Rotary vane pump: Difference between revisions
Doctormatt (talk | contribs) m fixed link |
m Add Dry rotary vane pump diagram |
||
| (243 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Positive-displacement pump consisting of vanes mounted to a rotor that rotates inside a cavity}} |
|||
[[Image:Rotary vane pump.svg|thumb|300px|Rotary vane pump]]A '''rotary vane pump''' is a positive displacement [[pump]] that consists of vanes mounted to a [[rotor]] that rotates inside of a cavity. In some cases these vanes can be variable length and/or tensioned to maintain contact with the walls as the pump rotates. The most simple vane pump is a circular rotor rotating inside of a larger circular cavity. The centers of these two circles are offset, causing eccentricity. Vanes are allowed to slide into and out of the rotor and seal on all edges, creating vane chambers that do the pumping work. On the intake side of the pump, the vane chambers are increasing in volume. These increasing volume vane chambers are filled with fluid forced in by the inlet pressure. Often this inlet pressure is nothing more than pressure from the atmosphere. On the discharge side of the pump, the vane chambers are decreasing in volume, forcing fluid out of the pump. The action of the vane drives out the same volume of fluid with each rotation. Multistage rotary vane vacuum pumps can attain pressures as low as 10<sup>-3</sup> [[Torr]]. |
|||
[[File:Pompe à palettes.gif|thumb|An eccentric rotary vane pump]] |
|||
[[File:Rotary vane pump.svg|thumb|300px|Another eccentric rotary-vane pump design. Note that modern pumps have an area contact between rotor and stator (and not a line contact).<br /> |
|||
1. pump housing<br /> |
|||
2. rotor<br /> |
|||
3. vanes<br /> |
|||
4. spring]] |
|||
A '''rotary vane pump''' is a type of [[positive-displacement pump]] that consists of [[Wiktionary:vane#Noun|vanes]] mounted to a [[rotor (turbine)|rotor]] that rotates inside a cavity. In some cases, these vanes can have variable length and/or be tensioned to maintain contact with the walls as the pump rotates. |
|||
This type of pump is considered less suitable than other [[vacuum pump]]s for high-viscosity and high-pressure fluids{{Citation needed|date=December 2022}}, and is {{clarify|text=complex to operate|reason=What? How does the term operate even apply here?|date=December 2022}}{{Citation needed|date=December 2022}}. They can endure short periods of dry operation, and are considered good for low-viscosity fluids{{Citation needed|date=December 2022}}. |
|||
Common uses of vane pumps include high pressure [[Hydraulic machinery#Pumps|hydraulic pumps]] and automotive uses including [[power steering]] and [[automatic transmission]] pumps. Pumps for mid-range pressures include applications such as carbonators for fountain soft drink dispensers and espresso coffee machines. They are also often used as [[vacuum pump]]s for providing braking assistance (through a braking [[booster]]) in [[diesel]]-engined vehicles. Furthermore, vane pumps can be used in low-vacuum applications including evacuating refrigerant lines in [[air conditioners]], and laboratory freeze dryers, extensively in semiconductor low pressure chemical vapor deposition systems, and [[vacuum]] experiments in physics. |
|||
==Types== |
|||
See also: [[Rotary vane pump principle (System Willimczik)]] |
|||
The simplest vane pump has a circular rotor rotating inside a larger circular cavity. The centers of these two circles are offset, causing eccentricity. Vanes are mounted in slots cut into the rotor. The vanes are allowed a certain limited range of movement within these slots such that they can maintain contact with the wall of the cavity as the rotor rotates. The vanes may be encouraged to maintain such contact through means such as [[spring (device)|springs]], [[gravity]], or [[centrifugal force]]. A small amount of [[oil]] may be present within the mechanism to help create a better seal between the tips of the vanes and the cavity's wall. The contact between the vanes and the cavity wall divides up the cavity into "vane chambers" that do the pumping work. On the suction side of the pump, the vane chambers are increased in volume and are thus filled with fluid forced in by the inlet vacuum pressure, which is the pressure from the system being pumped, sometimes just the atmosphere. On the discharge side of the pump, the vane chambers decrease in volume, compressing the fluid and thus forcing it out of the outlet. The action of the vanes pulls through the same volume of fluid with each rotation. |
|||
Multi-stage rotary-vane vacuum pumps, which force the fluid through a series of two or more rotary-vane pump mechanisms to enhance the pressure, can attain vacuum pressures as low as 10<sup>−6</sup> [[bar (unit)|bar]] (0.1 [[Pascal (unit)|Pa]]). |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Uses== |
|||
*[http://www.mekanizmalar.com/vanepump.html Flash Animation of Rotary Vane Pump] |
|||
Vane pumps are commonly used as high-pressure [[hydraulic pump]]s and in automobiles, including [[supercharger|supercharging]], [[power steering|power-steering]], [[automobile air conditioning|air conditioning]], and [[automatic transmission|automatic-transmission]] pumps{{Citation needed|date=December 2022}}. Pumps for mid-range pressures include applications such as carbonators for fountain soft-drink dispensers and espresso coffee machines{{Citation needed|date=December 2022}}. Furthermore, vane pumps can be used in low-pressure gas applications such as [[secondary air injection]] for auto exhaust emission control, or in low-pressure [[chemical vapor deposition]] systems{{Citation needed|date=December 2022}}. |
|||
Rotary-vane pumps are also a common type of [[vacuum pump]], with two-stage pumps able to reach pressures well below 10<sup>−6</sup> [[bar (unit)|bar]]. These are found in such applications as providing braking assistance in large trucks and diesel-powered passenger cars (whose engines do not generate intake vacuum) through a braking [[vacuum servo|booster]], in most light aircraft to drive gyroscopic [[flight instruments]], in evacuating refrigerant lines during installation of [[air conditioner]]s, in laboratory freeze dryers, and [[vacuum]] experiments in physics{{Citation needed|date=December 2022}}. In the vane pump, the pumped gas and the oil are mixed within the pump, and so they must be separated externally. Therefore, the inlet and the outlet have a large chamber, perhaps with swirl, where the oil drops fall out of the gas. Sometimes the inlet has [[louver]]s cooled by the room air (the pump is usually 40 K hotter) to condense cracked pumping oil and water, and let it drop back into the inlet. When these pumps are used in high-vacuum systems (where the inflow of gas into the pump becomes very low), a significant concern is contamination of the entire system by molecular oil back streaming. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
== History == |
|||
[[de:Drehschieberpumpe]] |
|||
Like many simple mechanisms, it is unclear when the rotary vane pump was invented. [[Agostino Ramelli]]'s 1588 book ''Le diverse et artificiose machine del capitano Agostino Ramelli'' ("The Various and Ingenious Machines of Captain Agostino Ramelli") contains a description and an engraving of a rotary vane pump<ref>{{cite web | url=https://digital.sciencehistory.org/works/9k41zd698 | title=Plate 108: Device for two men to drain water from a marsh or foundation }}</ref> along with other types of rotary pumps, which suggests that the design was known at the time. In more recent times, vane pumps also show up in 19th-century patent records. In 1858, a US patent was granted to one W. Pierce for "a new and useful Improvement in Rotary Pumps", which acknowledged as [[prior art]] sliding blades "used in connection with an eccentric inner surface".<ref>{{cite web | url=https://patents.google.com/patent/US19581A/ | title=Rotary pump }}</ref> In 1874, a Canadian patent was granted to Charles C. Barnes of [[Sackville, New Brunswick]].<ref>Mario Theriault, ''Great Maritime Inventions 1833-1950'', Goose Lane Editions, 2001, p. 53.</ref><ref>Bill Snowdon, "[https://tantramarheritage.ca/2012/02/white-fence-54/ Charles C. Barnes: Farmer, Fisherman, Ship-builder, Inventor]", in The White Fence, Issue #54, February 2012, Tantramar Heritage Trust"</ref><ref>{{cite patent |country=CA |number=3559A |status= |title=Rotary Pump |pubdate=1874-06-15 |gdate= |fdate= |pridate= |inventor=Charles C. Barnes |invent1= |invent2= |assign1= |assign2= |class= |url=}}</ref> There have been various improvements since, including a variable vane pump for gases (1909).<ref>{{cite patent |inventor-last = Hoffmann |inventor-first = C. |publication-date = 1906 |issue-date = 1908 |title = Rotary pump for gases |country-code = US |patent-number = 878528 }}</ref> |
|||
[[et:Labapump]] |
|||
== Variable-displacement vane pump == |
|||
One of the major advantages of the vane pump is that the design readily lends itself to become a variable-displacement pump, rather than a fixed-displacement pump such as a [[gear pump|spur-gear]] or a [[gerotor]] pump. The centerline distance from the rotor to the eccentric ring is used to determine the pump's displacement. By allowing the eccentric ring to pivot or translate relative to the rotor, the displacement can be varied. It is even possible for a vane pump to pump in reverse if the eccentric ring moves far enough. However, performance cannot be optimized to pump in both directions. This can make for a very interesting hydraulic-control oil pump. |
|||
A variable-displacement vane pump is used as an energy-saving device and has been used in many applications, including automotive transmissions, for over 30 years.<ref name="DAE1">Vane Pumps: DAE Pumps' Rotary Vane & Vacuum Pumps. Retrieved from: https://www.daepumps.com</ref><ref name="Castle1">Rotary Vane Pump Guide & Sliding Vane Pump Design | Castle Pumps. Retrieved from: https://www.castlepumps.com</ref><ref name="Anderson1">What is a Rotary Vane Pump and How Does it Work? - Anderson Process. Retrieved from: https://www.andersonprocess.com</ref> |
|||
== Materials == |
|||
* Externals (head, casing) – cast iron, ductile iron, steel, brass, plastic, and stainless steel |
|||
* Vane, pushrods – carbon graphite, [[Polyether ether ketone|PEEK]] |
|||
* End plates – carbon graphite |
|||
* Shaft seal – component mechanical seals, industry-standard cartridge mechanical seals, and magnetically driven pumps |
|||
* Packing – available from some vendors, but not usually recommended for thin liquid service |
|||
==See also== |
|||
*[[Guided-rotor compressor]] |
|||
*[[Powerplus supercharger]] |
|||
*[https://www.oxiliair.com/principe-fonctionnement-pompe Dry rotary vane pump diagram] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[http://www.videosafety.com/compressor/details2.htm H. Eugene Bassett's articulated displacer compressor] |
|||
*[https://media.giphy.com/media/TkDyhfw9N9HWHSN8ML/giphy.gif Vane Pump Animation] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 16:07, 30 December 2024

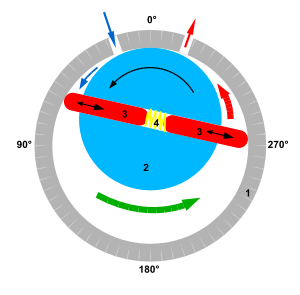
1. pump housing
2. rotor
3. vanes
4. spring
A rotary vane pump is a type of positive-displacement pump that consists of vanes mounted to a rotor that rotates inside a cavity. In some cases, these vanes can have variable length and/or be tensioned to maintain contact with the walls as the pump rotates.
This type of pump is considered less suitable than other vacuum pumps for high-viscosity and high-pressure fluids[citation needed], and is complex to operate[clarification needed][citation needed]. They can endure short periods of dry operation, and are considered good for low-viscosity fluids[citation needed].
Types
[edit]The simplest vane pump has a circular rotor rotating inside a larger circular cavity. The centers of these two circles are offset, causing eccentricity. Vanes are mounted in slots cut into the rotor. The vanes are allowed a certain limited range of movement within these slots such that they can maintain contact with the wall of the cavity as the rotor rotates. The vanes may be encouraged to maintain such contact through means such as springs, gravity, or centrifugal force. A small amount of oil may be present within the mechanism to help create a better seal between the tips of the vanes and the cavity's wall. The contact between the vanes and the cavity wall divides up the cavity into "vane chambers" that do the pumping work. On the suction side of the pump, the vane chambers are increased in volume and are thus filled with fluid forced in by the inlet vacuum pressure, which is the pressure from the system being pumped, sometimes just the atmosphere. On the discharge side of the pump, the vane chambers decrease in volume, compressing the fluid and thus forcing it out of the outlet. The action of the vanes pulls through the same volume of fluid with each rotation.
Multi-stage rotary-vane vacuum pumps, which force the fluid through a series of two or more rotary-vane pump mechanisms to enhance the pressure, can attain vacuum pressures as low as 10−6 bar (0.1 Pa).
Uses
[edit]Vane pumps are commonly used as high-pressure hydraulic pumps and in automobiles, including supercharging, power-steering, air conditioning, and automatic-transmission pumps[citation needed]. Pumps for mid-range pressures include applications such as carbonators for fountain soft-drink dispensers and espresso coffee machines[citation needed]. Furthermore, vane pumps can be used in low-pressure gas applications such as secondary air injection for auto exhaust emission control, or in low-pressure chemical vapor deposition systems[citation needed].
Rotary-vane pumps are also a common type of vacuum pump, with two-stage pumps able to reach pressures well below 10−6 bar. These are found in such applications as providing braking assistance in large trucks and diesel-powered passenger cars (whose engines do not generate intake vacuum) through a braking booster, in most light aircraft to drive gyroscopic flight instruments, in evacuating refrigerant lines during installation of air conditioners, in laboratory freeze dryers, and vacuum experiments in physics[citation needed]. In the vane pump, the pumped gas and the oil are mixed within the pump, and so they must be separated externally. Therefore, the inlet and the outlet have a large chamber, perhaps with swirl, where the oil drops fall out of the gas. Sometimes the inlet has louvers cooled by the room air (the pump is usually 40 K hotter) to condense cracked pumping oil and water, and let it drop back into the inlet. When these pumps are used in high-vacuum systems (where the inflow of gas into the pump becomes very low), a significant concern is contamination of the entire system by molecular oil back streaming.
History
[edit]Like many simple mechanisms, it is unclear when the rotary vane pump was invented. Agostino Ramelli's 1588 book Le diverse et artificiose machine del capitano Agostino Ramelli ("The Various and Ingenious Machines of Captain Agostino Ramelli") contains a description and an engraving of a rotary vane pump[1] along with other types of rotary pumps, which suggests that the design was known at the time. In more recent times, vane pumps also show up in 19th-century patent records. In 1858, a US patent was granted to one W. Pierce for "a new and useful Improvement in Rotary Pumps", which acknowledged as prior art sliding blades "used in connection with an eccentric inner surface".[2] In 1874, a Canadian patent was granted to Charles C. Barnes of Sackville, New Brunswick.[3][4][5] There have been various improvements since, including a variable vane pump for gases (1909).[6]
Variable-displacement vane pump
[edit]One of the major advantages of the vane pump is that the design readily lends itself to become a variable-displacement pump, rather than a fixed-displacement pump such as a spur-gear or a gerotor pump. The centerline distance from the rotor to the eccentric ring is used to determine the pump's displacement. By allowing the eccentric ring to pivot or translate relative to the rotor, the displacement can be varied. It is even possible for a vane pump to pump in reverse if the eccentric ring moves far enough. However, performance cannot be optimized to pump in both directions. This can make for a very interesting hydraulic-control oil pump.
A variable-displacement vane pump is used as an energy-saving device and has been used in many applications, including automotive transmissions, for over 30 years.[7][8][9]
Materials
[edit]- Externals (head, casing) – cast iron, ductile iron, steel, brass, plastic, and stainless steel
- Vane, pushrods – carbon graphite, PEEK
- End plates – carbon graphite
- Shaft seal – component mechanical seals, industry-standard cartridge mechanical seals, and magnetically driven pumps
- Packing – available from some vendors, but not usually recommended for thin liquid service
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Plate 108: Device for two men to drain water from a marsh or foundation".
- ^ "Rotary pump".
- ^ Mario Theriault, Great Maritime Inventions 1833-1950, Goose Lane Editions, 2001, p. 53.
- ^ Bill Snowdon, "Charles C. Barnes: Farmer, Fisherman, Ship-builder, Inventor", in The White Fence, Issue #54, February 2012, Tantramar Heritage Trust"
- ^ CA 3559A, Charles C. Barnes, "Rotary Pump", published 1874-06-15
- ^ US 878528, Hoffmann, C., "Rotary pump for gases", published 1906, issued 1908
- ^ Vane Pumps: DAE Pumps' Rotary Vane & Vacuum Pumps. Retrieved from: https://www.daepumps.com
- ^ Rotary Vane Pump Guide & Sliding Vane Pump Design | Castle Pumps. Retrieved from: https://www.castlepumps.com
- ^ What is a Rotary Vane Pump and How Does it Work? - Anderson Process. Retrieved from: https://www.andersonprocess.com
