Cone (category theory): Difference between revisions
→External links: Edited |
|||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://ncatlab.org/nlab nLab], a wiki project on mathematics, physics and philosophy with emphasis on the ''n''-categorical point of view |
* [http://ncatlab.org/nlab nLab], a wiki project on mathematics, physics and philosophy with emphasis on the ''n''-categorical point of view |
||
* [http://wildcatsformma.wordpress.com WildCats] is a category theory package for [[Mathematica]]. Manipulation and visualization of objects, [[morphism]]s, categories, [[functor]]s, [[natural transformation]]s, [[universal properties]]. |
* [http://wildcatsformma.wordpress.com WildCats] is a category theory package for [[Mathematica]]. Manipulation and visualization of objects, [[morphism]]s, categories, [[functor]]s, [[natural transformation]]s, [[universal properties]] and Cones. |
||
* [http://www.youtube.com/user/TheCatsters The catsters], a YouTube channel about category theory. |
* [http://www.youtube.com/user/TheCatsters The catsters], a YouTube channel about category theory. |
||
*{{planetmath reference|id=5622|title=Category Theory}} |
*{{planetmath reference|id=5622|title=Category Theory}} |
||
Revision as of 14:07, 27 December 2012
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, the cone of a functor is an abstract notion used to define the limit of that functor. Cones make other appearances in category theory as well.
Definition
Let F : J → C be a diagram in C. Formally, a diagram is nothing more than a functor from J to C. The change in terminology reflects the fact that we think of F as indexing a family of objects and morphisms in C. The category J is thought of as an "index category". One should consider this in analogy with the concept of an indexed family of objects in set theory. The primary difference is that here we have morphisms as well.
Let N be an object of C. A cone from N to F is a family of morphisms
for each object X of J such that for every morphism f : X → Y in J the following diagram commutes:
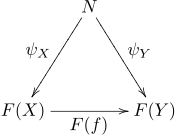
The (usually infinite) collection of all these triangles can be (partially) depicted in the shape of a cone with the apex N. The cone ψ is sometimes said to have vertex N and base F.
One can also define the dual notion of a cone from F to N (also called a co-cone) by reversing all the arrows above. Explicitly, a cone from F to N is a family of morphisms
for each object X of J such that for every morphism f : X → Y in J the following diagram commutes:
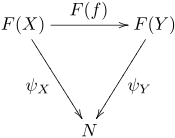
Equivalent formulations
At first glance cones seem to be slightly abnormal constructions in category theory. They are maps from an object to a functor (or vice-versa). In keeping with the spirit of category theory we would like to define them as morphisms or objects in some suitable category. In fact, we can do both.
Let J be a small category and let CJ be the category of diagrams of type J in C (this is nothing more than a functor category). Define the diagonal functor Δ : C → CJ as follows: Δ(N) : J → C is the constant functor to N for all N in C.
If F is a diagram of type J in C, the following statements are equivalent:
- ψ is a cone from N to F
- ψ is a natural transformation from Δ(N) to F
- (N, ψ) is an object in the comma category (Δ ↓ F)
The dual statements are also equivalent:
- ψ is a co-cone from F to N
- ψ is a natural transformation from F to Δ(N)
- (N, ψ) is an object in the comma category (F ↓ Δ)
These statements can all be verified by a straightforward application of the definitions. Thinking of cones as natural transformations we see that they are just morphisms in CJ with source (or target) a constant functor.
Category of cones
By the above, we can define the category of cones to F as the comma category (Δ ↓ F). Morphisms of cones are then just morphisms in this category. As one might expect a morphism from a cone (N, ψ) to a cone (L, φ) is just a morphism N → L such that all the "obvious" diagrams commute (see the first diagram in the next section).
Likewise, the category of co-cones from F is the comma category (F ↓ Δ).
Universal cones
Limits and colimits are defined as universal cones. That is, cones through which all other cones factor. A cone φ from L to F is a universal cone if for any other cone ψ from N to F there is a unique morphism from ψ to φ.

Equivalently, a universal cone to F is a universal morphism from Δ to F (thought of as an object in CJ), or a terminal object in (Δ ↓ F).
Dually, a cone φ from F to L is a universal cone if for any other cone ψ from F to N there is a unique morphism from φ to ψ.

Equivalently, a universal cone from F is a universal morphism from F to Δ, or an initial object in (F ↓ Δ).
The limit of F is a universal cone to F, and the colimit is a universal cone from F. As with all universal constructions, universal cones are not guaranteed to exist for all diagrams F, but if they do exist they are unique up to a unique isomorphism.
References
- Mac Lane, Saunders (1998). Categories for the Working Mathematician (2nd ed. ed.). New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-98403-8.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help)
External links
- nLab, a wiki project on mathematics, physics and philosophy with emphasis on the n-categorical point of view
- WildCats is a category theory package for Mathematica. Manipulation and visualization of objects, morphisms, categories, functors, natural transformations, universal properties and Cones.
- The catsters, a YouTube channel about category theory.
- "Category Theory". PlanetMath.
- Video archive of recorded talks relevant to categories, logic and the foundations of physics.
- Interactive Web page which generates examples of categorical constructions in the category of finite sets.


