Transnistria
Transnistrian Moldovan Republic Република Молдовеняскэ Нистрянэ (Republica Moldovenească Nistreană) Приднестровская Молдавская Республика (Pridnestrovskaya Moldavskaya Respublika) Придністровська Молдавська Республіка (Pridnistrovs'ka Moldavs'ka Respublika) | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Anthem of Transnistria | |
 | |
| Capital | Tiraspol |
| Official languages | Moldovan, Russian, Ukrainian |
| Ethnic groups (2005) | 32% Moldovans 31% Russians 29% Ukrainians |
| Government | internationally unrecognized de facto independent territory of Transnistrian Moldovan Republic |
| Igor Smirnov | |
| Status | |
• declared independence | 1992 |
| March 2 - July 21, 1992 | |
• Recognition | none |
• Water (%) | 2.35 |
| Population | |
• 2005 estimate | 555,000 (166) |
• 2004 census | 555,347 |
| Currency | Transnistrian ruble1 (PRB) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Calling code | 373 5 +373 2 |
| Internet TLD | none1 |
| |
Transnistria, also known as Pridnestrovie, is a de facto independent territory within the internationally recognised borders of Moldova. Transnistria's independence is not recognised by any state or international organisation, and it is de jure part of Moldova. Although it does not have such legal status within Moldova, Transnistria functions like a state, and calls itself a republic.[1]
Transnistria declared independence from Moldova, but within the Soviet Union on September 2, 1990, as the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic. This was declared void by then-Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachov. Subsequent to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Transnistria fought the War of Transnistria in 1992, backed by Russian volunteers (cossacks) and the Russian (former Soviet) 14th Army ("80% of its personnel come from Transnistria" [2]; mid-1994 data), and since then (1992) has exercised de facto control over most of the Transnistrian region, located on the eastern bank between the Dniester River and Ukraine, and over several localities on the west bank of the river. A three-party (Russia, Moldova, Transnistria) Joint Control Commission supervizes the security arrangements in the de-militarized zone, comprizing 20 localities on both sides of the river.
Transnistria is seeking recognition as an independent state. However, it has not been recognised by any state or international organisation, who regard it as part of Moldova. Transnistria functions as a presidential republic, with its own government, parliament, military and police (militsia) force, constitution, currency, postal system and stamps, flag, national anthem, and coat of arms.
A 2,500-strong Russian military contingent(14th Army), as well as over 20,000 tons of Russian-owned weapons and munition are present in Transnistria. Moldova and OSCE demand their withdrawal. According to a verdict issued by European Court of Human Rights, the presence of these troops is illegal (breaking the July 21 1992 agreement), and Transnistria is "under the effective authority or at least decisive influence of Russia".[3]
Names
It is most commonly known in English by its Romanian name Transnistria, its formal long name is Pridnestróvskaia Moldávskaia Respública (Moldovan: Република Молдовеняскэ Нистрянэ, ‹See Tfd›Russian: Приднестровская Молдавская Республика, Ukrainian: Придністровська Молдавська Республіка, ПМР, English: Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic), as used by the breakaway Transnistrian authorities. This is abbreviated PMR.
The short form of this name is Pridnestrovie (transliteration of the Russian "Приднестровье").[4] Several other names are also in common use. Etymologically, they all come down to similar spelling variants of Transnistria, meaning "beyond the river Dniester", or Pridnestrovie, meaning "by the river Dniester".
From 1998 until 2003, another official name, Stânga Nistrului [Left bank of Dniester], was in use by the Moldovan central authorities.

Geography
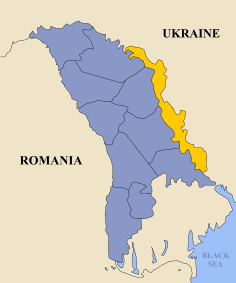
Transnistria is landlocked and borders Bessarabia (i.e. the rest of Moldova, for 411 km) to the West, and Ukraine (for 405 km) to the East. It is a narrow valley stretching in the North-South direction along the bank of the Dniester River, which forms a natural boundary along most of the border with (the rest of) Moldova. Tiraspol, the capital and largest city of Transnistria, has 159,163 inhabitants.
The territory of Transnistria is mostly, but not completely coincident with the left (eastern) bank of Moldova (with respect to Dniester). It includes ten cities and towns, and 69 communes, with a totality of of 147 localities (counting the unincorporated ones as well). Ten localities on the left bank, are controlled by the Moldovan government, as part of the Dubăsari district. They are situated north and south of the city of Dubăsari, which itself is under Transnistrian control.
On the west bank, the city of Tighina (Bender) and six villages to its south and south-east, roughly opposite Tiraspol, are controlled by Transnistrian authorities.
The ten localities controlled by the Moldovan authorities on the eastern bank, the city of Dubăsari (situated on the eastern bank and controlled by Tiraspol), the seven localities controlled by the Transnistrian authorities on the western bank, as well as two (Varniţa and Copanca) on the same bank under Chişinău control form a security zone. The security situation inside it is subject to the Joint Control Commission rulings.
The main transportation route in Transnistria is the road Tiraspol-Dubăsari-Rîbniţa. North and south of Dubăsari it passes trough the lands of the villages controlled by the central government (Doroţcaia, Cocieri, Roghi, while Vasilevca is entirely situated east of the road). Conflict erupted on several occasions when the Tiraspol authorities prevented the villagers from reaching their farmland east of the road.[5][6][7]
- See also List of places in Transnistria, Disputed status of Transnistria#Border issues, Geography of Transnistria template

Administrative subdivisions
Transnistria is subdivided into five raions (Russian names are listed in parantheses):
- Camenca (Каменка, Kamenka)
- Dubăsari (Дубоссары, Dubossary)
- Grigoriopol (Григориополь)
- Rîbniţa (Рыбница, Rybnitsa)
- Slobozia (Слободзея)
and one (two) municipalities:
- Tighina (Бендеры, Bender or Bendery), officially a separate municipality from Transnistria
- Tiraspol (Тирасполь)
Political status
Transnistria is internationally recognised as being a legal part of the Republic of Moldova, although de facto control is exercised by its internationally unrecognised government which declared independence from Moldova as the Pridnestrovskaia Moldavskaia Respublica or Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), in 1990 with Tiraspol as its declared capital. Prior to unification of the territory with Moldova in 1940, Tiraspol was the capital of the Moldavian ASSR, an autonomous republic within Ukrainian SSR, which existed from 1924 to 1940.
Although exercising no direct control over the territory, the Moldovan government passed the "Law on Basic Provisions of the Special Legal Status of Localities from the Left Bank of the Dniester" on July 22, 2005, which established Transnistria as a separate territorial unit within the Republic of Moldova, which can be given a status of a large autonomy. The law was passed without any prior consultation with the de facto government in Transnistria, which felt that it was a provocation and has since ignored it.
There are unsettled border issues between the PMR and Moldova. Nine villages from the Dubăsari district, including Cocieri and Doroţcaia which geographically belong to Transnistria, have been under the control of the central government of Moldova after the involvement of local inhabitants on the side of Moldovan forces during the War of Transnistria. These villages along with Varniţa and Copanca, near Tighina and Tiraspol, are claimed by the PMR. One city and six villages on the west bank are controlled by the Transnistrian authorities, but are considered by Moldova as a separate municipality (Tigina and two villages), or part of the Căuşeni district (four villages).
Tense situations have periodically surfaced due to these territorial disputes, for example in 2005, when Transnistrian forces entered Vasilievca[8], in 2006 around Varniţa, and in 2007 in Dubăsari-Cocieri area, when a confrontation between Moldovan and Transnistrian forces occurred, however without any casualties.
According Moldovan sources, in 13 May 2007 the mayor of the village Corjova, which is under Moldovan government control, was arrested by Transnistrian police, together with a councillor of Moldovan-controlled part of Dubăsari district.[9]
Politics

Transnistria has a multi-party system and a unicameral parliament named the Supreme Council. Its legislature has 43 members elected by proportional representation.[10] The president is elected to a five year term by popular vote.
Igor Smirnov has been the President of Transnistria since the declaration of independence in 1990 and he is currently serving his fourth mandate after being reelected in December 2006. In the latest parliamentary election in December 2005 the Renewal movement defeated the Republic movement and won an overall majority, its leader Yevgeni Shevchuk becoming speaker of parliament.[11] Transnistria has announced that it will introduce the proportional representation vote counting system in its next elections in replacement of its current first past the post system[citation needed].
According to official PMR data, only 15 of the 43 members of the separatist parliament were born in the territory of Transnistria (including 12 in Transnistria proper, and 3 in the Bessarabian area of Tighina-Chiţcani, which is controlled by Transnistria), while 4 others in the rest of Moldova, with the remainder mainly born in Russia or Ukraine.[12] Igor Smirnov, the leader of PMR, has arrived in the region in 1987. Most of the MPs who were born elsewhere had moved to the region ten years or more before the conflict erupted. [13]
There is disagreement as to whether elections in Transnistria are free and fair.[14] The political regime been described as one of 'super-presidentialism'. [15]
Election results are considered suspicious, as in 2001 in one region it was reported that Igor Smirnov collected 103.6% of the votes.[16] Nevertheless, some organizations, such as CIS-EMO, have participated and have called them democratic.

The Narodovlastie party and Power to the People movement faced numerous problems in 2001-2002 and were eventually closed.[17][18]
A list published by the European Union bans travel to the EU of some members of the leadership of Transnistria.[19]
In 2007 the registration of Social Democratic Party was allowed. This party, lead by former separatist leader and member of Transnistrian government Andrey Safonov, is allegedly accepting actually a union with Moldova [20]. In latest presidential election the registration of opposition candidate Andrey Safonov was delayed until a few days before the vote remained so that he had little time to conduct an election campaign[21].
Despite the fact that Moldovans are around a third of Transnistrian population, no ethnic Moldovans are members in the Transnistrian government[22]
A referendum was organised in September 17, 2006 by the PMR authorities, and according to them people have supported "independence from Moldova and free association with Russia".
International relations
Ukraine-Transnistria border customs dispute
On March 3, 2006, Ukraine introduced new customs regulations on its border with Transnistria. Ukraine declared it will only import goods from Transnistria with documents processed by Moldovan customs offices, as part of the implementation of the joint customs protocol between Ukraine and Moldova on December 30, 2005. Transnistria and Russia termed the act an "economic blockade". Moldova announced that it created favorable conditions for registration of Transnistria-based businesses: to obtain a 6-month export license is a half-hour simplified procedure.[citation needed]
The United States, the European Union and OSCE approved the Ukrainian move, while Russia saw it as a means of political pressure. On March 4, Transnistria responded by blocking the Moldovan and Ukrainian transport at the borders of Transnistria. The Transnistrian block was lifted after two weeks. However, the Moldovan/Ukrainian block remains in place, and holds up progress in status settlement negotiations between the sides.[23] In the months following the regulations, exports from Transnistria nosedived. Transnistria declared a "humanitarian catastrophe" in the region, while Moldova called it "deliberate misinformation."[24] Cargos of humanitarian aid were sent from Russia in response.[25]
Russian military presence in Transnistria
While Russian troops from Moldova proper and from the security zone were evacuated to Russia by January 1993, Russia continued to have a significant military presence in Transnistria. On 21 October 1994, Russia and Moldova signed an agreement that committed Russia to withdrawal of the troops in three years,[26] which however did not come into effect because only Moldova ratified it. Moldovan diplomacy took advantage of the negotiations concerning The Adaptation of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CAF), and managed to ensure that a special paragraph about the removal of Russian troops from Moldova’s territory was introduced into the text of the OSCE Summit Declaration of Istanbul (1999), through which Russia had committed itself to pulling out its troops from Transnistria by the end of 2002.[27] However, even after 2002, Russia continued to ignore the agreements made with the government in Chisinau and with the international community regarding the removal of its troops from Moldova. [28] President Vladimir Putin eventually signed the Law on the ratification of the Treaty on CAF in Europe on 19 July 2004, which were committing Russia to remove from Moldova the heavy armaments limited by this Treaty by the end of 2001.[29]
During 2000-2001, in order to comply to the CAF Treaty, Moscow withdrew 125 pieces of Treaty Limited Equipment (TLE) and 60 railway wagons containing ammunition from the Transnistrian region of Moldova. In 2002, Russia withdrew only 3 military equipment trains (118 railway wagons) and 2 of ammunition (43 wagons) from the Transnistrian region of Moldova, and in 2003, 11 rail convoys transporting military equipment and 31 transporting ammunitions. According to the OSCE Mission to Moldova, of a total of 42,000 tons of ammunitions stored in Transnistria, 1,153 tons (3%) was transported back to Russia in 2001, 2,405 tons (6%) in 2002 and 16,573 tons (39%) in 2003. Removal of troops has been stalled afterwards. [30] Andrei Stratan, the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Moldova stated in his speech during the 12th OSCE Ministerial Council Meeting in Sofia on December 6-December 7, 2004 that "The presence of Russian troops on the territory of the Republic of Moldova is against the political will of Moldovan constitutional authorities and defies the unanimously recognized international norms and principles, being qualified by Moldovan authorities as a foreign military occupation illegally deployed on the territory of the state[…]"[31]Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).
History
Antiquity and Middle Ages
The area where Transnistria is now located has been inhabited by Indo-European tribes for millennia, being a borderland between Dacia and Scythia. The Ancient Greek Miletians founded about 600 BC a colony named Tyras, situated on the right bank, in the mouth of the Dniester river (Tyras), on the cite of the present day city Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi in Ukraine. The city later fell to the Romans. Early Germanic and Mongolic tribes were present in the area during their invasions of the Roman Empire.
South Slavs were present in Transnistria from the second half of the 6th century. In the early Middle Ages, Slavic tribes of Tivertsi and Ulichs[32] populated larger areas, including Transnistria, followed by Turkic nomads such as the Petchenegs[33] and Cumans. Possibly an early part of Kievan Rus', after the Mongol invasion of Europe in 1241, the territory was briefly under Mongol control (yet probably without any permanent settlements), and later under the Crimean Khanate.
From the 15th century, northern Transnistria (current districts of Camenca and Rîbniţa) belonged to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania[34][35][36][37][38], and later to the Kingdom of Poland, which encouraged the migration of peasants into the territory from the neighboring populated areas (from north and from west). Prince of Moldavia Gheorghe Duca (1665-66, 1668-72, 1678-84) built a court at Ţicanova on the east bank of the Dniester, and one at Nimirov on the Southern Bug, last mentioned in Moldavian hands in 1765.[39] [40] The localities Dubăsari, Raşcov, Vasilcău, as well as four other currently in Ukraine are mentioned in 17th-18th centuries as fairs for the Dniester-Bug region. In 1769 a document dated at Tighina mentions the then tilte of the Mitropolitan of Moldavia as "Mitropolitan of Proilavia, of Tamarova, of Hotin, and of all the borders of the Danube, of the Dniester, and the Han's Ukraine"[41], the latter being a common reference to the then sparsely populated Dniester-Southern Bug-Dniepr area.

Prior to becoming part of the Russian Empire in 1792, the largest groups living between the Dniester and the Bug rivers were Moldavian (Romanian), Ruthenian (Ukrainian), and Tatar peasants.[42] The Russian census of 1793 of the Ochakov region (southern part of the Dniester-Bug area) mentions a totality of 67 villages, of which 49 are mentioned as Moldavian and 18 as Tatar. [43] The first candidate for the governor of the new Russian region was the Moldavian boyar Alexandru I. Mavrocordat. [44] The northern part of Transnistria had Ruthenian (Ukrainian) and Moldavian villages.
Russian Empire
In 1792 the region became part of the Russian Empire as a result of sixth Russo-Turkish War. In that year, the general Alexander Suvorov founded modern Tiraspol as a Russian border fortress.[45][46] Until the Russian Revolution of 1917, the current Transnistria was divided between imperial guberniyas of Podolia, Kherson, and Bessarabia. The territory which now is Transnistria was part of the larger New Russia region, hence it witnessed a strong colonization process, with a multitude of ethnies being settled: lands were given to enserfed peasantry from Russia and Ukraine (see also Nova Serbia), and Jews and Germans were brought to facilitate economic development.

Soviet Union
Transnistria became an autonomous political entity in 1924 with the proclamation of the Moldavian ASSR, which included today's Transnistria (4,000 km²) as well as an adjacent area (9,000 km²) around the city of Balta in modern-day Ukraine, but nothing from Bessarabia, which at the time was part of Romania. One of the reasons for the creation of the Moldavian ASSR was the desire of the Soviet Union at the time to eventually incorporate Bessarabia. The Moldavian SSR, which was organised by a decision of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR on 2 August 1940, was formed from a part of Bessarabia (taken from Romania on 28 June, following the Molotov-Ribbentrop pact), and a part of the Moldavian ASSR which is roughly equivalent to present-day Transnistria.
In 1941, after Axis forces invaded the Soviet Union in the course of the Second World War, they defeated the Soviet troops in the region and occupied it. By March 1943, a total of 185,000 Ukrainian and Romanian Jews had been deported and the majority died or were murdered in ghettos and concentration camps situated in an area immediately north and east of the current Transnistria, which as the latter was under Romanian and partially German occupation.
The Soviet Union regained the area in 1944, and the Soviet colonisation of the region was resumed.
Secession to the present
Mikhail Gorbachev's policy of perestroika in the Soviet Union allowed political liberalisation at a regional level in 1980s. On 2 September 1990, the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed as a Soviet republic by the "Second Congress of the Peoples' Representatives of Transnistria". On 22 December 1990, Mikhail Gorbachev, the leader of USSR, signed a decree that declared the decisions of this congress legally void. Nevertheless, neither the USSR, nor Moldova, a component republic of the former Soviet Union at the time, took any significant practical action, hence the new authorities in Transnistria slowly got control over the region.
The War of Transnistria followed armed clashes on a limited scale which broke out between Transnistrian separatists and Moldova as early as November 1990 at Dubăsari. Starting from 2 March 1992, there was concerted military action between Moldova and Transnistria. Throughout 1992 the fighting intensified until a ceasefire was signed on 21 July 1992, which has held ever since. The war left more than one thousand dead, many more wounded, and an estimated 100,000 refugees[citation needed].
The OSCE is trying to facilitate a negotiated settlement. Under OSCE auspices, on 8 May 1997, the Moldovan President Petru Lucinschi and the Transnistrian president Igor Smirnov, signed the "Memorandum on the principles of normalizations of the relations between the Republic of Moldova and Transnistria", also known as the "Primakov Memorandum", sustaining the establishment of legal and state relations, although the memorandum's provisions had diverging legal and political interpretations in Chişinău and Tiraspol.
In November 2003, Dmitry Kozak, a counselor of the Russian president Vladimir Putin, proposed a memorandum on the creation of an asymmetric federal Moldovan state, with Moldova holding a majority and Transnistria being a minority part of the federation.[47] Known as "the Kozak memorandum", it did not coincide with the Transnistrian position, which sought equal status between Transnistria and Moldova, but was giving Transnistria veto powers, which hence agreed to sign it. Vladimir Voronin was initially supportive of the plan, but refused to sign it after internal opposition and international pressure from the OSCE and US, and after Russia had endorsed the Transnistrian demand to maintain a Russian military presence for the next 20 years as a guarantee for the intended federation.[48] The refusal by the Moldovan side resulted in the sudden and long-term cooling of relations between Moldova and Russia, and halted further progress in the settlement negotiations.
Population
At the census of 1989, the population was 679,000 (including all the localities in the security zone, even those under Moldovan control). At the time of the 2004 census, the population was 555,347 (only localities under Transnistrian control)[49][50]. Recently, there has been a substantial emigration due to economic hardships and uncertain political situation.[citation needed] A large part of the population is past the age of retirement.
Transnistrian authorities organized a separate census from the 2004 Moldovan Census, and therefore demographic statistics of Moldova does not include data from Transnistria.[51].
According to the 2004 Census in Transnistria, ethnic Moldovans compose the plurality with 31.9%, followed by ethnic Russians 30.4%, and Ukrainians 28.8%. Smaller numbers of Bulgarians, Poles, Germans, Jews, Gagauz, Belorussians and others make up the rest, totaling 8.9%. 64.2% of the population belongs to some ethnic Slav group (Russians, Ukrainians, Bulgarians, Poles, Belorussians).
The ethnic composition of the region has not been entirely stable in the recent history.
Religion
Most religious Transnistrians are Orthodox Christians and the government has supported restoration and new construction of orthodox churches. Transnistria's government affirms that the republic has freedom of religion and 114 religious beliefs and congregations are officially registered. However, as of 2005, registration hurdles were encountered by some minor religious groups, notably the Jehovah's Witnesses.[52] In 2007, the US-based Christian Broadcasting Network denounced the persecution of Protestants.[53]
Economy
Transnistria has a mixed economy. Following a large scale privatization process, most of the companies in Transnistria are now privately owned. The economy bases on a mix of heavy industry (steel production), electricity production and manufacturing (textile production), which together accounts about 80% of the total industrial output.[54]
Transnistria has its own central bank, which issues Transnistrian currency, the Transnistrian ruble. It is convertible at a freely floating exchange rate but only in Transnistria.[55]
Economic history
After World War II, Transnistria was heavily industrialised, to the point that in 1990, it was responsible for 40% of Moldova's GDP and 90% of its electricity[56] despite the fact that it accounted for only 17% of Moldova's population. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Transnistria wanted to return to a "Brezhnev-style planned economy",[57] however, several years later, it decided to head toward a market economy.

Macroeconomics
According to the government of Transnistria, the 2006 GDP was $585.6 million and the GDP per capita was $1,076. The GDP increased 7.7% and inflation rate was 10.1%.[58] Transnistria's government budget for 2007 is US$246 million, with an estimated deficit of approximately US$100 million[59] which the government plans to cover with income from privatizations.[60]
In 2004, Transnistria had debt of $1.2 billion (two thirds of which are with Russia), which was per capita approximately 6 times higher than in Moldova (without Transnistria).[61] In March 2007 the debt to Gazprom for the natural gas has increased to $1.3 billion. On 22 March 2007 Gazprom sold Transnistria's gas debt to the Russian businessman Alisher Usmanov, who controls Moldova Steel Works, the largest enterprise in Transnistria. Transnistria's president Igor Smirnov has announced that Transnistria will not be paying off its gas debt because "Transdnistria has no legal debt [to Gazprom]".[62][63]
According to Yevgeni Shevchuk, speaker of Transnistrian Supreme Soviet, Transnistria is in a difficult economic situation. Despite a 30% tax increase in 2007 pension fund is still lacking money and emergency measures must be taken[64]. However, the situation is not hopeless and it can not be considered a crisis, as a crisis mean three-months delays in payment of pensions and salaries[65].
External trade
In 2005, the government of Transnistria reported exports of $579.7 million and imports of $855.6 million. The trade deficit reached $275.9 million.[66] In the first half of 2006 the Transnistrian Republican Bank reported that export decreased 49.0% and import decreased 15.9%.[67] Over 50% of export goes to the CIS, mainly to Russia.[54] The main exports are steel, brandy and wine, textile, and mineral products. The CIS accounts for over 60% of the imports, while the share of the EU is about 23%. The main imports are non-precious metals, food products and electricity.
Economic sectors
The leading industry is steel, due to the MMZ steel factory (part of the Russian Metalloinvest holding) in Rîbniţa (Rybnitsa), which accounts for about 50% of the budget revenue of Transnistria. The largest company in the textile industry is Tirotex, which claimed to be the second largest textile company in Europe.[68] The energy sector is dominated by the Russian companies. The largest power company Moldavskaya GRES (Cuchurgan power station), which is located in Dnestrovsk, is owned by Inter RAO UES, the joint subsidiary of RAO UES and Rosenergoatom,[69] and the gas transmission and distribution company Tiraspoltransgas is probably controlled by Gazprom, although Gazprom has not confirmed the ownership officially. The banking sector of Transnistria consists 8 commercial banks, including Gazprombank. The oldest alcohol producer Kvint, located in Tiraspol, produces and exports brandy, wines and vodka.
Human rights
The human rights record of Transnistria has been criticised by several governments and international organizations. The 2007 Freedom in the World report, published by the US-based Freedom House, described Transnistria as a "non-free" territory, having an equally bad situation in both political rights and civil liberties.[70]
The chairman of the Moldovan Helsinki Committee for Human Rights claimed that 20 people were killed in the village of Chiţcani, 5 km south of Tiraspol, between 1996 and 2000. He said that no government authority investigated these deaths because Moldova has no access to the village and Transnistrian authorities do not wish to investigate.[71]
In the best known political process, Ilie Ilaşcu was convicted in 1993 of killing two Transnistrian officials, and initially sentenced to death by Transnistria's Supreme Court, however this was repealed to a life prison sentence. Three other members of his group were sentenced to terms of 12 to 15 years’ imprisonment, and confiscation of their property. Ilaşcu was released in 2001, following a decision of the European Court of Human Rights, while the other three were released in 2004 and 2007, when they finished serving their "sentences". "[...] Some in Moldova and neighboring Romania saw the group's members as martyrs for their opposition to the separatists."[72] (ECHR stated the authorities have broken the right of freedom and safety to all 4 members of his group, and the treatment Ilie Ilaşcu suffered is qualified as torture. The court also ordered Moldova and Russia — which backs Transnistria — to pay the four a total of €750,000 (US$1,000,000) in compensation for the deprivation of their freedom, and for torture and inhumane treatment while in custody.[73])
In March 2007 several opponents of Transnistrian regime were arrested as they made public appeals for a protest rally against the Tiraspol regime's policy[74]. In 19 March 2007 Transnistrian authorities arrested also Ştefan Urîtu, leader of Moldovan Helsinki Comitee for Human Rights, and other two local political activits. They were released later[75] Transnistrian residents with automobiles registered in Moldova had seen their cars confiscated by Transnistrian authorities[76]
According to an U.S. Department of State report referring to year 2006, The right of citizens to change their government("their" refers to Moldovan government, Wikipedia editors note) was restricted[...] Authorities reportedly continued to use torture and arbitrary arrest and detention.[...]In Transnistria authorities limited freedom of speech and of the press.[...]Authorities usually did not permit free assembly.[...] In the separatist region of Transnistria the authorities continued to deny registration and harassed a number of minority religions groups.[...]The separatist region remained a significant source and transit area for trafficking in persons.[...] Homosexuality was illegal, and gays and lesbians were subject to governmental and societal discrimination.[77]
Situation of the media
According to OSCE, the media climate in Transnistria is restrictive and the authorities continue a long-standing campaign to silence independent opposition voices and groups.[78] Alternative viewpoints were stifled by widespread censorship
According to the same U.S. Department of State report for 2006, Both of region's major newspapers were controlled by the authorities. There was one independent weekly newspaper in Bender and another in the northern city of Rîbniţa.[...]Separatist authorities harassed independent newspapers for critical reporting of the Transnistrian regime.[...]Most television and radio stations and print publication were controlled by Transnistrian authorities, which largely dictated their editorial policies and finance operations. Some broadcast networks, such as the TSV television station and the INTER-FM radio station, were owned by Transnistria's largest monopoly, Sherriff, which also holds a majority in the region's legislature.[...]In July 2005 the Transnistrian Supreme Soviet amended the election code to prohibit media controlled by the Transnistrian authorities from publishing results of polls and forecasts related to elections.[79]
Moldovan schools
Transnistrian local authorities insist that public education for ethnic Moldovans in their mother tongue is done using the Soviet-originated Moldovan Cyrillic, having restricted the usage of the Latin script (the norm) for the Moldovan language to only 6 schools. Four schools (of the remaining six) that taught the Moldovan language using the Latin script were forcedly closed by the authorities, who claimed this was due to the refusal of the schools to apply for official accreditation. The schools were later reopened amid pressure from the European Union(Several Transnistrian officials were banned from traveling through EU), but as private institutions.
In November 2006, the European Court of Human Rights has accepted to examine the claims submitted by three Moldovan schools in Transnistria (from Tighina, Rîbniţa and Grigoriopol) regarding the violation of their right to education and their right to work in non-discriminiatory conditions. The three concerned schools regard the governments of Russia and Moldova as responsible for violation of their rights.[80]
The OSCE mission to Moldova has urged local authorities in the Transnistrian city of Rîbniţa to return a confiscated building to the Moldovan Latin script school located in the city. The unfinished building was nearing completion in 2004, when Transnistria took control of it during that year's school crisis.[81]
"In November 2005 Ion Iovcev, the principal of a Romanian-language school in Transnistria and active advocate for human rights as well as a critic of the Transnistrian leadership, received threatening calls that he attributed to his criticism of the separatist regime."[82]
- See also: Russification, Anti-Romanian discrimination
Profanation of military cemetery
According to the Moldovan and Romanian press, in February 2007, Transnistrian authorities destroyed and profaned the Drăgalina cemetery in Tighina (also known as the Romanian cemetery, which contains the tombs of many World War II solders), thus violating the Geneva Convention. The authorities did not exhume the bodies; but only removed the crosses and leveled the terrain with bulldozers.[83]
Security concerns
Arms control and disarmament
Following the collapse of the former Soviet Union the Russian 14th Army left behind 40,000 tonnes of weapony and ammunition. In the subsequent years there were concerns that the Transnistrian authorities may try to sell these stocks internationally and intense pressure was applied to have these removed by the Russian Federation.
In 2000 and 2001, the Russian Federation withdrew by rail 141 self-propelled artillery and other armoured vehicles and destroyed locally 108 T-64 tanks and 139 other pieces of military equipment limited by the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE). During 2002 and 2003 Russian military officials destroyed a further 51 armoured vehicles, all of which were types not limited by the CFE Treaty. The OSCE also observed and verified the withdrawal of the 48 trains with military equipment and ammunition in 2003. However, no further withdrawal activities have taken place since March 2004 and a further 20,000 tons of ammunition, as well as some remaining military equipment are still to be removed. In the Autumn of 2006 the Transnistria leadership agreed to let an OSCE inspectorate examine the munitions and further access agreed moving forward. Recent weapons inspections were permitted by Transnistria and conducted by the OSCE.[84][85] The onus of responsibility rests on the Russian Federation to remove the remainder of the supplies.
Analysts have expressed concern regarding potential threats posed by this large deposit of weapons, and the potential of their unauthorized sale.[citation needed]
Transnistrian authorities declared that they are not involved in the manufacture or export of weapons.[86] Some experts[dubious – discuss] and organizations[citation needed] support this view. Mark Almond of BHHRG stated that accusations of state-sponsored weapons smuggling in the PMR appear to be groundless and politically motivated, rather than based on any verified facts.[87]
The OSCE and European Union officials state that there is no evidence that Transnistria has ever, at any time in the past, trafficked arms or nuclear material.[88]
A United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) report states that there is currently a degree of transparency and good levels of co-operation with Transnistria in the field of weapons control[89], that the evidence for the illicit production and trafficking of weapons into and from Transnistria has in the past been exaggerated, that although the trafficking of light weapons is likely to have occurred before 2001 (the last year when export data showed US$ 900,000 worth of ‘weapons, munitions, their parts and accessories’ exported from Transnistria. However, it is also possible that these exports included old weapons from former Soviet stocks, or the export of weapon parts, rather than newly produced goods), and there is no reliable evidence that this still occurs. The report also states that the same holds true for the production of such weapons, which is likely to have been carried out in the 1990s primarily to equip the local forces but which are no longer produced.
The situation has been summed up by OSCE mission spokesman Claus Neukirch who cautioned: "There is often talk about sale of armaments from Transnistria, but there is no convincing evidence."[90]
Personal security
Some countries, including the United States,[91] the United Kingdom[92] and Australia[93] announced travel warnings for its citizens traveling to Transnistria.
On May 25, 2007, Valeri Emelianov, a Tiraspol city councelor, was shot dead in front of his house while irigating his flowers, with eleven 9-mm bullets fired by a person who did not even wear a mask.[94][95]
In March 2007, Victor Neumoin, a local politician was shot dead[96].
In April 2001, March 2004, and May 2005 there have been three isolated antisemitic incidents in Transnistria, involving a home made pipe bomb, tombstones in the Jewish cemetery of Tiraspol vandalized, and a synagogue hit with arson.
In July 2006, a bomb killed eight in a Tiraspol minibus[97], and in August 2006, a grenade explosion in a Tiraspol trolleybus killed two and injured ten.[98]
See also
References
This article has an unclear citation style. (May 2007) |
- ^ Barry Bartmann, Tozun. Bahcheli (2004). De Facto States: The Quest for Soverignty. Routledge. ISBN 0714654760.
- ^ Edward Ozhiganov, “The Republic of Moldova: Transdniester and the 14th Army,” in Managing Conflict in the Former Soviet Union: Russian and American Perspectives, Alexei Arbatov, et al. eds. (Cambridge: MIT Press, 1997), 179.
- ^ Template:Ro iconEuropean Court of Human Rights:Hotararea Marii Camere in afacerea Ilaşcu şi alţii contra Moldova şi Rusia
- ^ Pridnestrovie.net: "Pridnestrovie" vs "Transnistria" Pridnestrovie.net. Retrieved 2006, 12-26
- ^ OSCE, Moldovan Mission seeks solution to Dorotcaia's bitter harvest, 08/10/2005, accessed 05/29/2007
- ^ RIA Novosti, New checkpoint to appear in Moldova conflict zone after clash, 01/13/2007, accessed 05/29/2007
- ^ Template:Ro icon Deutsche Welle, Locuitorii satului Vasilievca de pe malul stâng al Nistrului trăiesc clipe de coşmar, 03/17/2005, accessed 05/29/2007
- ^ Moldova Azi, Transnistrian Militia Withdrew Its Posts from Vasilievca, accessed 2006-10-18
- ^ Moldpres News Agency, Ineffectiveness of peacekeeping mechanism leads to incidents in Moldova's security zone, May 14, 2007, accessed June 4, 2007
- ^ PMR Supreme Council (Parliament of Transnistria's official website)
- ^ BHHRG: Transnistria 2006: Is Regime Change Underway?
- ^ 9 were born in the Russian Federation, 8 in Ukraine, 2 in Kazakhstan, 1 in Germany, 1 in Belarus, and 3 did not declare.
- ^ PMR Supreme Concil: Members of Parliament Supreme Council of the PMR. Retrieved 2006, 12-27
- ^ (Some) international observers call elections free, democratic Pridnestrovie.net. Retrieved 2006, 12-27
- ^ Moldova and the Dniestr Region: Contest Past, Frozen Present, Speculative Futures? Herd, Graeme P.; Conflict Studies Research Centre; 2005; Accesed 25 May 2007;
- ^ US Department of State, Country Report on Human Rights Practices in Moldova - 2003
- ^ Ţăranu, A; Grecu, M. The policy of linguistic cleansing in Transnistria page 26-27 Retrieved 2006, 12-27
- ^ Министерство юстиции ПМР вынесло предупреждение общественному движению "Власть народу! За социальную справедливость!" и "Партии народовластия" (Ministry of Justice of PMR warned Power to the People movement and Narodovlastie party), Ольвия Пресс, 27-02-01 Template:Ru icon
- ^ Council Decision 2006/96/CFSP of 14 February 2006 implementing Common Position 2004/179/CFSP concerning restrictive measures against the leadership of the Transnistrian region of the Republic of Moldova European Union Law- Official Journal. Feb 2, 2006. Retrieved 2006, 12-27
- ^ Transnistria: New Social Democratic party wants union with Moldova Tiraspol Times. Feb. 6, 2007. Retrieved 2007, 2-19
- ^ Tiraspol not willing to register opposition representative in electoral race, Andrey Safonov will be able to enter the election for the seat of president
- ^ Transnistria's "Government" Showcases Foreign, Minority Rule by Vladimir Socor, Eurasia Daily Monitor
- ^ Olvia Press: "Valeri Litskai: A situation based on pressure and threats cannot be considered favorable for the revival of contacts"
- ^ http://politicom.moldova.org/stiri/eng/11365/
- ^ Pridnestrovie per-capita GDP up 17.3% despite economic warfare
- ^ "Nezavisimaya Moldova", 25 October 1994; Informative Report of FAM of RM, nr.2, October 1994, pp. 5-6
- ^ Mihai Grecu, Anatol Ţăranu, Trupele Ruse în Republica Moldova (Culegere de documente şi materiale). Chişinău, 2004 , p. 600.
- ^ Mihai Gribincea, "Russian troops in Transnistria – a threat to the security of the Republic of Moldova", Institute of Political and Military Studies, Chişinău, Moldova
- ^ "Interfax", Moscow, in Russian, 0850 gmt, 7 July 2004
- ^ Mihai Grecu, Anatol Ţăranu, Trupele ruse în Republica Moldova (Culegere de documente şi materiale) [Russian Troops in the Republic of Moldova (Collection of documents and materials)] Chişinău, "Litera Internaţional", pp. 717-724; 766-770.
- ^ MC.DEL/21/04, 6 December 2004
- ^ The Laurentian Codex of the Primary Chronicle ([1]) contains the following lines (translated): Ulichi, Tivertsy lived along the Dniester; a lot of them settled on the Danube; settled along the Dniester down to the sea, their cities can be found unto this day.
- ^ Porphyrogenitus, Constantine. De Administrando Imperio ca. 950. Retrieved 2006, 12-27
- ^ George Reichersdorf: "Moldaviæ quæ olim Daciæ pers, chorographia, Georgio a Reichersdorf Transilvano auctore", Viennæ 1541.
- ^ Bronovius and Georg Werner: "Transylvania, Moldavia and Chersonesus Tauricæ'". Published by Arnold Mylius, Cologne, 1595.
- ^ Antonio Bonfini (1434 - 1503): "Rerum Ungaricarum decades quatuor cum dimidia"
- ^ Giovanni Botero (1540-1617): "Relazioni universali", Venice, 1591
- ^ Giovanni Antonio Magini (1555-1617): "Geographie universae", Venice, 1596.
- ^ N. Iorga, Românii de peste Nistru, ,,Basarabia", nr. 11/1992, page 87
- ^ Viorel Dolha, "Totul despre Transnistria", http://www.aiarad.ro/forum/viewtopic.php?t=39
- ^ E.Şt. Holban, Figuri basarabene, "Basarabia", nr.1/1992
- ^ Andrew Wilson: "The Ukrainians: Engaging the Eastern Diaspora" (Westview Press, 1998)
- ^ E. Lozovan, Românii orientali de la Nistru la Vladivostok, "Neamul Românesc", nr.1/1991, page 32
- ^ N. Iorga, Românii de peste Nistru, "Basarabia", nr.11/1992, page 89
- ^ Averko, Michael. Russia's Stance on Disputed Territories: Just How "Hypocritical" is it? The American Journal of Russian and Slavic Studies. Retrieved 2006, 12-27
- ^ About Transdnistrea World Window NGO. Retrieved 2006, 12-27
- ^ Moldova Matters: Why Progress is Still Possible on Ukraine’s Southwestern Flank, Pamela Hyde Smith, The Atlantic Council of the United States, March 2005
- ^ Netherlands Institute of International Relations - The OSCE Moldova and Russian diplomacy 2003 page - 109
- ^ Official data from 2004 census and comparison with the 1989 census, by Olvia Press
- ^ Pridnestrovie.net: "2004 Census: PMR urban, multilingual, multicultural" from http://www.pridnestrovie.net retrieved 2006, 2-24
- ^ Trends in Europe and North America (Explanatory Notes), United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).
- ^ Moldova, International Religious Freedom Report 2005, released by the US Department of State Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor
- ^ Christians Face Abuse from Corrupt Regime, by Gary Lane, CBN News, 6 April 2007
- ^ a b Transnistria, Center for Economic Polices of IDIS “Viitorul”
- ^ Pridnestrovie's own currency, Pridnestrovie.net
- ^ John Mackinlay and Peter Cross (editors), Regional Peacekeepers: The Paradox of Russian Peacekeeping, United Nations University Press, 2003, ISBN 92-808-1079-0 p. 135
- ^ John B. Dunlop, "Will a Large-Scale Migration of Russians to the Russian Republic Take Place over the Current Decade?", in International Migration Review, Vol. 27, No. 3. (Autumn, 1993), pp. 605-629, citing Russian Radio, September 21, 1992 in Russia and CIS Today, WPS, September 21, 1992, p. 976/16.
- ^ Социально-экономическое развитие Приднестровской Молдавской Республики 2006 (Socio-economical development of the Pridnestrovian Moldovan Republic), statistical service of the Ministry of Economy, Tiraspol 2007
- ^ Transnistrian parliament adopts region's budget for 2007
- ^ Privatization will solve the budget problem PMR News, February 21, 2007
- ^ Democracy in Secessionism: Transnistria and Abkhazia’s Domestic Policies, by Nicu Popescu, International Policy Fellowship Program 2005/2006
- ^ Moscow's Hand Tired of Giving, Kommersant 6 Aprill 2007
- ^ «Газпром» передал Приднестровье Алишеру Усманову, Nezavisimaya Gazeta 23 March 2007
- ^ Shevchuk answering a question about 2007 Transnistrian budget
- ^ Shevchuk explaining that economical situation is not critical
- ^ СОЦИАЛЬНО-ЭКОНОМИЧЕСКОЕ РАЗВИТИЕ ПРИДНЕСТРОВСКОЙ МОЛДАВСКОЙ РЕСПУБЛИКИ 2005, statistical service of the Ministry of Economy, Tiraspol 2006
- ^ Основные направления денежно-кредитной политики ПРБ на 2007 год, Transnistrian Republican Bank 2006
- ^ Tirotex official website
- ^ Annual Report of Inter RAO UES
- ^ Freedom House, http://www.freedomhouse.org/uploads/press_release/fiw07_charts.pdf 2007 "Freedom in the World" report]
- ^ Interview on Transnistria with Stefan Uritu, reporter Mrs Sara Еngstrum, Sweden Angstorm
- ^ International Herald Tribune, Pro-Russian separatists in Moldova release last political prisoner, June 4, 2007
- ^ IHT, ditto
- ^ TRANSNISTRIAN POWER WIELDING FORCES HOLD OVER TEN OPPONENTS OF BREAKAWAY REGIME
- ^ Separatiştii transnistreni l-au arestat pe Ştefan Urîtu şi doi membri ai unui ONG local
- ^ TRANSNISTRIAN RESIDENTS SAY MILITIA HAVE CONFISCATED AUTOMOBILES REGISTERED IN MOLDOVA
- ^ United States Department of State: Country Reports on Human Rights Practices - 2006
- ^ OSCE - Media in Transdniestria
- ^ United States Department of State report for 2006
- ^ ECHR to consider claims lodges by Moldovan schools in Transnistria
- ^ Ribnitsa's authorities must return the confiscated school building, says OSCE Mission Head
- ^ United States Department of State report for 2006
- ^ Moldova azi Party accuses Tiraspol authorities of vandalism and desecration of military cemetery
- ^ UN Report clears Transdniester of weapons smuggling; Praises transparency and co-operation Tiraspol Times. Oct 16, 2006. Retrieved 2007, 2-21
- ^ Confidence-building visit: OSCE delegation inspects Kolbasna military depots Tiraspol Times. Nov 13, 2006. Retrieved 2007, 2-21
- ^ PMR doesn't make weapons, experts admit
- ^ Mark Almond: Kafka and the Arms Smugglers
- ^ RFE/RL: Western Diplomats Say Reports Of Smuggling From Transdniester Likely Exaggerated
- ^ UNDP: 2006 Small arms and light weapons survey of Moldova, SEESAC 1 July 2007, ISBN 86-7728-014-6
- ^ Dumitru Lazur, “Tiraspol rockets for Chechens”, Jurnal de Chisinau, Chisinau (Moldova), 28 May 2004
- ^ U.S. State Department travel warning for Moldova
- ^ "United Kindom Foreign and Commonwealth Office" - Travel Advice
- ^ Australian Government - Travel advisories
- ^ (Romanian) Transnistria.md, La Tiraspol a mai fost asasinat un politician, 05/28/2007
- ^ (Russian) Lenta.pmr, "Лидер НДП "ПРОРЫВ!": Валерий Емельянов был хорошим депутатом, но не был политиком
- ^ Trans-Dniester politician close to separatist leader's son shot dead (Associated Press)
- ^ Trans-Dniester blast kills eight BBC
- ^ Grenade exploded in Tiraspol trolley bus
External links
- Profile of Trans-Dniester from the BBC
- OSCE Mission to Moldova OSCE
- Transdniester Conflict Was Long In The Making Radio Free Europe
- The black hole that ate Moldova Economist
- Moldova Strategic Conflict Assessment (SCA), Stuart Hensel, Economist Intelligence Unit.
- "Moldova, Transnistria, and European Democracy Polices" Jos Boonstra, FRIDE, February 2007
Pro-separatist sources
- Pridnestrovie.net (Official English site)
- VisitPMR.com (Official tourist information)
- Website of the Transnistrian Parliament (Supreme Council) (Official site)
- PMR News (English language news from Transnistria)
Anti-separatist sources
- Moldova Azi: News from Moldova
- Moldova.org non-governmental country portal
- Transnistria.md
- Conflict.md


