he died from axe blows, I killed him."[55] Hindley denied any knowledge that the photographs of Saddleworth Moor found by police had been taken near the graves of their victims.[56]
A 16-minute tape recording[37][a] of Lesley Anne Downey, on which the voices of Brady and Hindley were audible, was played in open court. Hindley admitted[failed verification] that her attitude towards Downey was "brusque and cruel", but claimed that was only because she was afraid that someone might hear Downey screaming. Hindley claimed that when Downey was being undressed she herself was "downstairs"; when the pornographic photographs were taken she was "looking out the window"; and that when Downey was being strangled she "was running a bath".[failed verification][56]
On 6 May, after having deliberated for a little over two hours,[58] the jury found Brady guilty of all three murders and Hindley guilty of the murders of Downey and Evans. As the death penalty for murder had been abolished while Brady and Hindley were held on remand, the judge passed the only sentence that the law allowed: life imprisonment. Brady was sentenced to three concurrent life sentences and Hindley was given two, plus a concurrent seven-year term for harbouring Brady in the knowledge that he had murdered John Kilbride.[44] Brady was taken to Durham Prison and Hindley was sent to Holloway Prison.[56]
In his closing remarks Atkinson described the murders as a "truly horrible case" and condemned the accused as "two sadistic killers of the utmost depravity".[3] He recommended that both Brady and Hindley spend "a very long time" in prison before being considered for parole but did not stipulate a tariff. He stated that Brady was "wicked beyond belief" and that he saw no reasonable possibility of reform. He did not consider that the same was necessarily true of Hindley, "once she is removed from [Brady's] influence".[59] Throughout the trial Brady and Hindley "stuck rigidly to their strategy of lying"[failed verification],[60] and Hindley was later described as "a quiet, controlled, impassive witness who lied remorselessly".[44]
Later investigation
In 1985, Brady allegedly confessed to Fred Harrison, a journalist working for The Sunday People, that he had also been responsible for the murders of Pauline Reade and Keith Bennett,[61] something that the police already suspected, as both children lived in the same area as Brady and Hindley and had disappeared at about the same time as their other victims[failed verification]. The subsequent newspaper reports prompted Greater Manchester Police (GMP) to reopen the case, in an investigation headed by Detective Chief Superintendent[failed verification] Peter Topping, who had been appointed head of GMP's Criminal Investigation Department (CID) the previous year[failed verification].[62]
Since the Moors Murders came to light in 1965, regional and national newspapers had been keen to name other missing children and teenagers from in and near the Manchester area as possible victims of Brady and Hindley. One victim was Stephen Jennings, a three-year-old West Yorkshire boy who was last seen alive in December 1962. His body was finally found buried in a field in 1988, but the following year his father William Jennings was found guilty of his murder.[63] Jennifer Tighe, a 14-year-old girl who disappeared from an Oldham children's home in December 1964, was mentioned in the press as a possible Moors Murders victim some 40 years later, but after a few more years Greater Manchester Police confirmed that she was indeed still alive.[64] This followed claims in February 2004 that Hindley had confessed to another inmate that she and Brady had murdered a sixth victim, a teenage girl.[65]
On 3 July 1985, DCS Topping visited Brady, then being held at Gartree Prison, Leicestershire, but found him "scornful of any suggestion that he had confessed to more murders".[66] Police nevertheless decided to resume their search of Saddleworth Moor, once more using the photographs taken by Brady and Hindley to help them identify possible burial sites.[failed verification] In November 1986, Keith Bennett's mother Winnie Johnson wrote a letter to Hindley begging to know what had happened to her son, a letter that Hindley seemed to be "genuinely moved" by.[67] It ended:
I am a simple woman, I work in the kitchens of Christie's Hospital. It has taken me five weeks labour to write this letter because it is so important to me that it is understood by you for what it is, a plea for help. Please, Miss Hindley, help me.[68]
Police visited Hindley, then being held in Cookham Wood, Kent, a few days after she had received the letter, and although she refused to admit any involvement in the killings, she agreed to help by looking at photographs and maps to try to identify spots that she had visited with Brady.[69] She showed particular interest in photographs of the area around Hollin Brown Knoll and Shiny Brook, but said that it was impossible to be sure of the locations without visiting the moor.[70] The security considerations for such a visit were significant; there were threats made against her should she visit the moors, but Home Secretary Douglas Hurd agreed with Topping that it would be worth the risk.[71] Writing in 1989, Topping said that he felt "quite cynical" about Hindley's motivation in helping the police. Although the letter from Winnie Johnson may have played a part, he believed that Hindley's real concern was that, knowing of Brady's "precarious" mental state, she was afraid that he might decide to co-operate with the police, and wanted to make certain that she, and not Brady, was the one to gain whatever benefit there may have been in terms of public approval.[72]
On 16 December 1986, Hindley made the first of two visits to assist the police search of Saddleworth Moor.[73] Four police cars left Cookham Wood at 4:30 am. At about the same time, police closed all roads onto the moor, which was patrolled by 200 officers, 40 of them armed. Hindley and her solicitor arrived by helicopter from an airfield near Maidstone, then she was driven, and walked, around the area. It was difficult for Hindley to make a connection between her memories of the area and what she saw on the day, and she was apparently nervous of the helicopters flying overhead. At 3:00 pm she was returned to the helicopter, and taken back to Cookham Wood.[71] Topping was criticised by the press, who described the visit as a "fiasco", a "publicity stunt", and a "mindless waste of money".[74] He was forced to defend the visit, pointing out its benefits:
We had taken the view that we needed a thorough systematic search of the moor ... It would never have been possible to carry out such a search in private.[74]
On 19 December, David Smith, then 38, also returned to the moor. He spent about four hours helping police pinpoint areas where he thought more bodies might be buried.[75] Topping continued to visit Hindley in prison, along with her solicitor Michael Fisher and her spiritual counsellor, Peter Timms, who had been a prison governor before becoming a Methodist minister[failed verification].[74] She made a formal confession to police on 10 February 1987[failed verification], admitting her involvement in all five murders,[76] but news of her confession was not made public for more than a month.[77] The tape recording of her statement was over 17 hours long; Topping described it as a "very well worked out performance in which, I believe, she told me just as much as she wanted me to know, and no more".[78] He added that he "was struck by the fact that she was never there when the killings took place. She was in the car, over the brow of the hill, in the bathroom and even, in the case of the Evans murder, in the kitchen". Topping concluded that he felt he "had witnessed a great performance rather than a genuine confession".[79]

Police visited Brady in prison again and told him of Hindley's confession, which at first he refused to believe. Once presented with some of the details that Hindley had provided of Pauline Reade's abduction, Brady decided that he too was prepared to confess, but on one condition: that immediately afterwards he be given the means to commit suicide, a request with which it was impossible for the authorities to comply.[80]
At about the same time, Winnie Johnson sent Hindley another letter, again pleading with her to assist the police in finding the body of her son Keith. In the letter, Johnson was sympathetic to Hindley over the criticism surrounding her first visit. Hindley, who had not replied to the first letter, responded by thanking Johnson for both letters, explaining that her decision not to reply to the first resulted from the negative publicity that surrounded it. She claimed that, had Johnson written to her 14 years earlier, she would have confessed and helped the police. She also paid tribute to Topping, and thanked Johnson for her sincerity.[81] Hindley made her second visit to the moor in March 1987. This time, the level of security surrounding her visit was considerably higher. She stayed overnight in Manchester, at the flat of the police chief in charge of GMP training at Sedgley Park, Prestwich, and visited the moor twice.[82] She confirmed to police that the two areas in which they were concentrating their search—Hollin Brown Knoll and Hoe Grain—were correct, although she was unable to locate either of the graves. She later remembered that as Pauline Reade was being buried she had been sitting next to her on a patch of grass and could see the rocks of Hollin Brown Knoll silhouetted against the night sky.[83]
In April 1987, news of Hindley's confession became public. Amidst strong media interest Lord Longford pleaded for her release, writing that her continuing detention to satisfy "mob emotion" was not right. Fisher persuaded Hindley to release a public statement, in which she explained her reasons for denying her complicity in the murders, her religious experiences in prison, the letter from Johnson, and that she saw no possibility of release. She also exonerated David Smith from any part in the murders, except that of Edward Evans.[84]
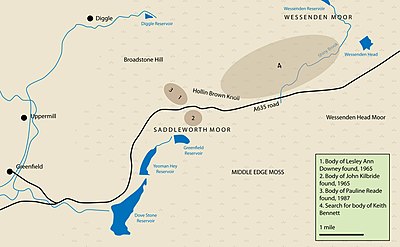
Over the next few months interest in the search waned, but Hindley's clue had directed the police to focus their efforts on a specific area[failed verification]. On the afternoon of 1 July 1987, after more than 100 days of searching, they found a body buried 3 feet (0.9 m) below the surface, only 100 yards (90 m) from the place where Lesley Ann Downey had been found.[85] Brady had been co-operating with the police for some time, and when news reached him that Reade's body had been discovered he made a formal confession to Topping.[86] He also issued a statement to the press, through his solicitor, saying that he too was prepared to help the police in their search. Brady was taken to the moor on 3 July, but he seemed to lose his bearings, blaming changes that had taken place in the intervening years, and the search was called off at 3:00 pm, by which time a large crowd of press and television reporters had gathered on the moor.[87]
Topping refused to allow Brady a second visit to the moors,[failed verification][86] and a few days after his visit Brady wrote a letter to BBC television reporter Peter Gould, giving some sketchy details of five additional murders that he claimed to have carried out.[88] Brady refused to identify his alleged victims, and the police failed to discover any unsolved crimes matching the few details that he supplied.[89] Hindley told Topping that she knew nothing of these killings.[failed verification][86]

On 24 August 1987, police called off their search of Saddleworth Moor, despite not having found Keith Bennett's body.[91] Brady was taken to the moor for a second time on 1 December, but he was once again unable to locate the burial site.[failed verification] Earlier that month, the BBC had received a letter from Ian Brady, in which he claimed that he had committed a further five murders - including a man in the Piccadilly area of Manchester, another victim on Saddleworth Moor, two more victims in Scotland, and a woman whose body he allegedly dumped in a canal at a location which he declined to identify. The police decided that there was insufficient evidence from this letter to launch an official investigation.[92] Although Brady and Hindley had confessed to the murders of Pauline Reade and Keith Bennett, the Director of Public Prosecutions (DPP) decided that nothing would be gained by a further trial; as both were already serving life sentences no further punishment could be inflicted.[93]
In 2003, the police launched Operation Maida, and again searched the moor for the body of Keith Bennett.[94] They read statements from Brady and Hindley, and also studied photographs taken by the pair. Their search was aided by the use of sophisticated modern equipment, including a US satellite used to look for evidence of soil movement.[95] The BBC reported on 1 July 2009 that Greater Manchester Police had officially given up the search for Keith Bennett, saying that "only a major scientific breakthrough or fresh evidence would see the hunt for his body restart".[96] Detectives were also reported as saying that they would never again give Brady the attention or the thrill of leading another fruitless search on the moor where they believe Keith Bennett's remains are buried.[97] Donations from members of the public funded a search of the moor for Bennett's body by volunteers from a Welsh search and rescue team that began in March 2010.[98] In August 2012, it was claimed that Brady may have given details of the location of Keith Bennett's body to one of his visitors. A woman was subsequently arrested on suspicion of preventing the burial of a body without lawful excuse, but a few months later the Crown Prosecution Service announced that there was insufficient evidence to press charges.[99] Keith Bennett's body remains undiscovered as of 2024, although his family continues to search the moor.[100]
Perpetrators' backgrounds
Ian Brady
Ian Brady was born in Glasgow as Ian Duncan Stewart on 2 January 1938 to Margaret "Peggy" Stewart, an unmarried tea room waitress.[101] The identity of Brady's father has never been reliably ascertained, although his mother said he was a reporter working for a Glasgow newspaper, who died three months before Brady was born. Stewart had little support, and after a few months was forced to give her son into the care of Mary and John Sloan, a local couple with four children of their own. Brady took their name, and became known as Ian Sloan. His mother continued to visit him throughout his childhood.[102] Various authors have stated that he tortured animals, although Brady objected to such accusations.[103] Aged nine, he visited Loch Lomond with his family, where he reportedly discovered an affinity for the outdoors, and a few months later the family moved to a new council house on an overspill estate at Pollok. He was accepted for Shawlands Academy, a school for above-average pupils.[104]
At Shawlands his behaviour worsened; as a teenager he twice appeared before a juvenile court for housebreaking. He left the academy aged 15, and took a job as a tea boy at a Harland and Wolff shipyard in Govan. Nine months later, he began working as a butcher's messenger boy. He had a girlfriend, Evelyn Grant, but their relationship ended when he threatened her with a flick knife after she visited a dance with another boy. He again appeared before the court, this time with nine charges against him,[105] and shortly before his 17th birthday he was placed on probation, on condition that he live with his mother.[106] By then she had moved to Manchester and married an Irish fruit merchant named Patrick Brady, and it was the latter who got Brady a job as a fruit porter at Smithfield Market. Ian took his new stepfather's surname.[107]
Within a year of moving to Manchester, Ian Brady was caught with a sack full of lead seals he had stolen and was trying to smuggle out of the market. He was sent to Strangeways for three months.[108] As he was still under 18, he was sentenced to two years in borstal for "training".[109] He was sent to Latchmere House in London,[108] and then Hatfield borstal in the West Riding of Yorkshire. After being discovered drunk on alcohol he had brewed he was moved to the much tougher unit at Hull.[93] Released on 14 November 1957, Brady returned to Manchester, where he took a labouring job, which he hated, and was dismissed from another job in a brewery. Deciding to "better himself", he obtained a set of instruction manuals on book-keeping from a local public library, with which he "astonished" his parents by studying alone in his room for hours.[110]
In January 1959, Brady applied for and was offered a clerical job at Millwards, a wholesale chemical distribution company based in Gorton. He was regarded by his colleagues as a quiet, punctual, but short-tempered young man. He read books including Teach Yourself German and Mein Kampf, as well as works on Nazi atrocities. He rode a Tiger Cub motorcycle, which he used to visit the Pennines.[111]
Myra Hindley
Myra Hindley was born in Crumpsall on 23 July 1942[112][113] and raised in Gorton, then a working-class area of Manchester. Her parents, Nellie and Bob Hindley (the latter an alcoholic), beat her regularly when she was a young child. The small house the family lived in was in such poor condition that Hindley and her parents had to sleep in the only available bedroom, she in a single bed next to her parents' double. The family's living conditions deteriorated further when Hindley's sister, Maureen, was born in August 1946. About a year after the birth, Hindley, then 5, was sent by her parents to live with her grandmother, whose home was nearby.[114]
Hindley's father had served with the Parachute Regiment and had been stationed in North Africa, Cyprus and Italy during the Second World War.[115] He had been known in the army as a "hard man" and he expected his daughter to be equally tough; he taught her how to fight, and insisted that she "stick up for herself". When Hindley was 8, a local boy approached her in the street and scratched both of her cheeks with his fingernails, drawing blood. She burst into tears and ran into her parents' house, to be met by her father, who demanded that she "Go and punch him [the boy], because if you don't I'll leather you!" Hindley found the boy and succeeded in knocking him down with a sequence of punches, as her father had taught her. As she wrote later, "at eight years old I'd scored my first victory".[116]
Malcolm MacCulloch, professor of forensic psychiatry at Cardiff University, has suggested that the fight, and the part that Hindley's father played in it, may be "key pieces of evidence" in trying to understand Hindley's role in the Moors murders:
The relationship with her father brutalised her ... She was not only used to violence in the home but rewarded for it outside. When this happens at a young age it can distort a person's reaction to such situations for life.[117]
One of her closest friends was 13-year-old Michael Higgins, who lived on a nearby street. In June 1957, he invited her to go swimming with friends at a local disused reservoir. Although she was a good swimmer, Hindley chose not to go and instead went out with a friend, Pat Jepson. Higgins drowned in the reservoir, and upon learning of his fate, Hindley was deeply upset and blamed herself for his death. She collected for a funeral wreath, and his funeral at St Francis's Monastery in Gorton Lane—the church where Hindley had been baptised a Catholic on 16 August 1942—had a lasting effect on her.[118] Hindley's mother had agreed to her father's insistence that she be baptised a Catholic only on the condition that she was not sent to a Catholic school, as her mother believed that "all the monks taught was the catechism".[119] Hindley was increasingly drawn to the Catholic Church after she started at Ryder Brow Secondary Modern, and began taking instruction for formal reception into the Church soon after Higgins's funeral. She took the confirmation name of Veronica, and received her first communion in November 1958.
Hindley's first job was as a junior clerk at a local electrical engineering firm. She ran errands, made tea, and typed. She was well-liked at the firm, enough so that when she lost her first week's wage packet, the other girls had a collection to replace it.[120] Beginning at Christmas 1958, Hindley began a short relationship with Ronnie Sinclair, and became engaged at 17. The engagement was called off several months later; Hindley apparently thought Sinclair immature, and unable to provide her with the life she envisaged for herself.[121] Shortly after her 17th birthday, she changed her hair colour with a pink rinse. She took judo lessons once a week at a local school, but found partners reluctant to train with her, as she was often slow to release her grip. She took a job at Bratby and Hinchliffe, an engineering company in Gorton, but was dismissed for absenteeism after six months.[122]
As a couple
In January 1961, the 18-year-old Myra Hindley joined Millwards as a typist.[123] She soon became infatuated with Brady, despite learning that he had a criminal record.[124] She began a diary and, although she had dates with other men, some of the entries detail her fascination with Brady, to whom she eventually spoke for the first time on 27 July 1961.[125] Over the next few months she continued to make entries, but grew increasingly disillusioned with him, until 22 December when Brady asked her on a date to the cinema,[126] where they watched the biblical epic King of Kings.[127][b] Their dates together followed a regular pattern; a trip to the cinema, usually to watch an X-rated film, and then back to Hindley's house to drink German wine.[128] Brady then gave her reading material, and the pair spent their work lunch breaks reading aloud to one another from accounts of Nazi atrocities. Hindley began to emulate an ideal of Aryan perfection, bleaching her hair blonde and applying thick crimson lipstick.[44] She expressed concern at some aspects of Brady's character; in a letter to a childhood friend, she mentioned an incident where she had been drugged by Brady, but also wrote of her obsession with him. A few months later, she asked her friend to destroy the letter.[129] In her 30,000-word plea for parole, written in 1978 and 1979 and submitted to Home Secretary Merlyn Rees, Hindley said:
Within months he [Brady] had convinced me that there was no God at all: he could have told me that the earth was flat, the moon was made of green cheese and the sun rose in the west, I would have believed him, such was his power of persuasion.[130]
Hindley began to change her appearance further, wearing clothing considered risqué such as high boots, short skirts and leather jackets, and the two became less sociable to their colleagues.[131] The couple were regulars at the library, borrowing books on philosophy, as well as crime and torture.[132] They also read works by the Marquis de Sade, Friedrich Nietzsche[132] and Fyodor Dostoevsky's Crime and Punishment.[44][133][c] Although Hindley was not a qualified driver (she passed her test on 7 November 1963 after failing three times[136]), she often hired a van, in which the two planned bank robberies. Hindley befriended George Clitheroe, the President of the Cheadle Rifle Club, and on several occasions visited two local shooting ranges. Clitheroe, although puzzled by her interest, arranged for her to buy a .22 rifle from a gun merchant in Manchester. She also asked to join a pistol club, but she was a poor shot and allegedly often bad-tempered, so Clitheroe told her that she was unsuitable; she did though manage to purchase a Webley .45 and a Smith & Wesson .38 from other members of the club.[137] Brady and Hindley's plans for robbery came to nothing, but they became interested in photography. Brady already owned a Box Brownie, which he used to take photographs of Hindley and her dog, Puppet, but he upgraded to a more sophisticated model, and also purchased lights and darkroom equipment. The pair took photographs of each other that, for the time, would have been considered explicit. For Hindley, this demonstrated a marked change from her earlier, more shy and prudish nature.[138]
As murderers
What they were doing was out of the scope of most people's understanding, beyond the comprehension of the workaday neighbours who were more interested in how they were going to pay the gas bill or what might happen in the next episode of Coronation Street or Doctor Who. In 1960s Britain, people did not kidnap and murder children for fun. It was simply beyond the realms of most people's comprehension, and this is why they managed to get away with it for so long.
Chris Cowley[139]
Hindley claimed that Brady began to talk about "committing the perfect murder" in July 1963,[140] and often spoke to her about Meyer Levin's Compulsion, published as a novel in 1956 and adapted for the cinema in 1959. The story tells a fictionalised account of the Leopold and Loeb case, two young men from well-to-do families who attempt to commit the perfect murder of a 12-year-old boy, and escape the death penalty because of their age.[141]
By June 1963, Brady had moved in with Hindley at her grandmother's house in Bannock Street, and on 12 July 1963, the two murdered their first victim, 16-year-old Pauline Reade. Reade had attended school with Hindley's younger sister, Maureen, and had also been in a short relationship with David Smith, a local boy with three criminal convictions for minor crimes. Police could find nobody who had seen Reade before her disappearance, and although the 15-year-old Smith was questioned by police, he was cleared of any involvement in her death.[142] Their next victim, John Kilbride, was killed on 23 November 1963. A huge search was undertaken, with over 700 statements taken, and 500 "missing" posters printed. Eight days after he failed to return home, 2,000 volunteers scoured waste ground and derelict buildings.[143]
Hindley hired a vehicle a week after Kilbride went missing, and again on 21 December 1963, apparently to make sure the burial sites had not been disturbed. In February 1964, she bought a second-hand Austin Traveller, but soon after traded it for a Mini van. Twelve-year-old Keith Bennett disappeared on 16 June 1964. His stepfather, Jimmy Johnson, became a suspect; in the two years following Bennett's disappearance, Johnson was taken for questioning on four occasions. Detectives searched under the floorboards of the Johnsons' house, and on discovering that the houses in the row were connected, extended the search to the entire street.[144]
Maureen Hindley married David Smith on 15 August 1964. The marriage was hastily arranged and performed at a register office. None of Hindley's relatives attended; Myra did not approve of the marriage, and her mother was too embarrassed—Maureen was seven months pregnant. The newlyweds moved into Smith's father's house. The next day, Brady suggested that the four take a day-trip to Windermere. This was the first time Brady and Smith had met properly, and Brady was apparently impressed by Smith's demeanour. The two talked about society, the distribution of wealth, and the possibility of robbing a bank. The young Smith was similarly impressed by Brady, who throughout the day had paid for his food and wine. The trip to the Lake District was the first of many outings. Hindley was apparently jealous of their relationship, but became closer to her sister.[145]
In 1964, Hindley, her grandmother, and Brady were rehoused as part of the post-war slum clearances in Manchester, to 16 Wardle Brook Avenue in the new overspill estate of Hattersley. Brady and Hindley became friendly with Patricia Hodges, an 11-year-old girl who lived at 12 Wardle Brook Avenue. Hodges accompanied the two on their trips to Saddleworth Moor to collect peat, something that many householders on the new estate did to improve the soil in their gardens, which were full of clay and builder's rubble.[146] She remained unharmed; living only a few doors away, her disappearance would have been easily solved.[147]
Early on Boxing Day 1964, Hindley left her grandmother at a relative's house and refused to allow her back to Wardle Brook Avenue that night.[148] On the same day, 10-year-old Lesley Ann Downey disappeared from a funfair in Ancoats.[149] Despite a huge search, she was not found. The following day, Hindley brought her grandmother back home.[150] By February 1965, Patricia Hodges had stopped visiting 16 Wardle Brook Avenue, but David Smith was still a regular visitor. Brady gave Smith books to read, and the two discussed robbery and murder.[151] On Hindley's 23rd birthday, her sister and brother-in-law, who had until then been living with relatives, were rehoused in Underwood Court, a block of flats not far from Wardle Brook Avenue. The two couples began to see each other more regularly, but usually only on Brady's terms.[152][153]
During the 1990s, Hindley claimed that she took part in the killings only because Brady had drugged her, was blackmailing her with pornographic pictures he had taken of her, and had threatened to kill her younger sister, Maureen.[124] In a 2008 television documentary series on female serial killers broadcast on ITV3, Hindley's solicitor, Andrew McCooey, reported that she had said to him:
I ought to have been hanged. I deserved it. My crime was worse than Brady's because I enticed the children and they would never have entered the car without my role ... I have always regarded myself as worse than Brady.[154]
Incarceration
Brady

Following his conviction, Brady was moved to Durham Prison, where he asked to live in solitary confinement.[155] He spent 19 years in mainstream prisons before being diagnosed as a psychopath in November 1985 and sent to the high-security Park Lane Hospital, now Ashworth Psychiatric Hospital, in Sefton;[156] he made it clear that he never wanted to be released.[157]
The trial judge recommended that his life sentence should mean life, and successive Home Secretaries agreed with that decision. In 1982, the Lord Chief Justice Lord Lane said of Brady: "this is the case if ever there is to be one when a man should stay in prison till he dies".[158] The death, in November 2007, of John Straffen, who had spent 55 years in prison for murdering three children meant that Brady became the longest-serving prisoner in England and Wales.[159]
Although he refused to work with Ashworth's psychiatrists, Brady occasionally corresponded with people outside the hospital,[d] including Lord Longford, writer Colin Wilson and various journalists.[161] In one letter, written in 2005, he claimed that the murders were "merely an existential exercise of just over a year, which was concluded in December 1964". By then, he went on to claim, he and Hindley had turned their attention to armed robbery, for which they had begun to prepare by acquiring guns and vehicles.[e][163]
During several years of interactions with forensic psychologist Chris Cowley, including face-to-face meetings,[164] Brady told him of an "aesthetic fascination [he had] with guns",[165] despite his never having used one to kill. He complained bitterly about conditions at Ashworth, which he hated.[166] In 1999, his right wrist was broken in what he claimed was an "hour-long, unprovoked attack" by staff.[167] Brady subsequently went on hunger strike, but while English law allows patients to refuse treatment, those being treated for mental disorders under the Mental Health Act 1983 have no such right if the treatment is for their mental disorder.[168][169] He was therefore force-fed and transferred to another hospital for tests, after he fell ill.[170] He recovered, and in March 2000 asked for a judicial review of the legality of the decision to force-feed him, but was refused permission.[168][171]
Myra gets the potentially fatal brain condition, whilst I have to fight simply to die. I have had enough. I want nothing, my objective is to die and release myself from this once and for all. So you see my death strike is rational and pragmatic. I'm only sorry I didn't do it decades ago, and I'm eager to leave this cesspit in a coffin.[171]
While at Ashworth, in 2001 Brady wrote The Gates of Janus, which was published by Feral House, an underground US publisher. The book, Brady's analysis of serial murder and specific serial killers, sparked outrage when announced in Britain.[172] According to Chris Cowley, Brady regretted Hindley's imprisonment and the consequences of their actions, but not necessarily the crimes themselves. He saw no point in making any kind of public apology; instead, he "expresse[d] remorse through actions".[173] Twenty years of transcribing classical texts into Braille came to an end when the authorities confiscated his translation machine, for fear it might be used as a weapon. He once offered to donate one of his kidneys to "someone, anyone who needed one",[174] but was blocked from doing so. According to Colin Wilson, "it was because these attempts to express remorse were thrown back at him that he began to contemplate suicide".[169] He might have achieved this in 2006, when a female friend sent him 50 paracetamol pills, stored in two Smarties tubes hidden inside a hollowed-out crime novel. The potentially lethal dose of tablets was intercepted.[169][175]
Winnie Johnson, the mother of the sole remaining undiscovered victim, 12-year-old Keith Bennett, received a letter from Brady at the end of 2005 in which, she said, he claimed that he could take police to within 20 yards (18 m) of her son's body but the authorities would not allow it. Brady did not refer directly to Keith by name and did not claim he could take investigators directly to the grave, but spoke of the "clarity" of his recollections.[176]
In 2012, Brady applied to be returned to prison, reiterating his desire to starve himself to death.[177] At a mental health tribunal in June the following year, Brady claimed that he suffered not from paranoid schizophrenia, as his doctors at Ashworth maintained, but a personality disorder. His application was rejected and the judge stated that Brady "continues to suffer from a mental disorder which is of a nature and degree which makes it appropriate for him to continue to receive medical treatment".[178]
After receiving end-of-life care, Brady died of restrictive pulmonary disease at Ashworth Hospital on 15 May 2017.[179] On 21 September 2017, the inquest found that he died of natural causes and his hunger strike had not been a contributory factor.[180] Brady had refused food and fluids for more than 48 hours on various occasions, causing him to be fitted with a nasogastric tube, although his inquest noted that his body mass index was not a cause for concern.[181] Brady was cremated without ceremony by Sefton Borough Council on 25 October 2017 and his ashes were disposed of at sea during the night.[182]
Hindley
Hindley lodged an unsuccessful appeal against her conviction immediately after the trial.[183] Brady and Hindley corresponded by letter until 1971, when she ended their relationship. The two remained in sporadic contact for several months,[184] but Hindley had fallen in love with one of her prison warders, Patricia Cairns. A former assistant governor claimed that such relationships were not unusual in Holloway at that time, as "many of the officers were gay, and involved in relationships either with one another or with inmates".[185] Hindley successfully petitioned to have her status as a category A prisoner changed to category B, which enabled Governor Dorothy Wing to take her on a walk round Hampstead Heath, part of her unofficial policy of reintroducing her charges to the outside world when she felt they were ready. The excursion caused a furore in the national press and earned Wing an official rebuke from the then Home Secretary Robert Carr.[186] With help from Cairns, and the outside contacts of another prisoner, Maxine Croft, Hindley planned a prison escape, but it was thwarted when impressions of the prison keys were intercepted by an off-duty policeman. Cairns was sentenced to six years in jail for her part in the plot.[187]
Hindley was told that she should spend 25 years in prison before being considered for parole. The Lord Chief Justice agreed with that recommendation in 1982, but in January 1985 Home Secretary Leon Brittan increased her tariff to 30 years.[158] By that time Hindley claimed to be a reformed Catholic. Ann West, the mother of Lesley Ann Downey, was at the centre of a campaign to ensure that Hindley was never released from prison, and until West's death in February 1999, she regularly gave television and newspaper interviews whenever Hindley's release was rumoured.[188] In February 1985, Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher told Brittan that his proposed minimum sentences of 30 years for Hindley and 40 years for Brady were too short, saying "I do not think that either of these prisoners should ever be released from custody. Their crime was the most hideous and cruel in modern times."[189][190]
In 1987, Hindley admitted that the plea for parole she had submitted to the Home Secretary eight years earlier was "on the whole ... a pack of lies",[191] and to some reporters her co-operation in the searches on Saddleworth Moor "appeared a cynical gesture aimed at ingratiating herself to the parole authorities".[192] Then Home Secretary David Waddington imposed a whole life tariff on Hindley in July 1990, after she confessed to having been more involved in the murders than she had admitted.[158] Hindley was not informed of the decision until 1994, when a Law Lords ruling obliged the Prison Service to inform all life sentence prisoners of the minimum period they must serve in prison before being considered for parole.[193] In 1997, the Parole Board ruled that Hindley was low risk and should be moved to an open prison.[158] She rejected the idea and in early 1998 was moved to the medium-security Highpoint Prison;[194] the House of Lords ruling left open the possibility of later freedom. Between December 1997 and March 2000, Hindley made three separate appeals against her life tariff, claiming she was a reformed woman and no longer a danger to society, but each was rejected by the courts.[195][196]
When in 2002 another life sentence prisoner challenged the Home Secretary's power to set minimum terms, Hindley and hundreds of others, whose tariffs had been increased by politicians, looked likely to be released from prison.[197] Hindley's release seemed imminent and plans were made by supporters for her to be given a new identity.[198] Home Secretary David Blunkett ordered Greater Manchester Police to find new charges against her, to prevent her release from prison. The investigation was headed by Superintendent Tony Brett, and initially looked at charging Hindley with the murders of Pauline Reade and Keith Bennett, but the advice given by government lawyers was that because of the DPP's decision taken 15 years earlier, a new trial would probably be considered an abuse of process.[199]
On 25 November 2002, the Law Lords agreed that judges, not politicians, should decide how long a criminal spends behind bars, and stripped the Home Secretary of the power to set minimum sentences.[200] On 15 November 2002, aged 60, Hindley died from bronchial pneumonia, caused by heart disease, at West Suffolk Hospital.[201] She was a 40-a-day smoker who in 1999 had been diagnosed with angina and hospitalised after suffering a brain aneurysm.[202][203] Camera crews "stood rank and file behind steel barriers" outside, but none of Hindley's relatives were among the small congregation of eight to ten people who attended a short service at Cambridge crematorium.[204] Such was the strength of feeling more than 35 years after the murders that a reported 20 local undertakers refused to handle her cremation.[205] Four months later, her ashes were scattered by her ex-partner, Patricia Cairns, less than 10 miles (16 km) from Saddleworth Moor in Stalybridge Country Park.[43][206] Fears were expressed that the news might result in visitors choosing to avoid the park, a local beauty spot, or even that the park might be vandalised.[207]
Aftermath
Smith became "reviled by the people of Manchester", despite having been instrumental in bringing Brady and Hindley to justice.[208] While her sister was on trial, Maureen—eight months pregnant—was attacked in the lift of the building in which she and David lived. Their home was vandalised, and hate mail was regularly posted through their letterbox. Maureen feared for her children: "I couldn't let my children out of my sight when they were little. They were too young to tell them why they had to stay in, to explain why they couldn't go out to play like all the other children."[209]
After stabbing another man during a fight, in an attack he claimed was triggered by the abuse he had suffered since the trial, Smith was sentenced to three years in prison in 1969.[208] That same year his children were taken into the care of the local authority. Maureen moved from Underwood Court to a single-bedroom property and found work in a department store. Subjected to whispering campaigns and petitions to remove her from the estate where she lived, she received no support from her family—her mother had supported Myra during the trial. On his release from prison, Smith moved in with the girl who became his second wife and won custody of his three sons. Maureen managed to repair the relationship with her mother, and moved into a council property in Gorton. She divorced Smith in 1973,[210] and married a lorry driver, Bill Scott, with whom she had a daughter.[211]
Maureen and her immediate family made regular visits to see Hindley, who reportedly adored her niece. In 1980, Maureen suffered a brain haemorrhage; Hindley was granted permission to visit her sister in hospital, but she arrived an hour after Maureen's death.[212] Sheila and Patrick Kilbride, who were by then divorced,[213] were present at Maureen's funeral, believing that Hindley might make an appearance. Patrick mistook Bill Scott's daughter from a previous relationship, Ann Wallace, for Hindley and tried to attack her before being knocked to the ground by another mourner; the police were called to restore order.[214] Shortly before her death at the age of 70, Sheila said: "If she [Hindley] ever comes out of jail I'll kill her".[215] It was a threat repeated by her son Danny, and Ann West.[216][217]
In 1972 Smith was acquitted of the murder of his father, who had been suffering from terminal cancer. He pleaded guilty to manslaughter and was sentenced to two days' detention.[218] He remarried and moved to Lincolnshire with his three sons,[208][219] and was exonerated of any participation in the Moors murders by Hindley's confession in 1987. In 2011 he co-authored the book Witness with biographer Carol Ann Lee.[220] He died in Ireland in 2012.[221][222]
A 1977 BBC television debate discussed arguments for and against Myra Hindley's release, with Lord Longford, a Roman Catholic convert, on the side who argued that Hindley should be released and Ann West (the mother of Lesley Ann Downey) on the side arguing against any suggestion of Hindley being released and threatening to kill her if she ever got out of prison.[223]
Joan Reade, Pauline Reade's mother, was admitted to Springfield Mental Hospital in Manchester. She was present, under heavy sedation, at the funeral of her daughter on 7 August 1987.[224] Five years after their son was murdered, Sheila and Patrick Kilbride divorced.[213] Ann West, mother of Lesley Ann Downey, died in 1999 from cancer of the liver. Since her daughter's death, she had campaigned to ensure that Hindley remained in prison, and doctors said that the stress had contributed to the severity of her illness.[225] Winnie Johnson, mother of Keith Bennett, continued to visit Saddleworth Moor, where it is believed that the body of her son is buried.[226][227][228] She died in August 2012.[229]
Manchester City Council decided in 1987 to demolish the house in which Brady and Hindley had lived on Wardle Brook Avenue, and where Lesley Anne Downey and Edward Evans were murdered, citing "excessive media interest [in the property] creating unpleasantness for residents".[230]
Lasting notoriety
The photographs and tape recording of the torture of Lesley Ann Downey, exhibited in court to a disbelieving audience, and the nonchalant responses of Brady and Hindley, helped to ensure the lasting notoriety of their crimes. Brady, who said that he did not want to be released, was rarely mentioned in the news, but Hindley's gender, her repeated insistence on her innocence, followed by her attempts to secure her release after confessing her guilt, resulted in her becoming a figure of hate in the national media. Her oft reprinted photograph, taken shortly after she was arrested, is described by some commentators as similar to the mythical Medusa and, according to author Helen Birch, has become "synonymous with the idea of feminine evil".[192][231] Given Hindley's status as co-defendant in the first serial-murder trial held since the abolition of the death penalty,[232] retribution was a common theme among those who sought to keep her locked away. Even her mother insisted that she should die in prison, partly for fear for her daughter's safety and partly out of the desire to avoid the possibility that one of the victims' relatives might kill her. Some commentators expressed the view that of the two, Hindley was the "more evil".[233]
Lord Longford, a Catholic convert, campaigned to secure the release of "celebrated" criminals, and Myra Hindley in particular, which earned him constant derision from the public and the press. He described Hindley as a "delightful" person and said "you could loathe what people did but should not loathe what they were because human personality was sacred even though human behaviour was very often appalling".[234] The tabloid press branded him a "loony" and a "do-gooder" for supporting Hindley, described as "evil". She became a long-running source of material for the press, which printed embellished tales of her "cushy" life at the "5-star" Cookham Wood Prison and her liaisons with prison staff and other inmates.[235]
The case has been dramatised on television twice: in See No Evil: The Moors Murders and the award-winning Longford (both 2006).[236][237]
See also
References
Notes
- ^ Brady made more than one copy of the tape recording;[57] the version played in court was 16 minutes in length.[37]
- ^ Many sources state that Brady and Hindley's first date was to watch the film Judgment at Nuremberg; Hindley recollected that it was King of Kings.[127]
- ^ Brady told the police 30 years later that everything he had ever done was in Crime and Punishment.[134] Brady also claimed that Dostoevsky and Nietzsche were his biggest influences.[135]
- ^ His communications were sometimes censored by the prison authorities.[160]
- ^ Forensic psychologist Chris Cowley writes "So there was a gap in the murder cycle, this is not unusual with serial killers, but in most cases the gaps between murders get shorter, not longer. The so-called 'cooling-off' periods diminish on a timeline. In Brady's case, this did not happen: it went the other way. So their next killing [Edward Evans] was out of sequence and it went badly wrong for pretty much everyone concerned, not least their victim.[162]
Citations
- ^ Hindley: I wish I'd been hanged, BBC News, 29 February 2000, retrieved 11 August 2009
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 294
- ^ a b Carmichael (2003), p. 2
- ^ a b c d Topping (1989), pp. 82–85
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 111
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 137
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 146
- ^ "Coroner commends police after Moors verdict", The Herald – Google News Archive Search, 13 April 1988, retrieved 17 October 2016
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 115
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 140–141
- ^ Lee (2010), pp. 130–135
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 90–92
- ^ Lee (2010), pp. 144–146
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 95–96
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 106
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 34
- ^ a b Staff (2007), pp. 184–186
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 22
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 183–184
- ^ Lee (2010), pp. 199–200
- ^ Williams (1992), p. 266
- ^ a b Staff (2007), p. 186
- ^ Gibson (2006), p. 67
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 78
- ^ a b Topping (1989), p. 120–121 Cite error: The named reference "FOOTNOTETopping1989120–121" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 85
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 193–194
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 122–124
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 122
- ^ Lee (2010), pp. 234–235
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 107
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 35
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 35–36
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 33
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 91
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 93–94
- ^ a b c "Two women at 'bodies on moors' trial cover their ears", The Times, no. 56616, Times Digital Archive, p. 9, 27 April 1966, retrieved 11 August 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ a b c Topping (1989), p. 37 Cite error: The named reference "FOOTNOTETopping198937" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Couple on Moors Murder Charge", The Times, no. 56459, Times Digital Archive, p. 8, 22 October 1965, retrieved 11 August 2009
- ^ "Couple in Court Two Minutes", The Times, no. 56465, Times Digital Archive, p. 15, 29 October 1965, retrieved 11 August 2009
- ^ "Clerk Accused Of Three Murders", The Times, no. 56495, Times Digital Archive, p. 17, 3 December 1965, retrieved 25 September 2009
- ^ "Hearing Of Moors Murder Case In Camera", The Times, no. 56498, Times Digital Archive, p. 6, 7 December 1965, retrieved 25 September 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ a b Staff (2007), p. 18. Cite error: The named reference "FOOTNOTEStaff200718" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b c d e f g Davenport-Hines, Richard, "Hindley, Myra (1942–2002)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.), Oxford University Press, retrieved 5 July 2009 (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 213
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 222
- ^ Hamilton, Fiona (20 April 1966), "Boy tricked into seeing murder, moors trial Q.C. says", The Times, Times Digital Archive, retrieved 16 September 2009
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 225
- ^ "Mr Godfrey Heilpern", The Times, no. 58774, Times Digital Archive, p. 14, 5 May 1973 (subscription required)
- ^ UK Retail Price Index inflation figures are based on data from Clark, Gregory (2017). "The Annual RPI and Average Earnings for Britain, 1209 to Present (New Series)". MeasuringWorth. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 225–226
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 272
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 143
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 38
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 227–228
- ^ a b c Topping (1989), p. 39
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 70
- ^ "Life sentences on couple in moors case", The Times, Times Digital Archive, 7 May 1966, retrieved 29 July 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ Obituary: Myra Hindley, BBC News, 15 November 2002, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 229
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 252
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 10
- ^ "Life for man who killed son in 1962". Evening Times. Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ Linton, Deborah (20 April 2010). "Moors murder 'victim' is 'alive". Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ Chronicle, Evening (14 February 2004). "Myra told of victim No. 5". Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 13
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 260–261
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 42–43
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 262
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 43–52
- ^ a b Ritchie (1988), pp. 264–265
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 44
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 55
- ^ a b c Ritchie (1988), p. 266
- ^ Smith, Ian (20 December 1986), Witness helps in search of moors, The Times, hosted at find.galegroup.com, p. 3
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) (subscription required) - ^ Topping (1989), pp. 72–75
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 268
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 153
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 146–147
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 157–158
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 268–269
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 269
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 160–164, 171–172
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 270–274
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 274
- ^ a b c Ritchie (1988), p. 276
- ^ Topping (1989), pp. 188–196
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 206
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 232
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 253
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 223
- ^ "1987: Moors murderer claims more killings". 4 August 1987. Retrieved 20 September 2018 – via news.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ a b Topping (1989), p. 249
- ^ "Police call off search for Moors murder victim". independent.co.uk. 1 July 2009. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ^ "Spy satellite used in fresh bid to reveal Moors Murderers final secret". standard.co.uk. 6 June 2008. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
- ^ Moors victim mother's Brady plea, BBC News, 1 January 2009, retrieved 1 July 2009
- ^ Parmenter, Tom (2 July 2009), Brady Banned From Fresh Moors Searches, Sky News, archived from the original on 5 October 2012, retrieved 24 September 2009
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Moors Murders: Donations fund search for Keith Bennett, BBC News, 27 March 2010, retrieved 27 March 2010
- ^ Ian Brady's mental health advocate will not face charges, BBC News, 11 February 2013, retrieved 9 June 2014
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 298
- ^ Keightley (2017), p. 24.
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 17–19
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 28
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 19–20
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 20–21
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 24
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 122
- ^ a b Cowley (2011), p. 29
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 122–123
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 123
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 23–25
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 2
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 30
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 39–46
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 38
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 49–50
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 50
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 7
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 36
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 8
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 12–13
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 14
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 69
- ^ a b McVeigh, Karen (16 November 2002), "Death at 60 for the woman who came to personify evil", The Scotsman, retrieved 17 February 2009
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 27
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 29
- ^ a b Lee (2010), p. 76
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 31
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 32
- ^ Carmichael (2003), p. 6
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 32–33
- ^ a b Lee (2010), p. 93.
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 35
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 89.
- ^ Keightley (2017), p. 36.
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 126.
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 37–40
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 40–41
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 140
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 81
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 80
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 41–45
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 46–47
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 50–55
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 56–58
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 137
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 62–65
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 65
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 67
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 69
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 70–71
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 73
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 71–73
- ^ Edge, Simon (11 October 2008), "Evil of the Lady Killers", The Express, retrieved 10 September 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ "Brady chooses to remain alone", The Times, no. 56656, Times Digital Archive, p. 1, 13 June 1966, retrieved 25 September 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ Ian Brady: A fight to die, BBC News, 3 October 2000, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ Gould, Peter (October 2002), Ian Brady seeks public hearing, BBC News, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ a b c d What will Hindley's lawyers argue?, BBC News, 7 December 1997, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ "UK's longest-serving prisoner, Straffen, dies", The Daily Telegraph, 20 November 2007, retrieved 22 September 2009
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 17
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 16
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 41
- ^ Gould, Peter (27 October 2005), Brady claims murders 'had ended', BBC News, retrieved 11 August 2009
- ^ Cowley (2011), pp. 51, 74
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 61
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 124
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 177
- ^ a b Dyer, C (18 March 2000), "Force feeding of Ian Brady declared lawful", BMJ, 320 (7237): 731, doi:10.1136/bmj.320.7237.731/a (inactive 9 February 2019), PMC 1117753, PMID 10720341
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of February 2019 (link) - ^ a b c Chancellor, Alexander (4 February 2006), "Let Ian Brady die", The Guardian, retrieved 29 August 2012
- ^ Finn, Gary (30 October 1999), "Ian Brady force-fed in secure hospital", The Independent, retrieved 25 September 2009
- ^ a b Tran, Mark (10 March 2000), "Brady loses bid to die", The Guardian, retrieved 29 September 2009
- ^ US publisher defends Brady book, BBC News, 18 October 2001, retrieved 22 September 2009
- ^ Cowley (2011), pp. 256–257
- ^ Cowley (2011), p. 256
- ^ Brady drugs smuggling bid foiled, BBC News, 28 January 2006, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ Brady writes to victim's mother, BBC News, 21 February 2006, retrieved 22 September 2009
- ^ Ian Brady will not necessarily kill himself if moved to jail, tribunal hears, guardian.co.uk, 25 June 2013, retrieved 29 June 2013
- ^ Pidd, Helen (28 June 2013). "Ian Brady should stay in psychiatric hospital, tribunal rules". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 July 2018.
- ^ "Ian Brady's ashes 'not to be scattered at Saddleworth Moor'". BBC News Online. 16 May 2017. Retrieved 16 May 2017.
- ^ "Ian Brady: Moors Murderer 'would remove feeding tube'". BBC News. 21 September 2017. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ^ "Moors Murderer Ian Brady died of natural causes, coroner confirms". Glasgow Evening Times. 21 September 2017. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ^ "Moors Murders: Ian Brady's ashes disposed of at sea". BBC News. 3 November 2017. Retrieved 3 November 2017.
- ^ "Myra Hindley Loses Murder Appeal", The Times, no. 56765, Times Digital Archive, p. 1, 18 October 1966, retrieved 25 September 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 162
- ^ Staff (2007), p. 250
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 164–166
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 250–253
- ^ Last wish of Moors murder mother, BBC News, 11 February 1999, retrieved 5 July 2009
- ^ Travis, Alan (20 July 2017). "Thatcher overruled minister to keep Moors murderers locked up for life". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ Easton, Mark (20 May 2017). "Ian Brady: How the Moors Murderer came to symbolise pure evil". BBC News. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
Margaret Thatcher described their crimes as 'the most hideous and evil in modern times'.
- ^ Topping (1989), p. 140
- ^ a b Stanford, Peter (16 November 2002), "Myra Hindley", The Guardian, retrieved 25 September 2009
- ^ "Timetable of Moors murders case", The Guardian, 15 November 2002, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 354
- ^ Regina v. Secretary of State For The Home Department, Ex Parte Hindley, House of Lords, 30 March 2000, retrieved 16 March 2007
- ^ 1966: Moors murderers jailed for life, BBC News, 6 May 1966, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ Killer challenges 'whole life' tariff, BBC News, 21 October 2002, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ "Hindley could be freed 'in months'", London Evening Standard, 10 September 2002
- ^ Staff (2007), pp. 17–18
- ^ Gould, Peter (25 November 2002), Raising killers' hopes of freedom, BBC News, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 346
- ^ Sapsted, David; Bunyan, Nigel (16 November 2002). "Myra Hindley, the Moors monster, dies after 36 years in jail". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 20 September 2018 – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
- ^ Inquest tribute to Hindley's victims, BBC News, 18 November 2002, retrieved 1 October 2009
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 10
- ^ Addley, Esther (21 November 2002), "Funeral pariah", The Guardian, retrieved 29 September 2009
- ^ Lee (2010), p. 22
- ^ "Hindley's ashes "scattered in park"", Manchester Evening News, 27 February 2003, retrieved 8 August 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ a b c Topping (1989), pp. 64–65
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 232
- ^ "Decree for wife of Moors witness", The Times, no. 58734, Times Digital Archive, p. 2, 17 March 1973, retrieved 25 September 2009
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 232–239
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 238–240
- ^ a b Ritchie (1988), p. 49
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 240
- ^ Herbert, Ian (16 November 2002), "I have no compassion for her. I hope she goes to Hell. I wanted her to suffer like I have.", The Independent, archived from the original on 30 January 2011, retrieved 29 September 2009
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Lister, Sam (20 November 2002), "Family glad Hindley died behind bars", Manchester Evening News, retrieved 11 November 2011
- ^ Why Myra must never be freed; Scots detective who arrested evil Hindley ends 30-year silence, Scottish Daily Record and Sunday Mail, 29 October 1997
- ^ "Moors case witness cleared", The Times, no. 58626, p. 2, 8 November 1972, retrieved 25 September 2009
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 249
- ^ Naomi Cornwell (28 June 2011). "Book by Moors Murder witness David Smith recalls horror". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 6 June 2018.
- ^ Fallon, John (9 May 2012), Man who helped jail Moors murderers dies of cancer, irishtimes.com, archived from the original on 20 July 2012, retrieved 27 May 2012
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Obituaries – David Smith", The Daily Telegraph, 30 June 2012, retrieved 28 December 2015
- ^ "No Way To Consider Clemency", The Times, no. 60052, Times Digital Archive, p. 13, 11 July 1977, retrieved 25 September 2009 (subscription required)
- ^ Ritchie (1988), p. 45
- ^ Moors murder mother was 'incredible', BBC News, 10 February 1999, retrieved 29 September 2009
- ^ Moors Murder mother Winnie Johnson in DVD appeal to Brady, bbc.co.uk, 25 April 2011, retrieved 18 August 2012
- ^ Copping, Jasper (18 August 2012), Winnie Johnson, mother of Moors Murders victim Keith Bennett, dies, telegraph.co.uk, retrieved 18 August 2012
- ^ Gould, Peter (1 July 2009), What does Ian Brady know?, BBC News, retrieved 29 September 2009
- ^ Moors Murder victim Keith Bennett's mother dies, BBC News, 18 August 2012, retrieved 18 August 2012
- ^ Hindley Link Goes, The Times, hosted at find.galegroup.com, 6 October 1987, p. 2
{{citation}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) (subscription required) - ^ Birch (1994), p. 32
- ^ Birch (1994), p. 43
- ^ Ritchie (1988), pp. 281–90
- ^ Lord Longford: Aristocratic moral crusader, BBC News, 3 August 2001, retrieved 12 June 2007
- ^ Birch (1994), pp. 44–46
- ^ "From Myra Hindley to Three Girls: Maxine Peake's life and career", The Daily Telegraph, 15 May 2017,
ITV was preparing to make a film about the aftermath of the Moors Murders
- ^ Stanley, Alessandra (16 February 2007), "Longford – TV – Review", The New York Times, retrieved 17 June 2017
Bibliography
- Birch, Helen, ed. (1994), Moving Targets: Women, Murder, and Representation, University of California Press, ISBN 978-0-520-08574-9
- Carmichael, Kay (2003), Sin and Forgiveness: New Responses in a Changing World, Ashgate Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7546-3406-5
- Cowley, Chris (2011), Face to Face with Evil: Conversations with Ian Brady, Metro Books, ISBN 978-1-84454-981-8
- Gibson, Dirk Cameron (2006), Serial murder and media circuses, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN 978-0-275-99064-0
- Keightley, Alan (2017), Ian Brady: The Untold Story of the Moors Murders, Pavilion Books, ISBN 978-1861057549
- Lee, Carol Ann (2010), One Of Your Own: The Life and Death of Myra Hindley, Mainstream Publishing, ISBN 978-1-84596-545-7
- Ritchie, Jean (1988), Myra Hindley—Inside the Mind of a Murderess, Angus & Robertson, ISBN 978-0-207-15882-7
- Staff, Duncan (2007), The Lost Boy (1st ed.), Bantam Press, ISBN 978-0-593-05692-9
- Topping, Peter (1989), Topping: The Autobiography of the Police Chief in the Moors Murder Case, Angus & Robertson, ISBN 978-0-207-16480-4
- Williams, Emlyn (1992), Beyond Belief: A Chronicle of Murder and Its Detection, Pan Macmillan, ISBN 978-0-330-02088-6
Further reading
- Boar, Roger; Blundell, Nigel (1988), The World's Most Infamous Murders, Berkley, ISBN 978-0-425-10887-1
- Goodman, Jonathan (1986), The Moors Murders: The Trial of Myra Hindley and Ian Brady, David & Charles, ISBN 978-1-85813-539-7
- Hansford Johnson, Pamela (1967), On Iniquity, Macmillan, ISBN 978-0-684-12984-6
- Harrison, Fred (1986), Brady and Hindley: The Genesis of the Moors Murders, Grafton, ISBN 978-0-906798-70-6
- Hawkins, Cathy (2004). "The Monster Body of Myra Hindley". Scan: Journal of Media Arts Culture.
- Potter, John Deane (1967), The Monsters Of The Moors: The full account of the Brady-Hindley case, Ballantine Books
- Robins, Joyce (1993), Serial Killers and Mass Murderers: 100 Tales of Infamy, Barbarism and Horrible Crime, Bounty Books, ISBN 978-1-85152-363-4
- Smith, David; Lee, Carol Anne (2011), Witness: The Story of David Smith, Chief Prosecution Witness in the Moors Murders Case, Mainstream Publishing, ISBN 978-1-84596-739-0
- West, Ann (1989), For the Love of Lesley, W. H. Allen/Virgin Books, ISBN 978-1-85227-160-2
- Wilson, Colin; Wilson, Damon; Wilson, Rowan (1993). World Famous Murders. London: Parragon. pp. 432–441. ISBN 978-0-752-50122-2.
External links
- CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of February 2019
- 1963 in England
- 1964 in England
- 1965 in England
- 1966 in England
- Child sexual abuse in England
- History of Greater Manchester
- Murder in Greater Manchester
- Murder in Yorkshire
- Murdered English children
- Rape in England
- Serial murders in the United Kingdom
- Torture in England
- 1963 murders in the United Kingdom
- 1964 murders in the United Kingdom
- 1965 murders in the United Kingdom
- 1966 murders in the United Kingdom
