Carbon trioxide
Appearance
Carbon Trioxide
Carbon Trioxide is a unstable product of reactions between carbon dioxide and a single oxygen atom[1]. It has also been detected in reactions between carbon monoxide and molecular oxygen. Among other places it has been shown to be created in the drift zone of a negative Corona discharge[2]. This pathway arises from reactions between Carbon Dioxide and atomic oxygen ions, created from molecular oxygen by free electrons in the plasma.
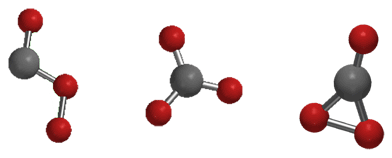
Three possible isomers of carbon trioxide exist, denoted Cs, D3h, and C2v. The C2v state has been shown by various studies to be the ground state of the molecule[3].
References
- 1: Sabin, J. R.; Kim, H. Chemical Physics Letters, Volume 11, Issue 5, p.593-597
- 2: V. Sobek;J. D. Skalný, Czechoslovak Journal of Physics, Volume 43, Number 8, August 1993
- 3: Electronic structure and spectroscopy of carbon trioxide