Czech Republic
| |||||
| National motto: Truth prevails (Czech: Pravda vítězí) | |||||

| |||||
| Official language | Czech | ||||
| Capital | Praha (Prague) | ||||
| President | Václav Klaus | ||||
| Prime Minister | Jiří Paroubek | ||||
| Area - Total - % water |
Ranked 114th 78,866 km² 2% | ||||
| Population - Total (2003) - Density |
Ranked 76th 10.25 million 130/km² | ||||
| GDP - Total - GDP per capita |
(PPP 2005) $199.0 billion (42nd) $19,475 (38th) | ||||
| UN HDI | Ranked 32nd (2004) | ||||
| Christianized - Date |
Bořivoj I AD 883 | ||||
| Independence - Date |
Regained October 28, 1918 as Czechoslovakia, divided January 1 1993 | ||||
| Currency | Czech koruna (CZK) | ||||
| Time zone - in summer |
CET (UTC+1) CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| National anthem | Where is My Home? Czech: Kde domov můj | ||||
| Internet TLD | .cz | ||||
| Calling Code | 420 ("0" appended to Czechoslovakia's "42") | ||||
The Czech Republic (Czech: Česká republika ⓘ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The republic borders Poland to the north, Germany to the northwest and west, Austria to the south, and Slovakia to the east. Historic Prague (Czech: Praha), a major tourist attraction, is its capital and largest city. The country is composed of two older regions, Bohemia and Moravia, and part of a third one, Silesia. As of May 1, 2004, it is a member state of the European Union.
The Czech Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1993 announced that the name Czechia (Czech: Česko) is to be used in all situations other than formal official documents and the full names of government institutions [1], [2], but this is controversial in the Czech Republic [3] and has not caught on in English usage. See also: Czech lands.
History
Main article: History of the Czech Republic
The Czech lands emerged in the late 9th century when it was unified by the Premyslids. The kingdom of Bohemia was a significant local power, but religious conflicts such as the 15th century Hussite Wars and the 17th century Thirty Years War were devastating. It later came under the Habsburg influence and became part of Austria-Hungary.
Following the collapse of this state after World War I, the Czechs and neighbouring Slovaks joined together and formed the independent republic of Czechoslovakia in 1918. This new country contained a large German minority, which would lead to the dissolution of Czechoslovakia when Germany successfully annexed the minority through the Munich Agreement in 1938, and Slovakia gained greater autonomy, with the state renamed "Czecho-Slovakia". Slovakia broke away further in 1939 and the remaining Czech state was occupied by the Germans.
After World War II, a reconstituted Czechoslovakia fell within the Soviet sphere of influence. In 1968, an invasion by Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts of the country's leaders to liberalise party rule and create "socialism with a human face" during the Prague Spring. In 1989, Czechoslovakia regained its freedom through a peaceful "Velvet Revolution". On January 1, 1993, the country peacefully split in two, creating independent Czech and Slovak republics.
The Czech Republic joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union in 2004.
Politics
Main article: Politics of the Czech Republic
According to its constitution the Czech Republic is a parliamentary democracy, whose head of state is a president, indirectly elected every five years by the parliament. The president is also granted specific powers such as the right to nominate Constitutional Court judges, dissolve parliament under certain conditions, and enact a veto on legislation. He also appoints the prime minister, who sets the agenda for most foreign and domestic policy, as well the other members of the cabinet on a proposal by the prime minister.
The Czech parliament (Parlament) is bicameral, with a Chamber of Deputies (Poslanecká sněmovna) and a Senate (Senát). The 200 Chamber delegates are elected for 4-year terms, on the basis of proportional representation. The 81 members of the Czech Senate serve for 6-year terms with one-third being elected every 2 years on the basis of two-round majority voting.
The country's highest court of appeals is the Supreme Court. The Constitutional Court, which rules on constitutional issues, is appointed by the president, and its members serve 10-year terms.
Regions
Main article: Regions of the Czech Republic; see also: Overview of regions in Czech Republic
The Czech Republic consists of 13 regions (kraje, singular - kraj) and one capital city (hlavní město), marked by a *:
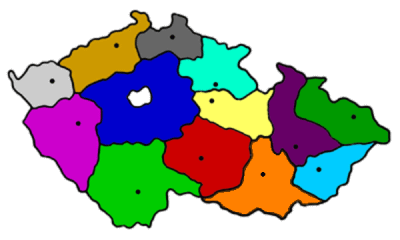
| Region (in Czech) | Capital (in Czech) | color |
| Prague* (Praha) | ||
| Central Bohemian Region (Středočeský kraj) | Kladno, but its offices are located in Prague (Praha) | |
| South Bohemian Region (Jihočeský kraj) | České Budějovice | |
| Plzeň Region (Plzeňský kraj) | Plzeň | |
| Carlsbad Region (Karlovarský kraj) | Carlsbad (Karlovy Vary) | |
| Ústí nad Labem Region (Ústecký kraj) | Ústí nad Labem | |
| Liberec Region (Liberecký kraj) | Liberec | |
| Hradec Kralove Region (Královéhradecký kraj) | Hradec Kralove | |
| Pardubice Region (Pardubický kraj) | Pardubice | |
| Olomouc Region (Olomoucký kraj) | Olomouc | |
| Moravian-Silesian Region (Moravskoslezský kraj) | Ostrava | |
| South Moravian Region (Jihomoravský kraj) | Brno | |
| Zlin Region (Zlínský kraj) | Zlin | |
| Vysocina Region (Vysočina) | Jihlava |
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Czech_Republic#History
Geography
Main article: Geography of the Czech Republic

The Czech landscape is quite varied; Bohemia to the west consists of a basin, drained by the Elbe (Czech: Labe) and Vltava rivers, surrounded by mostly low mountains such as the Sudeten with its part Krkonoše, where one also finds the highest point in the country, the Snezka at 1,602 m. Moravia, the eastern part, is also quite hilly and is drained predominantly by the Morava river, but also contains the source of the Oder (Czech: Odra) river. Water from the landlocked Czech Republic flows to three different seas: the North Sea, Baltic Sea and Black Sea.
The local climate is temperate with warm summers and cold, cloudy, humid winters, typified by a mixture of maritime and continental influences.
Economy
Main article: Economy of the Czech Republic
One of the most stable and prosperous of the post-Communist states, the Czech Republic has been recovering from recession since mid-1999. Growth in 2000-2001 was led by exports to the EU, especially Germany, and foreign investment, while domestic demand is reviving. With a GDP per capita of $19,475, the Czech Republic is approaching the living standards of EU-15 states such as Portugal and Greece. Its per-capita output is approximately two-thirds that of the leading European economies.
Uncomfortably high fiscal and current account deficits could be future problems.
Moves to complete banking, telecommunications, and energy privatisation will add to foreign investment, while intensified restructuring among large enterprises and banks and improvements in the financial sector should strengthen output growth.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of the Czech Republic
The majority of the inhabitants of the Czech Republic (95%) are ethnically Czech and speak Czech, a member of the Slavic languages. Other ethnic groups include Germans, Roma, Hungarians, Ukrainians and Poles. After the 1993 division, some Slovaks remained in the Czech Republic and comprise roughly 2% of the current population. The border between the Czech Republic and Slovakia is open for citizens of the former Czechoslovakia.
Major denominations and their estimated percentage populations are Roman Catholic (27%), Protestant (1%), Czechoslovak Hussites (1%), as well as a small Jewish community. A large percentage of the Czech population claim to be atheists (59%).
Culture
Main article: Culture of the Czech Republic
- Famous Czech People
- Music of the Czech Republic
- Cinema of the Czech Republic
- Literature of the Czech Republic
- National Theatre (Prague)
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in the Czech Republic
- Transportation in the Czech Republic
- Military of the Czech Republic
- Foreign relations of the Czech Republic
- Tourism in the Czech Republic
- List of cities in the Czech Republic
- Public holidays in the Czech Republic
- List of Czech Republic-related topics
Reference
- Much of the material in these articles comes from the CIA World Factbook 2000 and the 2003 U.S. Department of State website.
External links
- Portal of the Public Administration of Czech Republic
- Official Czech portal
- Czech Press Agency news in English
- Radio Prague - website of the English service of Czech Radio
- Prague Post - English-language newsweekly
- Government website, in English
- Presidential website, click for a pop-up overview of English-languge content
- Chamber of Deputies website, in English
- Senate website, in English
- CzechTourism - governmental agency aimed at promoting tourism in the Czech Republic
- Czech Republic at Wikitravel - share your tourist experience

