Thymine: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
add zh link |
m spacing |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Here is a table of data; skip past it to edit the text. --> |
<!-- Here is a table of data; skip past it to edit the text. --> |
||
<!-- <nowiki> Submit {{subst:chembox_simple_organic}} to get this template or go to [[Template:Chembox_simple_organic]]. </nowiki> --> |
<!-- <nowiki> Submit {{subst:chembox_simple_organic}} to get this template or go to [[Template:Chembox_simple_organic]]. </nowiki> --> |
||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="right" style="margin-left:1em" |
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="right" style="margin-left:1em" |
||
! colspan="2" align=center bgcolor="#cccccc" | '''Thymine''' |
! colspan="2" align=center bgcolor="#cccccc" | '''Thymine''' |
||
Revision as of 03:05, 2 July 2005
| Thymine | |
|---|---|
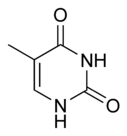
| Chemical name | 5-Methylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione |
| Chemical formula | C5H6N2O2 |
| Molecular mass | 126.11 g/mol |
| Melting point | 316 - 317 °C |
| CAS number | 65-71-4 |
| SMILES | CC1=CNC(NC1=O)=O |
| |
Thymine, also known as 5-methyluracil, is a pyrimidine nucleobase. It is found in the nucleic acid DNA. In RNA thymine is replaced with uracil. Thymine can base pair with adenine.
Thymine combined with deoxyribose creates the nucleoside thymidine. Thymidine can be phosphorylated with one, two or three phosphoric acid groups, creating respectively TMP, TDP or TTP (thymidine mono- di- or triphosphate).
