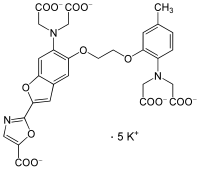
Fura-2
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C29H22N3O145- | |
| Molar mass | 636.50 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fura-2, a polyamino carboxylic acid, is a ratiometric fluorescent dye which binds to free intracellular calcium.[1] It was the first widely-used dye for calcium imaging, and remains very popular. Fura-2 is excited at 340 nm and 380 nm of light, and the ratio of the emissions at those wavelengths is directly correlated to the amount of intracellular calcium. The use of the ratio automatically cancels out confounding variables, such as variable dye concentration and cell thickness, making Fura-2 one of the most preferred tools to quantify calcium levels. More recently, genetically-encoded calcium indicators based on spectral variants of the green fluorescent protein, such as Cameleons[2], have supplemented the use of Fura-2 and other small molecule dyes for calcium imaging.
See also
External links
References
- ^ Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., and Tsien, R.Y. (1985). "A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties*" (PDF). J.Biol.Chem. 260 (6): 3440–3450. PMID 3838314.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Miyawaki A, Llopis J, Heim R; et al. (1997). "Fluorescent indicators for Ca2+ based on green fluorescent proteins and calmodulin". Nature. 388 (6645): 882–7. doi:10.1038/42264. PMID 9278050.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
