Tetragonal crystal system
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2011) |


In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base (a by a) and height (c, which is different from a).
Bravais lattices
There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal.
| Bravais lattice | Primitive tetragonal |
Body-centered tetragonal |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson symbol | tP | tI |
| Unit cell | 
|
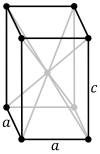
|
The body-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell.[1]
Crystal classes
The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.[2][3]
| # | Point group | Type | Example | Space groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name[4] | Intl | Schoen. | Orb. | Cox. | Primitive | Body-centered | |||
| 75–80 | Tetragonal pyramidal | 4 | C4 | 44 | [4]+ | enantiomorphic polar | pinnoite, piypite |
P4, P41, P42, P43 | I4, I41 |
| 81–82 | Tetragonal disphenoidal | 4 | S4 | 2× | [2+,4+] | cahnite, tugtupite | P4 | I4 | |
| 83–88 | Tetragonal dipyramidal | 4/m | C4h | 4* | [2,4+] | centrosymmetric | scheelite, wulfenite, leucite | P4/m, P42/m, P4/n, P42/n | I4/m, I41/a |
| 89–98 | Tetragonal trapezohedral | 422 | D4 | 224 | [2,4]+ | enantiomorphic | cristobalite, wardite | P422, P4212, P4122, P41212, P4222, P42212, P4322, P43212 | I422, I4122 |
| 99–110 | Ditetragonal pyramidal | 4mm | C4v | *44 | [4] | polar | diaboleite | P4mm, P4bm, P42cm, P42nm, P4cc, P4nc, P42mc, P42bc | I4mm, I4cm, I41md, I41cd |
| 111–122 | Tetragonal scalenohedral | 42m | D2d (Vd) | 2*2 | [2+,4] | chalcopyrite, stannite | P42m, P42c, P421m, P421c, P4m2, P4c2, P4b2, P4n2 | I4m2, I4c2, I42m, I42d | |
| 123–142 | Ditetragonal dipyramidal | 4/mmm | D4h | *224 | [2,4] | centrosymmetric | rutile, pyrolusite, zircon | P4/mmm, P4/mcc, P4/nbm, P4/nnc, P4/mbm, P4/mnc, P4/nmm, P4/ncc, P42/mmc, P42/mcm, P42/nbc, P42/nnm, P42/mbc, P42/mnm, P42/nmc, P42/ncm | I4/mmm, I4/mcm, I41/amd, I41/acd |
In two dimensions
There is only one tetragonal Bravais lattice in two dimensions: the square lattice.
| Bravais lattice | Square |
|---|---|
| Pearson symbol | tp |
| Unit cell | 
|
See also
References
- ^ Cubic-to-Tetragonal Transition
- ^ Webmineral data
- ^ Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, Manual of Mineralogy, 20th ed., pp. 73–78, ISBN 0-471-80580-7
- ^ "The 32 crystal classes". Retrieved 2018-06-19.
External links
 Media related to Tetragonal lattices at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tetragonal lattices at Wikimedia Commons
