Chloroalkyl ether
Chloroalkyl ethers are a class of organic compounds with the general structure R-O-(CH2)n-Cl, characterized as an ether connected to a chloromethyl group via a alkane chain
Chloromethyl methyl ether (CMME) is an ether with the formula Template:MethylTemplate:OxygenTemplate:CarbonTemplate:HydrogenTemplate:Chlorine. It is used as an alkylating agent and industrial solvent to manufacture dodecylbenzyl chloride, water repellents, ion-exchange resins, polymers, and as a chloromethylation reagent. It is a known human carcinogen [1]. In organic synthesis the compound is used for the introduction of the methoxymethyl (MOM) protecting group.
Closely related compounds of industrial importance are bis(chloromethyl ether) (BCME) (closely related to chemical weapon sulfur mustard) [2] and benzyl chloromethyl ether (BOMCl).
| Chloromethyl ether | R | Molar mass | CAS number | Boiling point °C | |
| benzyl chloromethyl ether | Benzyl | 121.93 | 98-80-6 | 102°C @14 mmHg | |
| methyl chloromethyl ether | Methyl |  |
80.51 | 107-30-2 | 55-57 |
| bischloromethyl ether | 114.96 | 542-88-1 | 106 | ||
| t-Butoxymethyl ether | Butyl | 124.5 | |||
| Methoxyethoxymethyl ether | 124.57 | 3970-21-6 | 50-52°C @13 mmHg | ||
| Representative chloroalkyl ethers [3] | |||||
MOM ethers
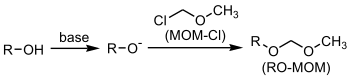
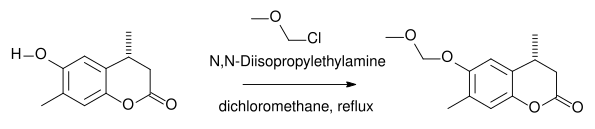
Methyl chloromethyl ether (often abbreviated MOMCl) is used as a protecting group for alcohols. The product formed is a MOM ether. A base such as N,N-diisopropylethylamine is a requirement.
The MOM group can be removed by application of dilute acid.
An example is the protection of a phenol group [4]:
With a benzyl group the protective group becomes a BOM-ether. See also the closely related methylthiomethyl ethers.
With a t-Butyl group the protective group becomes a Bum-ether. The chloride is prepaired from Methyl tert-butyl ether using a photochemical chlorination[5].
With a Methoxyethoxyl group the protective group becomes a MEM-ether. This ether is much more stable than the MOM ether to hydrolysis.
References
- ^ bis(Chloromethyl) Ether and Technical-Grade Chloromethyl Methyl Ether CAS Nos. 542-88-1 and 107-30-2 Report on carcinogens, eleventh edition
- ^ Bis(Chloromethyl) ether Safety Data Sheet Division of Occupational Health and Safety US National Institutes of Health LInk
- ^ www.sigmaaldrich.com
- ^ Enantioselective total synthesis of (2)-heliannuol A Hidetoshi Kishuku, Mitsuru Shindo and Kozo Shishido Chem. Commun., 2003, 350–351 Article link
- ^ Protection chemistry Professor Tore Benneche, University of Oslo