Aspartic acid
Appearance
| Aspartic acid | |
|---|---|
| Systematic name | (S)-Aminobutanedioic acid |
| Abbreviations | Asp D |
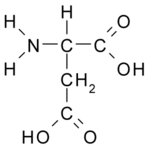
| Chemical formula | C4H7NO4 |
| Molecular mass | 133.10 g/mol |
| Melting point | 270-271 °C |
| Density | 1.66 g cm-3 |
| Isoelectric point | 2.77 |
| pKa | 1.95 3.71 9.66 |
| CAS number | [56-84-8] |
| EINECS number | 200-291-6 |
| SMILES | OC(=O)CC(N)C(=O)O |
| |
| Disclaimer and references | |
Aspartic acid, also known as aspartate, the name of its anion, is one of the 20 natural proteinogenic amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins.
Its three-letter abbreviation is Asp, and its one-letter abbreviation is D. A three-letter designation for either asparagine or aspartic acid is Asx (one-letter abbreviation: B).
As its name indicates, it is the carboxylic acid analog of asparagine. It is non-essential in mammals, and might serve as an excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. It is also a metabolite in the urea cycle, and participates in gluconeogenesis.
This neurotransmitter may provide resistance to fatigue and thus lead to possessing more endurance, although the evidence to support this idea is not strong.

