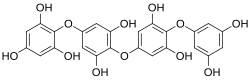
Tetraphlorethol C
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trioxa-1,7(1),3,5(1,4)-tetrabenzenaheptaphane-12,14,16,33,35,53,55,73,75-nonol | |
| Other names
2-[4-[4-(3,5-dihydroxyphenoxy)-3,5-dihydroxyphenoxy]-3,5-dihydroxyphenoxy]benzene-1,3,5-triol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H18O12 | |
| Molar mass | 498.396 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tetraphlorethol C is a phlorethol-type phlorotannin found in the brown alga Ascophyllum nodosum.[1] Chemically, it is a tetramer of 1,2,3,5-tetrahydroxybenzene.
References
[edit]- ^ Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Bach, S.J.; McAllister, T.A. (2008). "Effects of phlorotannins from Ascophyllum nodosum (Brown seaweed) on in vitro ruminal digestion of mixed forage or barley grain". Animal Feed Science and Technology. 145 (1–4): 375–395. doi:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2007.03.013.
