Acefylline
Appearance
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular, Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.447 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
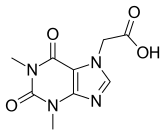
| Formula | C9H10N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 238.203 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Acefylline (INN),[1] also known as 7-theophyllineacetic acid, is a stimulant drug of the xanthine chemical class. It acts as an adenosine receptor antagonist. It is combined with diphenhydramine in the pharmaceutical preparation etanautine to help offset diphenhydramine induced drowsiness.[2]
A silanol–mannuronic acid conjugate of acefylline, acefylline methylsilanol mannuronate (INCI; trade name Xantalgosil C) is marketed as a lipolytic phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It is used as an ingredient in cosmeceuticals for the treatment of cellulite and as a skin conditioner.[3][4]
See also
References
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 21" (PDF). World Health Organization. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- ^ Zuidema J (1978). "Biofarmaceutische en farmacokinetische aspecten van theofylline en acefylline". Thesis (doctoral)--Universiteit van Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 2016-12-30. Retrieved 2012-09-29.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Biosil Technologies (2005). "Xantalgosil C® Datasheet" (PDF). Exsymol S.A.M. Retrieved 2022-01-20.
- ^ Winter, Ruth (2009-10-20). A Consumer's Dictionary of Cosmetic Ingredients (7th ed.). Harmony/Rodale. p. 42. ISBN 9780307459862.
