Portal:Cheshire
|
The Cheshire Portal
WelcomeCheshire Plain from the Mid Cheshire Ridge
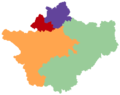
Cheshire is a ceremonial county in the North West of England. Chester is the county town, and formerly gave its name to the county. The largest town is Warrington, and other major towns include Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Macclesfield, Nantwich, Northwich, Runcorn, Sandbach, Widnes, Wilmslow and Winsford. The county is administered as four unitary authorities. Cheshire occupies a boulder clay plain (pictured) which separates the hills of North Wales from the Peak District of Derbyshire. The county covers an area of 2,343 km2 (905 sq mi), with a high point of 559 m (1,834 ft) elevation. The estimated population is a little over one million, 19th highest in England, with a population density of around 450 people per km2. The county was created in around 920, but the area has a long history of human occupation dating back to before the last Ice Age. Deva was a major Roman fort, and Cheshire played an important part in the Civil War. Predominantly rural, the county is historically famous for the production of Cheshire cheese, salt and silk. During the 19th century, towns in the north of the county were pioneers of the chemical industry, while Crewe became a major railway junction and engineering facility. Selected articleAdlington Hall is a grade-I-listed country house in the village of Adlington. The Legh family has lived on the site since the early 14th century. The hall follows a courtyard plan. The medieval Great Hall was built in 1480–1505 with a timber frame; it has a hammer-beam roof, a rare wooden canopy dated 1505, and an organ dating from the late 17th century, which was played by Handel, a friend of the Legh family. The Great Hall was encased in brick after the Civil War, when the hall was twice occupied by Parliamentary forces. The east wing dates from 1581, and retains its original "black and white" appearance. The remainder of the house largely dates from the 18th century, when Charles Legh transformed the hall into a Georgian manor. The grounds were laid out as gardens, woodland and parkland in the 18th century; they are listed at Grade II*. They include Shell House, which has an interior decorated with shells and coloured mirrors, and Tig House, a pavilion which is an early example of the Chinoiserie style. The hall and grounds remain in private ownership, and are occasionally open to the public. Selected imageDated 1562, Handforth Hall is one of many black-and-white, half-timbered former manor houses in the county. It was once the home of Sir William Brereton (1604–61), a Parliamentary commander in the Civil War. Credit: Mike in Macc (29 September 2013) In the news29 October, 1 November: Warrington council and the mayor of Crewe each announce plans to bid for city status in 2022. 13–14 October: Prince Edward visits Chester and opens a Fire Service training centre in Winsford. 8 October: Castle Street shopping area in Macclesfield reopens after refurbishment. 4 October: Restoration of the grade-I-listed Bridgegate, part of Chester city walls, is completed. 25 September: A bronze frieze by the sculptor Tom Murphy is unveiled in Warrington, as a memorial to the band Viola Beach. 9 September: The fifth stage of the Tour of Britain cycle race takes place in Cheshire, starting at Alderley Park and finishing in Warrington. 24 July: The grade-II-listed Crewe Market Hall (pictured) formally reopens after refurbishment. 15 July: Crewe, Runcorn and Warrington are awarded potential funding under the "Town Deal" government scheme. Selected listA total of 43 churches and chapels in Cheshire are listed at grade I. Although Christian churches have existed in the county since the Anglo-Saxon era, no significant Saxon features remain in its listed churches. Surviving Norman architecture is found, notably in Chester Cathedral and St John the Baptist, Chester. Most of the grade-I-listed churches are in the Gothic style, dating between the 13th and the 17th centuries, predominantly in the Perpendicular style. There are some examples of Neoclassical architecture, including St Peter, Aston-by-Sutton, and St Peter, Congleton. The only buildings dating from a later period are Waterhouse's Eaton Chapel in French Rayonnant style, and Bodley's Church of St Mary at Eccleston, in Gothic Revival style, both from the 19th century. Major building materials are the local sandstone and limestone. A handful of timber-framed churches survive, some of which have been encased in brick; examples include St Michael, Baddiley (pictured), St Luke, Holmes Chapel, St Oswald, Lower Peover, and St James and St Paul, Marton. GeographyTop: Map of modern Cheshire showing urban areas (grey) and the major road network. Chester (red) is the county town, and Warrington has the greatest population. Towns with more than 10,000 inhabitants in 2011 are highlighted; the size of dot gives a rough indication of the relative population. Wales and the adjacent English counties are shown in capitals. Bottom: Relief map showing the major hills. The Mid Cheshire Ridge is a discontinuous ridge of low hills running north–south from Beacon Hill (north of Helsby Hill) to Bickerton Hill. Most other high ground falls within the Peak District in the east of the county. Shining Tor (559 metres), on the boundary with Derbyshire, forms the county's high point. Administration The ceremonial county of Cheshire is administered by four unitary authorities (click on the map for details): 2 – Cheshire East 3 – Warrington 4 – Halton In the local government reorganisation of 1974, Cheshire gained an area formerly in Lancashire including Widnes and Warrington. The county lost Tintwistle to Derbyshire, part of the Wirral Peninsula to Merseyside, and a northern area including Stockport, Altrincham, Sale, Hyde, Dukinfield and Stalybridge to Greater Manchester. Selected biographyEdmund Sharpe (31 October 1809 – 8 May 1877) was an architect, architectural historian, railway engineer and sanitary reformer, who was born in Knutsford. As an architect, he predominantly designed churches, of which around forty survive; Cheshire examples include St Wilfrid's, Davenham, and Holy Trinity, Northwich. He pioneered the structural use of terracotta in the so-called "pot" churches, such as St Stephen and All Martyrs', Lever Bridge. He also developed railways in the north-west of England, and championed the construction of new sanitary works in Lancaster, where he practised in 1835–1851. Sharpe achieved his greatest recognition as an architectural historian, publishing many articles, books and detailed architectural drawings. He criticised the widespread practice of restoring medieval churches, and devised a scheme for the classification of English Gothic architectural styles. In 1875, he was awarded the Royal Gold Medal of the Royal Institute of British Architects. Did you know...
Selected town or villageWarrington stands at the lowest bridging point of the River Mersey. Historically within Lancashire, it became part of Cheshire in 1974. With an estimated population of around 210,000 in 2019, it is the county's largest town. The Warrington unitary authority also encompasses 18 civil parishes. The site has been an important crossing place on the Mersey since prehistoric times. A large Roman industrial settlement centred on modern Wilderspool stood on the south bank. It declined after the end of the 2nd century, and a Saxon settlement was established on the north bank, recorded in the Domesday Survey as Walintune. By the Middle Ages, it had emerged as a market town. Warrington's expansion and urbanisation coincided with the Industrial Revolution, particularly after the Mersey was made navigable in the 18th century. In the 19th century, industries included wire drawing, textiles, brewing, tanning and soap manufacture. Further growth occurred after it was designated a new town in 1968. An IRA bomb attack in the centre in 1993 killed two children. Several medieval churches survive, and the town has a museum and art gallery. In this monthNovember 1867: Grosvenor Park, Chester (pictured) opened. 1 November 1831: Harry Atkinson, Premier of New Zealand, born in Broxton. 4 November 1553: Lawyer Roger Wilbraham born in Nantwich. 7 November 1805: Railway builder Thomas Brassey born in Bulkeley. 11 November 1662: Lawyer John Chesshyre born in Halton. 14 November 1762: Tarporley Hunt Club first met. 15 November 1941: Author Heathcote Williams born in Helsby. 22 November 1961: Pianist Stephen Hough born in Heswall. 24 November 1935: Cyclist Vin Denson born in Chester. 24 November 1955: Cricketer Ian Botham born in Heswall. 26 November 1574: River Weaver in Nantwich flooded, affecting 40 dwellings and 24 salthouses. 29 November 1933: Musician John Mayall born in Macclesfield. QuotationHere is a property of building peculiar to the city, called the Rows, being galleries, wherein passengers go dry, without coming into the streets, having shops on both sides and underneath; the fashion whereof is somewhat hard to conceive. It is therefore worth their pains, who have money and leisure, to make their own eyes the expounders of the manner thereof; the like being said not to be seen in all England; no, nor in all Europe again. On Chester Rows, from The History of the Worthies of England by Thomas Fuller (1662)
Subcategories
TopicsRecommended articlesThings you can do
WikiProject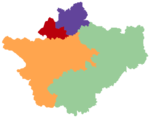 Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
|