Monaco
The Principality of Monaco, known as Munegu in the local dialect, is a city state and the second-smallest country in the world, wedged in between the Mediterranean Sea and France along the French Riviera or Côte d'Azur (The Blue Coast). Consisting mostly of just the old city of Monaco and later built up areas, it is also among the most densely populated countries of the world.
| ||||
| Princes of Monaco's motto: "Deo Juvante" (Latin: "With God's Help") | ||||
 | ||||
| Official language | French | |||
| Capital | Monaco | |||
| Prince | Rainier III | |||
| Minister of State | Patrick Leclercq | |||
| Area - Total - % water |
Ranked 193rd 1.95 km² Negligible | |||
| Population - Total (2000) - Density | Ranked 188th 31,842 16,329/km² | |||
| Independence | January 8, 1297 | |||
| Currency | Euro (EUR, €)¹ | |||
| Time zone - in summer | CET (UTC+1) CEST (UTC+2) | |||
| National anthem | Hymne Monégasque | |||
| Internet TLD | .mc | |||
| Calling Code | 377 | |||
| (1) Prior to 1999: French franc | ||||

History
Main article: History of Monaco
Founded in 1215 as a colony of Genoa, Monaco has been ruled by the House of Grimaldi since 1297, when François Grimaldi seized the fortress protecting the famous rock while dressed up as a Franciscan monk; the only exception to this was from 1789 to 1814, when Monaco was under French control. Designated as a protectorate of Sardinia from 1815 until 1860 by the Congress of Vienna, Monaco's sovereignty was recognised by the Franco-Monegasque Treaty of 1861.
The Prince of Monaco was an absolute ruler until a constitution was promulgated in 1911. In July 1918, a treaty was signed providing for limited French protection over Monaco. The treaty, written into the Treaty of Versailles, established that Monegasque policy would be aligned with French political, military, and economic interests.
Prince Rainier III, the current ruler of Monaco, acceded to the throne following the death of his grandfather, Prince Louis II, in 1949. The current heir apparent, Prince Albert of Monaco, was born in 1958. A new constitution, proclaimed in 1962, abolished capital punishment, provided for female suffrage, and established a Supreme Court to guarantee fundamental liberties. In 1993, Monaco became an official member of the United Nations with full voting rights.
In 2002, a new treaty between France and Monaco clarifies that if there are no heirs to carry on the dynasty, the Principality will remain an independent nation rather than revert to the French. Monaco's military defense, however, is still the responsibility of France.
See: List of the Princes of Monaco
Politics
Main article: Politics of Monaco
Monaco has been governed as a constitutional monarchy since 1911, with the Prince as head of state. The executive branch consists of a Minister of State (the head of government), who presides over a four-member Council of Government (the cabinet). The Minister of State is a French citizen appointed by the Prince for a 3-year term from among candidates proposed by the French Government. Under the 1962 constitution, the Prince shares his power with the unicameral National Council. The 18 members of this legislative body are elected from lists by universal suffrage for 5-year terms.
The principality's local affairs are directed by the Communal Council, which consists of 15 elected members and is presided over by the Mayor.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Monaco
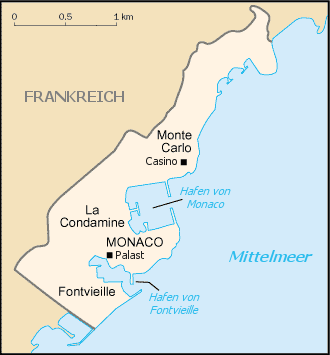
The Principality of Monaco is the second-smallest independent state in the world, after Vatican City. It is located on the Mediterranean coast, 18 kilometres east of Nice and near the Italian border, and is surrounded on three sides by France. It consists of a narrow strip along the coast at the bottom of the foothills of the Alps and its highest point is "Le Rocher" at 140 m.
The territory is almost entirely urbanised, resulting in it being the most densely populated country of the world. Monaco is divided into four sections or quarters (quartiers): Monaco-Ville, the old city on a rocky promontory extending into the Mediterranean; La Condamine, the section along the port; Monte Carlo, the principal residential and resort area with the casino; and Fontvieille, a newly constructed area reclaimed from the sea.
The principality is noted for its beautiful natural scenery and mild, sunny climate. The average minimum temperature in January and February is 8° C (47° F); in July and August the average maximum temperature is 26° C (78° F).
Economy
Main article: Economy of Monaco
One of Monaco's main sources of income is tourism; each year many are attracted to its casino and pleasant climate. In 2001, a major new construction project extended the pier used by cruise ships in the main harbour. The Principality has successfully sought to diversify into services and small, high-value-added, nonpolluting industries.
The state has no income tax for individuals. The state retains monopolies in a number of sectors, including tobacco and the postal service. (The telephone network used to be owned by the state. Now Monaco Telecom is owned by Cable and Wireless.) Living standards are high, roughly comparable to those in prosperous French metropolitan areas.
The lack of personal income tax has led to a considerable number of wealthy "tax exile" residents from European countries, who earn the majority of their income from activity outside Monaco; celebrities like Formula One drivers attract most of the attention but the majority of them are businesspeople.
In 2000 a report by French parliamentarians Arnaud Montebourg and Vincent Peillon alleged that Monaco has lax policies with respect to money laundering, including within its famed casino, and that the government of Monaco puts political pressure on the judiciary so that alleged crimes are not properly investigated. The government of Monaco ordered reports to OECD and GAFI that proved most of these allegations to be untrue.
Monaco is not a member of the European Union, but it is very closely linked to it via a customs union with France and as such its currency is the same as France's: the euro. Monaco has acquired the right to mint euro coins with Monegasque designs on their national side.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Monaco
Although Macau is more densely populated, by virtue of the fact that Macau is now part of China, Monaco is now the most densely populated country in the world. Monaco is also the second smallest country in the world, beaten only by Vatican City. See List of countries by population density.
Monaco's population is unusual in that the native Monegasques are a minority in their own country. The largest proportion of residents are French nationals (47%), while Monegasque and Italian nationals represent 16% each, and the remaining 21% belong to one of the other 125 nationalities that make up Monaco's international population.
French is the only official language, but English, Italian, and the local Monegasque dialect (a descendant of Genoese) are also spoken. The literacy rate is 99%. Roman Catholicism is the official religion, with freedom of other religions guaranteed by the constitution.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Monaco
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Monaco
- Transportation in Monaco
- Foreign relations of Monaco
- Grand Prix of Monaco
- Monte Carlo Rally
- AS Monaco FC
External links
- www.gouv.mc - Official governmental portal.
- In the House of Grimaldi
- Monaco Net - Monaco Portail (information, list of websites, etc.).
- I Love Monte Carlo - Monaco and Monte Carlo Guide - information, map, history, culture, tourism, politics, economy and finance


