Thailand
Kingdom of Thailand ราชอาณาจักรไทย Ratcha Anachak Thai | |
|---|---|
Royal Seal
| |
| Anthem: Phleng Chat | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Bangkok |
| Official languages | Thai |
| Government | Constitutional monarchy |
• King | Bhumibol Adulyadej |
| Thaksin Shinawatra | |
| Independence from Khmer Empire | |
| 1238–1368 | |
| 1350–1767 | |
| 1767–April 7, 1782 | |
| April 7, 1782–present | |
• Water (%) | 0.4% |
| Population | |
• July 2005 estimate | 64,233,0001 (19th) |
• 2000 census | 60,916,441 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
• Total | $560.7 billion (21st) |
• Per capita | $8,300 (69th) |
| HDI (2003) | 0.778 high (73rd) |
| Currency | ฿ Baht (THB) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+7 |
| Calling code | 66 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH |
| Internet TLD | .th |
1 Estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected. 2 Based on July 2005 figures | |
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, bordering Laos and Cambodia to the east, the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia to the south, and the Andaman Sea and Myanmar to the west. Thailand was also known as Siam (Template:Lang-th; IPA: [saˈjaːm]), which was the country's official name until May 11, 1949. The word Thai (ไทย) means "freedom" in the Thai language and is also the name of the majority Thai ethnic group.
History
Thailand's origin is traditionally tied to the short-lived kingdom of Sukhothai founded in 1238, after which the larger kingdom of Ayutthaya was established in the mid-14th century. Thai culture was greatly influenced by both China and India.
Contact with various European powers began in the 16th century but, despite continued pressure, Thailand is the only Southeast Asian country never to have been taken over by a European power. Western influence, however, including the threat of force, led to many reforms in the 19th century and major concessions to British mercantile interests. This included the loss of the 3 southern provinces, which later became Malaysia's 3 northern states.
Thailand was never colonised by a European power. There are two main reasons for this. First, it was left as a buffer state between parts of Asia that were colonised by the French and the British. Second, Thailand had a series of very able rulers in the 1800s.
A mostly bloodless revolution in 1932 led to a constitutional monarchy. Known previously as Siam, the country first changed its name to Thailand in 1939, and definitively in 1949 after reverting to the old name post-World War II. During that conflict Thailand was in a loose alliance with Japan; following its conclusion Thailand became an ally of the United States. Thailand then saw a series of military coups d'état, but progressed towards democracy from the 1980s onward. In 1997 was hit by the Asian financial crisis and the Thai Baht was soon worth 56 baht to the US Dollar compared to about 20 Baht to the dollar before 1997. Since then the baht has regained some strength and currently trades around 36-38 baht to the dollar.
The official calendar in Thailand is based on the Buddhist Era, which is 543 years ahead of the Gregorian (western) calendar. For example, the year AD 2006 is equal to the year 2549 BE.
Politics

The king has little direct power under the constitution but is the anointed protector of Thai Buddhism and a symbol of national identity and unity. The present monarch enjoys a great deal of popular respect and moral authority, which has on occasion been used to resolve political crises. It is illegal to mock or criticize the King and doing so can bring about charges of lèse majesté. The head of government is the Prime Minister, who is appointed by the king from among the members of the lower house of parliament, usually the leader of the party that can organise a majority coalition government.
The bicameral Thai parliament is the National Assembly (รัฐสภา, rathasapha) which consists of a House of Representatives (สภาผู้แทนราษฎร, sapha phuthaen ratsadon) of 500 seats and a Senate (วุฒิสภา, wuthisapha) of 200 seats. Members of both houses are elected by popular vote. The House of Representatives is elected by the first-past-the-post system, where only one candidate with a simple majority will be elected in one constituency. The Senate is elected based on the province system, where one province can return more than one Senator depending on its population size. Members of House of Representatives serve four-year terms, while Senators serve six-year terms. The court system (ศาล, saan) has three layers, the highest judicial body being the Supreme Court (ศาลฎีกา, sandika). Thailand is an active member of the regional Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
Administrative divisions
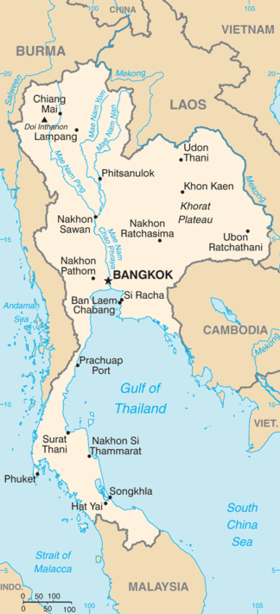
Thailand is divided into 75 provinces (จังหวัด, changwat), which are gathered into 5 groups of provinces by location. There are also 2 special governed districts: the capital Bangkok (Krung Thep Maha Nakhon in Thai) and Pattaya, of which Bangkok is also at a provincial level, while Pattaya is part of Chon Buri Province. Some Thai people still count Bangkok as a province, making Thailand a 76-province country.
Each province is divided into smaller districts. As of 2000 there are 796 districts (อำเภอ, amphoe), 80 sub-districts (กิ่งอำเภอ, king amphoe) and the 50 districts of Bangkok (เขต, khet). Some parts of the provinces bordering Bangkok are also referred to as Greater Bangkok (ปริมณฑล, pari monthon). These provinces include Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan, Nakhon Pathom, Samut Sakhon. The name of each province's capital city (เมือง, mueang) is the same as that of the province: for example, the capital of Chiang Mai province (changwat Chiang Mai) is Mueang Chiang Mai. The 75 provinces are as follows:-
- Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Kamphaeng Phet, Lampang, Lamphun, Mae Hong Son, Nakhon Sawan, Nan, Phayao, Phetchabun, Phichit, Phitsanulok, Phrae, Sukhothai, Tak, Uthai Thani, Uttaradit
- Amnat Charoen, Buri Ram, Chaiyaphum, Kalasin, Khon Kaen, Loei, Maha Sarakham, Mukdahan, Nakhon Phanom, Nakhon Ratchasima, Nong Bua Lamphu, Nong Khai, Roi Et, Sakon Nakhon, Si Sa Ket, Surin, Ubon Ratchathani, Udon Thani, Yasothon.
- Ang Thong, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Chachoengsao, Chai Nat, Kanchanaburi, Lop Buri, Nakhon Nayok, Nakhon Pathom, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Phetchaburi, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Ratchaburi, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram, Saraburi, Sing Buri, Suphan Buri
- Chumphon, Krabi, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Narathiwat, Pattani, Phang Nga, Phatthalung, Phuket, Ranong, Satun, Songkhla, Surat Thani, Trang, Yala
Special Governed Districts
A 77th province — Nakhon Suvarnabhumi — is about to be established in the near future. It will also become a special governed district.
See also: List of cities in Thailand, List of cities in Thailand by population
Geography

Thailand is home to several distinct geographic regions, partly corresponding to the provincial groups. The north of the country is mountainous, with the highest point being Doi Inthanon at 2,576 metres (8,451 ft). The northeast consists of the Khorat Plateau, bordered to the east by the Mekong river. The centre of the country is dominated by the predominantly flat Chao Phraya river valley, which runs into the Gulf of Thailand. The south consists of the narrow Kra Isthmus that widens into the Malay Peninsula.
The local climate is tropical and characterised by monsoons. There is a rainy, warm, and cloudy southwest monsoon from mid-May to September, as well as a dry, cool northeast monsoon from November to mid-March. The southern isthmus is always hot and humid. Major cities beside the capital Bangkok include Nakhon Ratchasima, Udon Thani, Nakhon Sawan, Chiang Mai, Surat Thani, Phuket and Hat Yai (Songkhla Province).
See also: List of islands of Thailand
Economy

After enjoying the world's highest growth rate from 1985 to 1995 - averaging almost 9% annually - increased pressure on Thailand's currency, the baht, in 1997 led to a crisis that uncovered financial sector weaknesses and forced the government to float the currency. Long pegged at 25 to the US dollar, the baht reached its lowest point of 56 to the US dollar in January 1998 and the economy contracted by 10.2% that same year. The collapse prompted a wider Asian financial crisis.
Thailand entered a recovery stage in 1999, expanding 4.2% and grew 4.4% in 2000, largely due to strong exports - which increased about 20% in 2000. Growth was dampened by a softening of the global economy in 2001, but picked up in the subsequent years due to strong growth in China and the various domestic stimulation programs of Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra, popularly known as Thaksinomics. Growth in 2003 and 2004 was over 6% annually.[1]
Substantial industries include electric appliances, components, computer parts and automobiles, while tourism contributes about 5% of the Thai economy's GDP.
Demographics
Thailand's population is dominated by ethnic Thai and Lao, the latter concentrated in the north-eastern Isan region and making up around one third of the population. There is also a large community of Thai Chinese, who have historically played a disproportionately significant role in the economy. Bangkok's Chinatown is located on Yaowarat Road. Other ethnic groups include Malays in the south, Mon, Khmer and various indigenous hill tribes. After the end of the Vietnam War, many Vietnamese refugees settled in Thailand, mainly in the northeastern regions.
According to the last census (2000) 94.6% of Thais are Buddhists of the Theravada tradition. Muslims are the second religious group in Thailand at 4.6%. Most of them are ethnic Malays and they are mostly concentrated in the south, where they form a strong majority in four provinces. Christians, mainly Catholics, represent 0.75% of the population. A tiny but influential community of Sikhs and some Hindus also live in the country's cities.
The Thai language is Thailand's national language, written in its own alphabet, but many ethnic and regional dialects exist as well as areas where people speak predominantly Isan or Mon-Khmer languages. Although English is widely taught in schools, proficiency is low.
Culture

Theravada Buddhism is central to modern Thai identity and belief. However, in areas in the southernmost parts of Thailand, Islam is prevalent. Several different ethnic groups, many of which are marginalized, populate Thailand. Some of these groups overlap into Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Malaysia and have maintained a distinctly traditional way-of-life despite strong Thai cultural influence. Ethnic Chinese also form a significant part of Thai society, particularly in and around Bangkok. Their successful integration into Thai society has allowed for this group to hold positions of economic and political power, the most noteworthy of these being the Thai Prime Minister.
Worship of ancestors is a large part of Thai spiritual practice, as well as charity towards Buddhist monks. Thais have a very strong sense of graciousness and hospitality, but also a strong sense of social hierarchy. Honorifics are important in day-to-day Thai speech, especially titles of seniority.
Seniority is a very important concept in Thai culture. Thais respect the elderly so much that some natives wai or krab (bow) to the feet of their parents and grandparents. They honor the eldest first, and the elderly take precedence in all family decisions and any sort of ceremony.
Muay Thai, or Thai boxing, is the national sport in Thailand and its native martial art. It reached popularity all over the world in the 1990s. Although similar martial art styles exist in other southeast Asian countries, few enjoy the recognition that Muay Thai has received with its full-contact rules allowing strikes including elbows, throws and knees. Association football, however, has possibly overtaken Muay Thai's position as most widely viewed and liked sport in contemporary Thai society and it is not uncommon to see Thais cheering their favourite English Premier League teams on television. Another widely enjoyed pastime, while not a sport per se, is kite flying.
The standard greeting in Thailand is a prayer-like gesture called the wai (see namaste). Taboos include touching someone's head or pointing with the feet, as the head is considered the most sacred and the foot the dirtiest part of the body. Stepping over someone, or over food, is considered insulting. However, Thai culture as in many other Asian cultures, is succumbing to the influence of westernization and some of the traditional taboos are slowly fading away with time. Books and other documents are considered the most revered of secular objects - therefore one should not slide a book across a table or place it on the floor.
Thailand is a constitutional monarchy and the King is extremely respected and revered. It is illegal to insult the Royal Family. Unfortunately, this fundamental respect of the Thai royal family has led to politically powerful individuals unfairly citing the offence of Lèse majesté against outspoken political rivals to manipulate the political process. Police act quickly on such matters and western liberal democratic ideals of justice may be overshadowed by the emotional response of both the police and courts. There have been incidents where Lèse majesté was alleged for just using parts of published royal speeches as this, according to the accusers, requires interpretation of the royal word.
The Thai King recently celebrated 60 years on the throne and millions of Thai citizens commemorated the event and showed their reverence by donning yellow t-shirts - the official royal colour.
Thai cuisine blends five fundamental tastes: sweet, spicy, sour, bitter and salty. Some common ingredients used in Thai cuisine include garlic, chillies, lime juice, lemon grass, and fish sauce. The staple food in Thailand is rice, which is included in almost every meal.
Thai culture has been greatly shaped in recent years by its vibrant and free press. There are numerous English, Thai and Chinese papers in circulation and Thailand is the largest newspaper market in South East Asia with an estimated circulation of at least 13 million copies daily in 2003. Thai culture has been greatly shaped in recent years by its vibrant and free press. There are numerous English, Thai and Chinese papers in circulation and Thailand is the largest newspaper market in South East Asia with an estimated circulation of at least 13 million copies daily in 2003.
See also
- Famous Places in Thailand:
- Patong, and Karon beach in Phuket
- Pattaya
- Khao Lak
- Chiang Mai
- Sukhothai Historical Park
- Cinema of Thailand
- Communications in Thailand
- Education in Thailand
- Historical parks of Thailand
- Foreign relations of Thailand
- List of Thailand-related topics
- Media in Thailand
- Military of Thailand
- National parks (Thailand)
- The National Scout Organization of Thailand
- List of shopping malls in Thailand
- Public holidays in Thailand
- Transportation in Thailand
- Buddhist temples in Thailand
- Medical tourism in Thailand
- Prostitution in Thailand
- South Thailand insurgency
- Thai Gem Scam
External links
Official
- Thaigov.go.th Royal Government of Thailand
- Tourism Authority of Thailand Official tourism website
- Thai National Assembly Official Thai Prliment website


