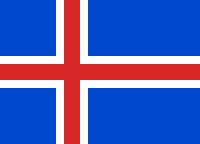
Flag of Iceland
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2017) |
 | |
| Use | Civil flag and ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 18:25[1] |
| Adopted | 17 June 1944 (standardization from 1918) |
| Design | A blue field with the white-edged red Nordic cross that extends to the edges; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side. In Blazon, "Azure, a cross gules fimbriated argent". |
| Designed by | Matthías Þórðarson |
 | |
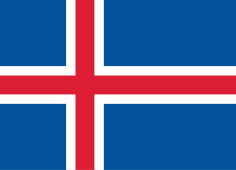
| Use | State and war flag, state and naval ensign |
| Proportion | 9:16[1] |

 The flag of the president of Iceland. It has an aspect ratio of 9:16.
The flag of the president of Iceland. It has an aspect ratio of 9:16.
 The flag of the Icelandic Customs Service. It has an aspect ratio of 9:16.
The flag of the Icelandic Customs Service. It has an aspect ratio of 9:16.The flag of Iceland (Icelandic: íslenski fáninn) was officially described in Law No. 34, set out on 17 June 1944, the day Iceland became a republic. The law is entitled "The Law of the National Flag of Icelanders and the State Arms" and describes the Icelandic flag as follows:
The civil national flag of Icelanders is blue as the sky with a snow-white cross, and a fiery-red cross inside the white cross. The arms of the cross extend to the edge of the flag, and their combined width is 2⁄9, but the red cross 1⁄9 of the combined width of the flag. The blue areas are right angled rectangles, the rectilinear surfaces are parallel and the outer rectilinear surfaces as wide as them, but twice the length. The dimensions between the width and length are 18:25.
Iceland's first national flag was a white cross on a deep blue background. It was first shown in parade in 1897. The modern flag dates from 1915, when a red cross was inserted into the white cross of the original flag. This cross historically stems from the symbol of Christianity.[2][3] It was adopted and became the national flag when Iceland was granted sovereignty by Denmark in 1918. For Icelanders, the flag's colouring represents a vision of their country's landscape. The colours stand for three of the elements that make up the island. Red is the fire produced by the island's volcanoes, white recalls the ice and snow that covers Iceland and blue represents the mountains of the island.[4]
History

According to a legend described in Andrew Evans' Iceland,[5] a red cloth with a white cross fell from the heavens, ensuring Danish victory at the Battle of Valdemar in the 13th century. Denmark then used the cross on its flag throughout its Nordic territories as a sign of divine right. Upon Iceland's independence, they continued to use the Christian symbol.
The civil flag of Iceland had been used as an unofficial symbol since the late 19th century, originally as a white cross on a blue background. The current design was adopted on 19 June 1915, when King Kristján X issued a decree allowing it to be flown in Icelandic territorial waters, where only the Danish flag had been permitted, and stipulating that a red cross was to be incorporated into the design to distinguish it from similar foreign flags.[6] Other symbolic meanings refer to the natural features of Iceland itself. Blue is the colour of the mountains when looked at from the coast, white represents the snow and ice covering the island for most of the year, and red the volcanoes on the island.[4]
-
 The civil flag as it appeared between 1918 and 1944, when the blue colour was classified as "ultramarine blue". It has an aspect ratio of 18:25.
The civil flag as it appeared between 1918 and 1944, when the blue colour was classified as "ultramarine blue". It has an aspect ratio of 18:25. -
 A former flag which never became official, known as Hvítbláinn ("the white-blue"), in use by Icelandic republicans around 1900. A very similar design has subsequently been adopted as the flag of Shetland.
A former flag which never became official, known as Hvítbláinn ("the white-blue"), in use by Icelandic republicans around 1900. A very similar design has subsequently been adopted as the flag of Shetland.
Laws regarding the flag
On 17 June 1944, the day Iceland became a republic, a law was issued that dealt with the national flag and the coat of arms. To date, this is the only major law to have been made about the flag and coat of arms, aside from two laws made in 1991: one that defines official flag days as well as the time of day the flag can be drawn, and another that defines the specific colours comprising the Icelandic flag. (The law codified what had been common custom.)
The law describes the dimensions of both the common flag and special governmental flags used by embassies and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. It also goes into details of usage, such as how the flag should be attached in different situations such as on a flagpole, on a house and on different kinds of ships.
According to the law, using the flag is a privilege and not a right. The owner must follow instructions on its usage and make sure that his or her flag is in mint condition regarding colouring, wear and tear. It also states that no one shall disrespect the flag in act or word, subject to a fine or imprisonment of up to one year.
The original law stated in its seventh article that another law would be set regarding official flag days and the time of day that the flag may be flown, but such a law was not put into effect until almost 50 years later in 1991. This law states that the flag shall not be flown until 7:00 in the morning and it should preferably not be flown beyond sunset but that it must not be flown beyond midnight. However, if the flag is raised at an outdoor assembly, an official gathering, funeral or a memorial the flag may be flown as long as the event lasts though never beyond midnight.
Icelandic flag days


According to Law No. 5 of 23 January 1991, the following are nationally sanctioned flag days. On these days the flag must be raised at official buildings, and those under the supervision of officials and special representatives of the state. Any additions to the list below can be decided each year by the Prime Minister's Office. On these days, the flag must be fully drawn, except on Good Friday where it must be drawn at half-mast.
- The birthday of the president of Iceland, currently the 11th of October
- New Year's Day
- Good Friday
- Easter
- First Day of Summer
- 1 May
- Pentecost
- Sailors Day
- Icelandic National Day
- Icelandic Language Day
- 1 December, Sovereignty Day
- Christmas
The state flag

The Icelandic state flag (Ríkisfáni), known as the Tjúgufáni, was first flown on 1 December 1918 from the house of ministry offices although laws regarding its uses had not been finished. It was not until 12 February 1919 that such a law was enacted.
The State flag is used on governmental buildings and embassies. It is also permitted to use the flag on other buildings, if they are being used by the government in some fashion. The Tjúgufáni is the Naval Ensign of the Icelandic Coast Guard as well, and state ships and other ships put to official uses are permitted to use it.
The customs service flag is used on buildings used by the Directorate of Customs and at checkpoints, as well as by ships used by the Directorate of Customs.
The Icelandic presidential flag is used on the dwellings of the President, as well as any vehicles that transports them.
Colours of the flag
Officially, the colours of the Icelandic flag follow a law set in 1991, which states that the colours must be the following Standard Colour of Textile (Dictionnaire International de la Couleur) hues:
| Scheme | Blue | White | Red |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCOTDIC | 693009 | 95 | ICELAND FLAG RED |
The government of Iceland has issued[7] colour specifications in the better known Pantone, CMYK, RGB, hex triplet and Avery systems.
| Scheme | Blue | White | Red |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex | #02529C | #FFFFFF | #DC1E35 |
| RGB | 2, 82, 156 | 255, 255, 255 | 220, 30, 53 |
| Pantone | 287 | 1c | 199 |
| CMYK | 100, 75, 2, 18 | 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 100, 72, 0 |
| Avery | 520 | 501 | 503 |
Construction sheets
See also
- Nordic Cross flag
- List of flags with blue, red, white in them and flags with three colours.
- Coat of arms of Iceland
References
- ^ a b Icelandic National Flag Proportion - Prime Minister's Office
- ^ Jeroen Temperman (2010). State Religion Relationships and Human Rights Law. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. ISBN 978-9004181489. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
Many predominantly Christian states show a cross, symbolising Christianity, on their national flag. Scandinavian crosses or Nordic crosses on the flags of the Nordic countries–Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden–also represent Christianity.
- ^ Carol A. Foley (1996). The Australian Flag: Colonial Relic or Contemporary Icon. William Gaunt & Sons. ISBN 9781862871885. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
The Christian cross, for instance, is one of the oldest and most widely used symbols in the world, and many European countries, such as the United Kingdom, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Iceland, Greece and Switzerland, adopted and currently retain the Christian cross on their national flags.
- ^ a b "History of the Icelandic Flag". www.government.is. Prime Minister's Office. Retrieved 2019-03-02.
- ^ Andrew Evans (2008). Iceland. Bradt. ISBN 9781841622156. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
Legend states that a red cloth with the white cross simply fell from the sky in the middle of the 13th-century Battle of Valdemar, after which the Danes were victorious. As a badge of divine right, Denmark flew its cross in the other Nordic countries that it ruled, and as each nation gained independence, it incorporated the Christian symbol.
- ^ Karlsson, Gunnar (2000). The History of Iceland. London: C. Hurst & Co. p. 283. ISBN 0-8166-3588-9.
- ^ "AUGLÝSING um liti íslenska fánans" (PDF). PMO.
- Lög um þjóðfána Íslendinga og ríkisskjaldarmerkið. ( 1944 nr. 34 17. júní ).
- Retrieved 14 May 2004 from http://www.althingi.is/lagas/130a/1944034.html
- Forsetaúrskurður um fánadaga og fánatíma. ( 1991 nr. 5 23. janúar ).
- Retrieved 14 May 2004 from http://www.althingi.is/lagas/125b/1991005.html
- Auglýsing um liti íslenska fánans. ( 1991 nr. 6 23. janúar ).
- Retrieved 14 May 2004 from http://www.althingi.is/lagas/125b/1991006.html
- Lög um breyting á lögum nr. 34 17. júní 1944, um þjóðfána Íslendinga.
- Retrieved 14 May 2004 from http://www.althingi.is/altext/stjt/1998.067.html