Danish Realm: Difference between revisions
In fact from the year 1814 |
Cyberbot II (talk | contribs) Rescuing 1 sources. #IABot |
||
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
** {{da icon}} [http://www.stm.dk/_p_7794.html ''Rigsfællesskabet''] (Statsministeriet). |
** {{da icon}} [http://www.stm.dk/_p_7794.html ''Rigsfællesskabet''] (Statsministeriet). |
||
* {{da icon}} [http://www.dr.dk/nyheder/htm/baggrund/tema2002/lagtingsvalg%20paa%20faroerne/43.htm Background on the Faroe Islands] ([[DR (broadcaster)|DR]] website). |
* {{da icon}} [http://www.dr.dk/nyheder/htm/baggrund/tema2002/lagtingsvalg%20paa%20faroerne/43.htm Background on the Faroe Islands] ([[DR (broadcaster)|DR]] website). |
||
* [http://www.dnag.dk/ The North Atlantic Group in the Danish Parliament] |
* [https://web.archive.org/20070811092408/http://www.dnag.dk:80/ The North Atlantic Group in the Danish Parliament] |
||
{{Denmark topics}} |
{{Denmark topics}} |
||
Revision as of 02:50, 23 February 2016
The Danish Realma
| |
|---|---|
 The Danish Realm on the Globe. (dark green) | |
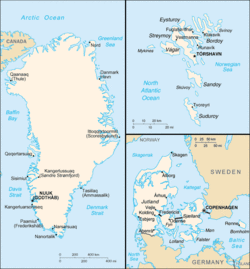 Clockwise from bottom right (sizes not to scale): Maps of Denmark (Northern Europe), Greenland (North Atlantic and Arctic) and the Faroe Islands (North Atlantic). | |
| Official languages | |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Margrethe II |
| Lars Løkke Rasmussen | |
| Aksel V. Johannesen | |
| Kim Kielsen | |
| Legislature | Folketing Løgting Inatsisartut |
| Establishment | |
• Faroese Home Rule | 24 March 1948[1] |
• Greenlandic Home Rule Act | 29 November 1978[2](effective 1 May 1979) |
• Faroese takeover act (overtagelsesloven) | 29 July 2005[3][4] |
• Greenlandic self rule | 21 June 2009 |
| Area | |
• Denmark[N 1] | 42,915.7 km2 (16,569.8 sq mi)[6] (130rd) |
• Greenland | 2,166,086 km2 (836,330 sq mi) |
• Faroe Islands | 1,399 km2 (540.16 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• July 2015 estimate | 5,678,348[7] (113th) |
• Greenland | 56,370[8][N 2] |
• Faroe Islands | 49,709[9][N 2] |
• Density (Denmark) | 131/km2 (339.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate |
• Total | $255.866 billion[10][N 3] (52nd) |
• Per capita | $45,451[10] (19th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2015 estimate |
• Total | $297.359 billion[10][N 3] (34th) |
• Per capita | $52,822[10] (6th) |
| Gini (2012) | low inequality |
| HDI (2013) | very high (10th) |
| Currency | Danish kroneb (DKK) |
| Time zone | UTC+1, +0, +0 to −4 (CET WET WGT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2, +1, +1 to −3a (CEST WEST WGST) |
| Date format | DD/MM/YYYY |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +45 +298 +299 |
| Internet TLD | .dk .fo .gl |
| |
The Danish Realm (Template:Lang-da;[14] Template:Lang-da; Template:Lang-fo; Template:Lang-kl) is an official term[14][15] for the relations between Denmark proper and the two overseas constituent countries, the Faroe Islands and Greenland, which collectively make up the Kingdom of Denmark.
The nature of the Kingdom of Denmark is fundamentally one of a unitary sovereign state. The Faroe Islands and Greenland have been integrated parts of the Kingdom of Denmark since the 19th century. However, due to their separate historical and cultural identities, these parts of the Realm have an extensive type of self-government and have assumed legislative and administrative responsibility in a substantial number of fields.[16]
The Danish Constitution stipulates that the foreign and security interests for all parts of the Kingdom of Denmark are the responsibility of the Danish government. The Faroes received home rule in 1948 and Greenland did so in 1979. Greenland received even greater powers in 2009 in the form of "self rule", thus leaving the Danish government with virtually no influence over Greenlandic internal affairs.
Constitutionality
The Kingdom of Denmark's unique state of internal affairs is acted out in the principle of the "unity of the Realm".[14] This principle is derived from Article 1 of the Danish Constitution, which specifies that constitutional law applies equally to all areas of the Danish Realm.[17] The Constitutional Act specifies that sovereignty is to continue to be exclusively with the authorities of the Realm (the Danish government and parliament). Faroese or Greenlandic self-governance cannot be established by international treaties but must be established by Danish law; the Danish parliament (the Folketing) delegates a precisely defined part of its competence to the home rule authorities.[18]
The language of Denmark is Danish, and the Danish state authorities are based in Denmark. The Kingdom of Denmark's parliament, with its 179 members, is located in the capital, Copenhagen. Two of the parliament's members are elected in each of Greenland the Faeroe Islands; the remaining 175 members are elected in Denmark. The Government ministries are located in Copenhagen, as is the highest court, the Supreme Court.[17]
Devolved powers
In principle, the Danish Realm constitutes a unified sovereign state, with equal status between its constituent parts.[13] Devolution differs from federalism in that the devolved powers of the subnational authority ultimately reside in central government, thus the state remains, de jure unitary.
The Self-Government Arrangements devolves political competence and responsibility from the Danish political authorities to the Faroese and the Greenlandic political authorities. The Faroese and Greenlandic authorities administer the tasks taken over from the state, enact legislation in these specific fields and have the economic responsibility for solving these tasks. The Danish government provides an annual grant to the Faroese and the Greenlandic authorities to cover the costs of these devolved areas.[16]

The 1948 "Home Rule Act of the Faroe Islands" sets out the terms of Faroese home rule. The Act states, "...the Faroe Islands shall constitute a self-governing community within the State of Denmark."[1] It establishes the home government of the Faroe Islands (Landsstýrid) and the Faroese parliament, the Løgting. More significantly, the Act specifies the powers devolved from the Government of Denmark, including: local government and municipal affairs; taxation, at a local and territorial level; public services, including police and town planning; welfare services, such as housing; primary and secondary education; Archives, libraries, museums; agriculture and fishing; entertainment; among other areas.[1] The Faroe Islands were previously administered as a Danish county (amt); the Home Rule Act abolished the post of Amtmand (County Governor) and replaced it with the role of Rigsombudsmand (High Commissioner to the Danish government).[1] These powers were expanded in a 2005 Act, which named the Faroese home government as an "equal partner" with the Danish government.[19]
The 1978 "Greenland Home Rule Act" devolves powers in much the same way as the Faroese Home Rule Act. It sets out a home rule government and Greenlandic parliament. Specific areas of governance specified in the act include: Organization of local government; Fishing and agriculture; Welfare system; protection of the environment; other areas affecting Greenlanders directly, etc.[2]
On 21 June 2009, Greenland assumed self-determination with responsibility for self-government of judicial affairs, policing, natural resources, immigration and border controls. Also, Greenlanders were recognized as a separate people under international law.[20] Greenland is now described as having "self rule", with its home government exercising a wider range of powers.
There are a number of matters that can not be acquired by the territories; Constitutional affairs, foreign policy, defence, the Supreme Court, citizenship, and monetary policy. Additionally, the Faroese and Greenlandic parliaments are subordinate to the Parliament of the Kingdom of Denmark, where the two territories are represented by two seats each (from a total of 179 seats).
Legal status
The arrangement between the areas of the Realm is sometimes described as constituent countries. Greenland's powers of self-government were increased in 2009 through the Greenland Self-Rule Act, which established the Greenlanders as a separate national people under international law, while the Faroe Islands have gradually taken control of more and more areas according to their Home Rule Act from 1948.[21] The Faroese/Danish act of 2005 states "This law is based on an agreement between the Governments of the Faroe Islands and Denmark as equal partners."[22] Despite this principle of unity among the three territories, some commentators consider the Danish Realm as a federation or a sui generis legal construction. In the opinion of Bogi Eliasen, the Kingdom of Denmark is not a unitary state "but a structure with some federative elements of divided power".[13] Danish justice Frederik Harhoff states that the Kingdom of Denmark is "neither a federation (since it lacks a treaty to this effect), nor is it a confederation"[13]
International community
Previously, most foreign relations were undertaken by the Government of Denmark exclusively on behalf of the entire realm, but more recently the Faroe Islands and Greenland have increased their role in the foreign policy. Representatives for both have joined Danish delegations in discussions on some international matters, such as fishing rights. Greenlandic representatives were included in the process of a new treaty between Denmark and the US regarding the Thule Air Base in northwest Greenland.
The Kingdom of Denmark as a whole is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the OECD and the World Trade Organization. The Faroe Islands and Greenland are associated members of the Nordic Council in their own right as part of the wider membership of the Kingdom. Although Denmark is a member of the European Union, both areas have special dispensation and remain outside the EU. Greenland joined the EU as part of Denmark in 1973, but opted to leave in 1985 after Greenlandic home rule was introduced in 1979.
The "Home Rule Act of the Faroe Islands" specifies that a 'Faroese' shall be understood to mean a person who is a "national of Denmark and a resident of the Faroe Islands".[1] The Government of Denmark issues special passports for its citizens living in the Faroe Islands and Greenland with the right to choose a regular Danish passport as well. The Faroese Home Rule Act states that, in Faroese passports, Føroyingur (Faroese) and Føroyar (Faroe Islands) shall be inserted after the words Dansk (Danish) and Danmark (Denmark).[1]
Population and area

The populations and areas of the three countries differ significantly. Though Greenland has an area of over two million km² (836,109 square miles), making it the largest island in the world, it had a population of just 57,695 in 2011 — scarcely a hundredth part of the population of Denmark. The Faroe Islands, too, are small in population, and they are small as well in area.
The disparity between the small population of the former colonies and the greater population of Denmark has helped to enforce the hegemonial position that Denmark holds in the Realm. When the areas of the three territories are combined, the Kingdom of Denmark ranks as the twelfth largest country in the world, the same rank held by Greenland alone.
| Country | Legislature | Area | Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km² | % | Estimates (2015) |
% | Density (per km²) | ||
| Folketing | 43,094 | 1.95 | 5,659,715 | 98.11 | 131 | |
| Løgting | 1,399 | 0.06 | 48,724 | 0.87 | 35 | |
| Inatsisartut | 2,166,086 | 97.99 | 55,984 | 1.02 | 0.026 | |
| Folketing | 2,210,579 | 100 | 5,764,423 | 100 | 2.6 | |
| [9][23][24] | ||||||
Terminology
- Hjemmestyre
- Meaning "home rule", it indicates an autonomous administration (present in both in Greenland and the Faroe Islands) that has power over all internal affairs. In this arrangement, the Danish government deals only with external matters such as defence and foreign affairs. Greenland and the Faroe Islands maintain their own parliaments and governments, headed by a prime minister who appoints a cabinet. This is synonymous with "self-governing."
- Selvstyre
- Following a referendum on 25 November 2008 (the 30th anniversary of the establishment of home rule in Greenland), the relationship between the Danish and Greenlandic governments changed, with Greenland gaining greater autonomy. Further powers were granted to the Greenlandic government on 21 June 2009, including control of the police force, coastguard, and courts. Additionally, Greenland now receives fewer Danish subsidies, becoming more self-sufficient.[25] As a result of these changes Greenland was now said to have self rule with minimal support from Denmark, as opposed to "home rule".
- Rigsombudsmand
- High Commissioners represent the interests of Denmark in the Faroe Islands and Greenland. There is one Danish High Commissioner in each country. He or she can attend the meetings at the Løgting in the Faroes and at the Inatsisartut in Greenland, but they can't vote.
- Folketingsmedlemmer fra Færøerne og Grønland
- Members of Folketing from the Faroe Islands and Greenland: Greenland and the Faroe Islands and their self-rule administrations take part in consultations on policies and decisions affecting their region, including negotiations with the devolved legislatures and the Danish parliament (Folketing). They have two members each, and these are full members of the Danish Folketing and are allowed to vote.
- Constituent countries
- Mirroring the terminology of the United Kingdom or the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Greenland, Denmark and the Faroes are sometimes referred to as constituent countries within the sovereign state of the Kingdom of Denmark. However, such usage is inconsistent; whilst Denmark proper may be referred to as a country, Greenland and the Faroe Islands are officially referred to as "self-governing territories".[26] Additionally, the recent law granting Greenland "self rule" in 2008 refers to Greenland as "a people", but not a country.[27]
See also
- List of Danish High Commissioners in Greenland
- List of Danish High Commissioners in the Faroe Islands
- Kingdom of Iceland
- Constituent country
- Constitution of Denmark
- Faroese independence
- Greenlandic independence
- Icelandic independence movement
- Danish colonization of the Americas
- Norwegian Realm
Notes
- ^ The Kingdom of Denmark's territory in continental Europe is referred to as "Denmark proper" (Template:Lang-da), "metropolitan Denmark",[5] or simply Denmark. In this article, usage of "Denmark" excludes Greenland and the Faroe Islands.
- ^ a b 2013 estimate
- ^ a b This data is for Denmark proper only. For data relevant to Greenland and the Faroe Islands see their respective articles.
References
- ^ a b c d e f "Home Rule Act of the Faroe Islands". Prime Minister's Office. 23 March 1948. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ a b "The Greenland Home Rule Act". Prime Minister's Office. 29 November 1978. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ "Lov om de færøske myndigheders overtagelse af sager og sagsområder" (in Danish). Retsinformation. 24 June 2005. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- ^ "Den færøske hjemmestyreordning" (in Danish). Statsministeriet. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- ^ Administrative divisions – Denmark The World Factbook. Access date: 14 April 2012
- ^ Statistics Denmark
- ^ July 2015 . Danish Ministry for Economic Affairs and the Interior
- ^ "Greenland in Figures 2013," Statistics Greenland. Retrieved 2 September 2013
- ^ a b "Faroe Islands" - The World Factbook. Accessed 6 June 2012
- ^ a b c d "Denmark". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 3 October 2014.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income (source: SILC)". Eurostat Data Explorer. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ^ "2014 Human Development Report Summary" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2014. pp. 21–25. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- ^ a b c d Denmark Regulations Handbook. Int'l Business Publications. 3 March 2008. p. 19. ISBN 9781433069710. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
"...a relationship known in Danish as Rigsfællesskabet (Commonwealth of the Realm)
- ^ a b c "The unity of the Realm". Prime Minister's Office. Retrieved 23 May 2014.
The Faroe Islands and Greenland are parts of the Danish Realm.
- ^ "Rigsfællesskabet" (in Danish). Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ a b "Greenland and the Faroe Islands". Denmark.dk. Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ a b Constitutional Act of Denmark. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ Dinšṭein, Yôrām. Models of Autonomy. Transaction Publishers. p. 36. ISBN 1412828848.
- ^ retsinformation.dk Lov om de færøske myndigheders overtagelse af sager og sagsområderTemplate:Da icon Denne lov bygger på en overenskomst mellem Færøernes landsstyre og den danske regering som ligeværdige parter.
- ^ Description of the Greenlandic Self-Government Act on the webpage of the Ministry of State of Denmark"The Self-Government Act provides for the Self-Government authorities to assume a number of new fields of responsibility, such as administration of justice, including the establishment of courts of law; the prison and probation service; the police; the field relating to company law, accounting and auditing; mineral resource activities; aviation; law of legal capacity, family law and succession law; aliens and border controls; the working environment; as well as financial regulation and supervision, cf. Schedule I and II in the Annex to the Self-Government Act."
- ^ Logting.elektron.fo
- ^ Retsinformation.dk, Lov om de færøske myndigheders overtagelse af sager og sagsområder
- ^ Population by region and time - Statistics Denmark. Published: 1 April 2011. Archived 2011-10-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Greenland Statistics
- ^ Greenland votes for more autonomy BBC News, 26 November 2008
- ^ Prime Minister of the Faroe Islands. "About the Faroe Islands". Retrieved 8 March 2011
- ^ Act on Greenland Self-Government 2008 Greenlanders are recognized as a separate people under international law.
External links
- The unity of the Realm; the status the Faroe Islands and Greenland (Prime Minister's Office).
- Template:Da icon Rigsfællesskabet (Statsministeriet).
- Template:Da icon Background on the Faroe Islands (DR website).
- The North Atlantic Group in the Danish Parliament


