Geography of Belgium
This article is about the geography of Belgium.
Belgium is located in Western Europe, bordering the North Sea, between France and the Netherlands.
Geographic coordinates: 50°50′N 4°00′E / 50.833°N 4.000°E
Map references: Europe
Area:
total:
32,545 km²
land:
30,278 km²
surface water:
250 km² (est)
sea:
2,017 km²
Area comparative
- Australia comparative: one third the size of Tasmania
- Canada comparative: about half the size of Nova Scotia
- United Kingdom comparative: 1.5 times larger than Wales
- United States comparative: about the size of Maryland
Land boundaries:
total:
1,379.0 km
border countries:
France 620.0 km, Germany 161.5 km, Luxembourg 148.0 km, Netherlands 449.5 km
Coastline: 72.3 km
Maritime claims:
continental shelf:
median line with neighbors
exclusive fishing zone:
median line with neighbors (extends about 68 km from coast)
territorial sea:
12 nautical miles
Climate: temperate; mild winters, cool summers; rainy, humid, cloudy
Terrain: flat coastal plains in northwest, central rolling hills, forested hills and valleys of the Ardennes Forest in southeast
Elevation extremes:
See the section: Extreme points.
lowest point:
North Sea 0 m
highest point:
Signal de Botrange 694 m
Natural resources: coal, natural gas
Land use:
arable land:
28% (2000)
permanent crops:
1% (2000)
permanent pastures:
17% (2000)
forests and woodland:
20% (2000)
other:
34%
Irrigated land: NA km²
Natural hazards: flooding is a threat in areas of reclaimed coastal land, protected from the sea by concrete dikes
Environment - current issues: the environment is exposed to intense pressures from human activities: urbanization, dense transportation network, industry, intense animal breeding and crop cultivation; air and water pollution also have repercussions for neighboring countries; uncertainties regarding federal and regional responsibilities (now resolved) have impeded progress in tackling environmental challenges
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Geography - note: crossroads of Western Europe; majority of West European capitals within 1,000 km of Brussels which is the seat of both the EU and NATO
Extreme points


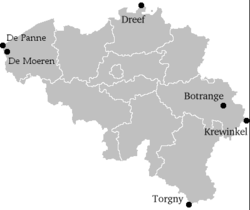
This is a list of the extreme points of Belgium, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost Point — Dreef, municipality of Hoogstraten, Antwerp
- Southernmost Point — Torgny, municipality of Rouvroy, Luxembourg
- Westernmost Point — De Panne, West Flanders
- Easternmost Point — Krewinkel, municipality of Büllingen, Liège
- Highest Point — Signal de Botrange (694 m)
- Lowest Point — North Sea (0 m)
Reference
Much of the material in this article is adapted from the CIA World Factbook 2000.
