4-Anisaldehyde
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Methoxybenzaldehyde | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
4-Methoxybenzenecarbaldehyde | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.185 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.119 g/cm3[2] | ||
| Melting point | −1 °C (30 °F; 272 K)[2] | ||
| Boiling point | 248 °C (478 °F; 521 K)[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H302 | |||
| P264, P270, P301+P312, P330, P501 | |||
| Flash point | 108 °C (226 °F; 381 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
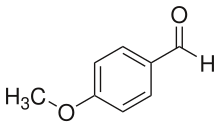
4-Anisaldehyde, or p-Anisaldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4CHO. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with a formyl and a methoxy group. It is a colorless liquid with a strong aroma. It provides sweet, floral and strong aniseed odor. Two isomers of 4-anisaldehyde are known, ortho-anisaldehyde and meta-anisaldehyde. They are less commonly encountered.
Production
Anisaldehyde is prepared commercially by oxidation of 4-methoxytoluene (p-cresyl methyl ether) using manganese dioxide to convert a methyl group to the aldehyde group. It can also be produced by oxidation of anethole, a related fragrance that is found in some alcoholic beverages, by oxidative cleavage of an alkene.[3]
Uses
Being structurally related to vanillin, 4-anisaldehyde is a widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry.[3] It is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds important in pharmaceuticals and perfumery. The related ortho isomer has a scent of licorice.
A solution of para-anisaldehyde in acid and ethanol is a useful stain in thin layer chromatography.[4] Different chemical compounds on the plate can give different colors, allowing easy distinction.
DNA breakage
Anisaldehyde in combination with copper (II) can induce single- and double-strand breaks in double stranded DNA.[5]
References
- ^ Budavari, Susan, ed. (1994). The Merck index: an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals (11. ed., 4. print ed.). Rahway, NJ: Merck. p. 693. ISBN 978-0-911910-28-5.
- ^ a b c "p-Anisaldehyde". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ a b Karl-Georg Fahlbusch; Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt; Johannes Panten; Wilhelm Pickenhagen; Dietmar Schatkowski; Kurt Bauer; Dorothea Garbe; Horst Surburg (2003). "Flavors and Fragrances". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Stains for Developing TLC Plates
- ^ Becker, T. W.; Krieger, G.; Witte, I. (1996). "DNA Single and Double Strand Breaks Induced by Aliphatic and Aromatic Aldehydes in Combination with Copper(II)". Free Radical Research. 24 (5): 325–332. doi:10.3109/10715769609088030. PMID 8733936.