Chichibu, Saitama
Chichibu
秩父市 | |
|---|---|
 View of central Chichibu, from Hitsujiyama Park | |
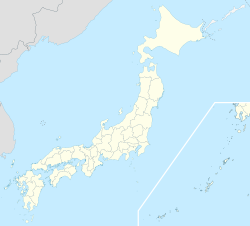
 Location of Chichibu in Saitama Prefecture | |
| Coordinates: 35°59′30.4″N 139°5′7.7″E / 35.991778°N 139.085472°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Saitama Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Kuniyasu Kuki (since April 2009) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 577.83 km2 (223.10 sq mi) |
| Population (February 2016) | |
| • Total | 63,357 |
| • Density | 110/km2 (300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Tree | Kaede |
| Flower | Shiba-zakura |
| Bird | Blue-and-white flycatcher |
| Phone number | 0494-22-2211 |
| Address | 8-15 Kumaki, Chichibu, Saitama 368-8686 |
| Website | http://www.city.chichibu.lg.jp/ |

Chichibu (秩父市, Chichibu-shi) is a city located in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 December 2015[update], the city had an estimated population of 63,358, and a population density of 110 persons per km2. Its total area is 577.83 km2.
Chichibu was incorporated as a city on April 1, 1950, although the region had already existed for hundreds of years and had developed many local traditions. Since that time, the area of the city has grown through a series of mergers, the most recent in 2005.
Geography

Chichibu is in the westernmost part of Saitama. Unlike other parts of the prefecture, it is largely mountainous and the population is concentrated in river terraces along the Arakawa River. It is Saitama's largest municipality in terms of surface area and shares borders with Tokyo, Yamanashi, Nagano and Gunma Prefectures. A large portion of the city belongs to Chichibu-Tama-Kai National Park.[1]
Because the region is not suitable for growing rice, many people have depended on sericulture farming. Limestone from Mount Bukō, which rises south of the city center, is another major source of income for the region. The city is shifting its focus toward sightseeing, taking advantages of its rich natural environment and relative closeness to the Tokyo metropolitan area. The city is also famous for its brewing industry.
Surrounding municipalities
Climate
Chichibu has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with hot summers and cold winters. Precipitation is significant throughout the year, but is heaviest from June to October.
| Climate data for Chichibu, Saitama | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.6 (47.5) |
8.9 (48.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.8 (73.0) |
25.0 (77.0) |
28.5 (83.3) |
30.5 (86.9) |
25.2 (77.4) |
20.0 (68.0) |
15.6 (60.1) |
11.2 (52.2) |
18.9 (66.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.8 (33.4) |
1.8 (35.2) |
5.3 (41.5) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.5 (61.7) |
20.0 (68.0) |
23.6 (74.5) |
25.0 (77.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
14.1 (57.4) |
8.3 (46.9) |
3.0 (37.4) |
12.5 (54.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −5.5 (22.1) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
5.5 (41.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.8 (69.4) |
16.8 (62.2) |
9.4 (48.9) |
2.6 (36.7) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
7.2 (45.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 28.2 (1.11) |
39.8 (1.57) |
59.9 (2.36) |
79.3 (3.12) |
98.4 (3.87) |
153.4 (6.04) |
152.6 (6.01) |
210.4 (8.28) |
205.2 (8.08) |
129.9 (5.11) |
56.9 (2.24) |
24.3 (0.96) |
1,238.3 (48.75) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 11 (4.3) |
17 (6.7) |
11 (4.3) |
2 (0.8) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
3 (1.2) |
44 (17.3) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 63 | 64 | 64 | 68 | 71 | 79 | 81 | 79 | 82 | 80 | 76 | 69 | 73 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 196.6 | 171.9 | 188.8 | 166.4 | 187.7 | 111.6 | 122.6 | 152.9 | 95.6 | 128.5 | 155.1 | 187.1 | 1,864.8 |
| Source: NOAA (1961-1990)[2] | |||||||||||||
History
The city was developed as a marketplace of the district as well as the town around Chichibu Shrine. The city's older name, Ōmiya ("big shrine"), was derived from the shrine.
Timeline
- 708: Deposits of the metal copper are discovered in the region and offered to the Imperial Court. The era name Wadō (和銅, meaning "Japanese copper") is proclaimed in recognition of this welcome event in the initial months of Empress Genmei's reign.[3] The copper is used to mint Wadō Kaihō or Wadō Kaichin, which are amongst the oldest examples of coinage in Japan.-- see image of Wado Kaichin from Japan Mint Museum
- 1884: The Chichibu incident: uprising of impoverished peasants under the influence of the Freedom and People's Rights Movement. Seven are sentenced to death and over 4,000 people punished.
- 1889: Ōmiya Town was founded within Chichibu District, Saitama with the establishment of the municipalities system
- 1914: The Chichibu Railway opened.
- 1916: Ōmiya Town was renamed as Chichibu Town.
- 1950: Chichibu was elevated to city status.
- 1954: Chichibu absorbed the villages of Odamaki, Haraya and Kuna.
- 1957: Chichibu absorbed the villages of Takashino and Ōta.
- 1958: Chichibu absorbed the town of Kagemori.
- 1969: The Seibu Chichibu Line opened.
- 2005: Chichibu absorbed the town of Yoshida, and the villages of Arakawa and Ōtaki (all from Chichibu District).
Economy
The local economy of Chichibu remains based on agricultural and forestry, as well as tourism.
Education
Chichibu has 16 elementary schools, nine middle schools and two high schools as well as two special education schools.
Transportation
Railway
Two lines serve the city: the Chichibu Main Line and Seibu Chichibu Line. The Chichibu Railway was constructed along the Arakawa River and first opened in 1914. Seibu Railway reached the city in 1969 and considerably reduced the travel time to Tokyo. It takes approximately one and a half hours to travel from Seibu-Chichibu Station to Ikebukuro Station, one of the major train terminals in Tokyo. These lines carry people as well as limestone from Mount Bukō. The two lines were directly connected on April 1, 1989. Chichibu Railway also operated the Mitsumine Ropeway, which carried passengers visiting Mitsumine Shrine. The ropeway was taken out of service since May 19, 2006, and was officially abandoned on December 1, 2007.[4]
- Seibu Railway – Seibu Chichibu Line
- Chichibu Railway – Chichibu Main Line
- Wadō-Kuroya – Ōnohara – Chichibu – Ohanabatake – Kagemori – Urayamaguchi – Bushū-Nakagawa – Bushū-Hino – Shiroku – Mitsumineguchi
Highway
Two national roads, Route 140 and 299, serve the city. Route 140 connects the city to its nearest expressway interchange, Hanazono Interchange of the Kan-Etsu Expressway. The city had no road communication to Yamanashi Prefecture due to steep Okuchichibu Mountains, but the opening of the Karisaka Tunnel in 1998 enabled the city to connect to Yamanashi.[5]
Twin towns and sister cities
 Toshima, Tokyo, since October 14, 1983
Toshima, Tokyo, since October 14, 1983 Sanyō-Onoda, Yamaguchi, since May 20, 1996
Sanyō-Onoda, Yamaguchi, since May 20, 1996 Antioch, California, United States,[6] since September 16, 1967
Antioch, California, United States,[6] since September 16, 1967 Gangneung, South Korea,[7] since February 16, 1983
Gangneung, South Korea,[7] since February 16, 1983 Linfen, Shanxi Province, China,[7] since October 7, 1988
Linfen, Shanxi Province, China,[7] since October 7, 1988 Warringah, Australia,[7] since April 26, 1996
Warringah, Australia,[7] since April 26, 1996 Yasothon, Thailand,[7] since May 6, 1999
Yasothon, Thailand,[7] since May 6, 1999
Local attractions




On December 3, Chichibu holds an annual night festival(Intangible cultural heritage). It attracts crowds from Chichibu, Saitama prefecture, neighboring Tokyo, and the Kantō region. Kawase matsuri is Chichibu shrine's summer festival. It takes place every July 19 and July 20. Eight groups carrying special dashi floats march along to festival music around the city. Mikoshi (sacred portable shrines) are brought to special places in each neighborhood where they are enshrined. Neighborhood association heads wash the mikoshi in the Arakawa River.
Other attractions of the city include:
- Chichibu Muse Park
- Chichibu Shrine
- Hitsujiyama Park
- Okuchichibu Mountains
- Lake Chichibu
- Lake Chichibu Sakura
- Mitsumine Shrine
- Nakatsugawa Gorge
- Chichibu 34 Kannon Pilgrimage
In popular media
As a picturesque area within fairly easy reach of Tokyo, Chichibu has been much photographed. However, the photography of Chichibu by the Chichibu native Bukō Shimizu (1913–1995) is particularly extensive: Shimizu presented photographs of the mountains, people and customs of Chichibu in numerous books for the Japanese market, starting in 1954.[8][9]
The town of Chichibu is the setting for the popular anime series Anohana: The Flower We Saw That Day and the anime films The Anthem of the Heart and Her Blue Sky, all of which were written by Mari Okada who was born in Chichibu.
Possible connection with The Mikado
The city considers itself as the inspiration for Gilbert and Sullivan's 1885 comic opera, The Mikado; the name of the opera's setting, "Titipu", is pronounced "Chichipu" in Japanese. Rokusuke Ei, a popular essayist, was convinced that Chichibu, the site of a peasant uprising in 1884, inspired the author, W. S. Gilbert, to set the opera in Japan. Other Japanese researchers have concluded that Gilbert may simply have heard of Chichibu silk, an important export in the 19th century. A theatre company from Chichibu has presented The Mikado in Japanese in Chichibu and throughout Japan.[10][11] In August 2006, it travelled with this production to the International Gilbert and Sullivan Festival in Buxton, England.[12]
Notable people from Chichibu
- Seijuro Arafune, Former Minister of Transport
- Mari Okada, screenwriter and director[13]
- Tatsuya Fujiwara, actor[14]
- Wakachichibu Komei, former sumo wrestler
- Arisa Nakajima, professional wrestler[15]
- Bukō Shimizu, photographer[9]
- Akira Taue, professional wrestler[16]
References
- ^ http://www.env.go.jp/park/chichibu/intro/index.html
- ^ "Chichibu Climate Normals 1961-1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved December 31, 2012.
- ^ Titsingh, Issac. (1834). Nipon o daï itsi ran, p. 63.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-10-11. Retrieved 2007-10-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ 雁坂トンネル Archived 2007-02-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "US-Japan Sister Cities by State". Asia Matters for America. Honolulu, HI: East-West Center. Archived from the original on 21 November 2015. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
- ^ a b c d "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Archived from the original on 4 January 2016. Retrieved 21 November 2015.
- ^ Mihashi Sumiyo (三橋純予), "Shimizu Bukō", Nihon shashinka jiten (日本写真家事典) / 328 Outstanding Japanese Photographers (Kyoto: Tankōsha, 2000; ISBN 4-473-01750-8), p.175. Template:Ja icon (Despite the English-language alternative title, all in Japanese.)
- ^ a b 埼玉ゆかりの偉人/検索結果(詳細)/清水 武甲 (in Japanese). Saitama, Japan: Saitama Prefecture. 19 March 2010. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- ^ Sumiko Enbutsu: The Mikado in the Town of Chichibu Archived February 20, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Brooke, James. "Japanese Hail The Mikado, Long-Banned Imperial Spoof", The New York Times, 3 April 2003, accessed 15 July 2014
- ^ [1] Archived September 4, 2006, at the Wayback Machine; and [2]
- ^ Mari Okada IMDB
- ^ Internet Movie Database
- ^ "JWP女子プロレス 中島安里紗" [JWP Female Professional Wrestling: Arisa Nakajima]. JWP Official Information (in Japanese). Japan: JWP Female Professional Wrestling. 2005. Archived from the original on 2013-12-15. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- ^ "Akira Taue profile". Pro Wrestling NOAH Official Site (in Japanese). Japan: NOAH. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
Further reading
- Titsingh, Isaac, ed. (1834). [Siyun-sai Rin-siyo/Hayashi Gahō, 1652], Nipon o daï itsi ran; ou, Annales des empereurs du Japon, tr. par M. Isaac Titsingh avec l'aide de plusieurs interprètes attachés au comptoir hollandais de Nangasaki; ouvrage re., complété et cor. sur l'original japonais-chinois, accompagné de notes et précédé d'un Aperçu d'histoire mythologique du Japon, par M. J. Klaproth. Paris: Oriental Translation Fund of Great Britain and Ireland. ...Click link for digitized, full-text copy of this book (in French)