Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
| Dihydroorotate oxidase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase monomer + inhibitor, Human | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.3.5.2 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9029-03-2 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
 Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase from E. coli | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | DHO_dh | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01180 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001295 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00708 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1dor / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 56 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1uum | ||||||||
| CDD | cd02810 | ||||||||
| Membranome | 250 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | DHODH | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 1723 | ||||||
| HGNC | 2867 | ||||||
| OMIM | 126064 | ||||||
| PDB | 1D3G | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_001361 | ||||||
| UniProt | Q02127 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| EC number | 1.3.3.1 | ||||||
| Locus | Chr. 16 q22 | ||||||
| |||||||
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DHODH gene on chromosome 16. The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the fourth enzymatic step, the ubiquinone-mediated oxidation of dihydroorotate to orotate, in de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. This protein is a mitochondrial protein located on the outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM).[1] Inhibitors of this enzyme are used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.[2]
Structure
[edit]DHODH can vary in cofactor content, oligomeric state, subcellular localization, and membrane association. An overall sequence alignment of these DHODH variants presents two classes of DHODHs: the cytosolic Class 1 and the membrane-bound Class 2. In Class 1 DHODH, a basic cysteine residue catalyzes the oxidation reaction, whereas in Class 2, the serine serves this catalytic function. Structurally, Class 1 DHODHs can also be divided into two subclasses, one of which forms homodimers and uses fumarate as its electron acceptor, and the other which forms heterotetramers and uses NAD+ as its electron acceptor. This second subclass contains an addition subunit (PyrK) containing an iron-sulfur cluster and a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). Meanwhile, Class 2 DHODHs use coenzyme Q/ubiquinones for their oxidant.[2]
In higher eukaryotes, this class of DHODH contains an N-terminal bipartite signal comprising a cationic, amphipathic mitochondrial targeting sequence of about 30 residues and a hydrophobic transmembrane sequence. The targeting sequence is responsible for this protein's localization to the IMM, possibly from recruiting the import apparatus and mediating ΔΨ-driven transport across the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes, while the transmembrane sequence is essential for its insertion into the IMM.[2][3] This sequence is adjacent to a pair of α-helices, α1 and α2, which are connected by a short loop. Together, this pair forms a hydrophobic funnel that is suggested to serve as the insertion site for ubiquinone, in conjunction with the FMN binding cavity at the C-terminal.[2] The two terminal domains are directly connected by an extended loop. The C-terminal domain is the larger of the two and folds into a conserved α/β-barrel structure with a core of eight parallel β-strands surrounded by eight α helices.[2][4]
Function
[edit]Human DHODH is a ubiquitous FMN flavoprotein. In bacteria (gene pyrD), it is located on the inner side of the cytosolic membrane. In some yeasts, such as in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (gene URA1), it is a cytosolic protein, whereas, in other eukaryotes, it is found in the mitochondria.[5] It is also the only enzyme in the pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway located in the mitochondria rather than the cytosol.[4]
As an enzyme associated with the electron transport chain, DHODH links mitochondrial bioenergetics, cell proliferation, ROS production, and apoptosis in certain cell types. DHODH depletion also resulted in increased ROS production, decreased membrane potential and cell growth retardation.[4] Also, due to its role in DNA synthesis, inhibition of DHODH may provide a means to regulate transcriptional elongation.[6]
Mechanism
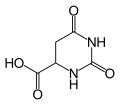
[edit]In mammalian species, DHODH catalyzes the fourth step in de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis, which involves the ubiquinone-mediated oxidation of dihydroorotate to orotate and the reduction of FMN to dihydroflavin mononucleotide (FMNH2):
- (S)-dihydroorotate + O2 orotate + H2O2
-
Orotic acid. Note the double bond in the ring.
The particular mechanism for the dehydrogenation of dihydroorotic acid by DHODH differs between the two classes of DHODH. Class 1 DHODHs follow a concerted mechanism, in which the two C–H bonds of dihydroorotic acid break in concert. Class 2 DHODHs follow a stepwise mechanism, in which the breaking of the C–H bonds precedes the equilibration of iminium into orotic acid.[2]
Inhibitors
[edit]Clinical significance
[edit]The immunomodulatory drugs teriflunomide and leflunomide have been shown to inhibit DHODH. Human DHODH has two domains: an alpha/beta-barrel domain containing the active site and an alpha-helical domain that forms the opening of a tunnel leading to the active site. Leflunomide has been shown to bind in this tunnel.[7] Leflunomide is being used for treatment of rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, as well as multiple sclerosis.[2][7] Its immunosuppressive effects have been attributed to the depletion of the pyrimidine supply for T cells or to more complex interferon or interleukin-mediated pathways, but nonetheless require further research.[2]
Additionally, DHODH may play a role in retinoid N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide (4HPR)-mediated cancer suppression. Inhibition of DHODH activity with teriflunomide or expression with RNA interference resulted in reduced ROS generation in, and thus apoptosis of, transformed skin and prostate epithelial cells.[8]
Mutations in this gene have been shown to cause Miller syndrome, also known as Genee-Wiedemann syndrome, Wildervanck-Smith syndrome or post-axial acrofacial dystosis.[9][10]
Interactions
[edit]DHODH binds to its FMN cofactor in conjunction with ubiquinone to catalyze the oxidation of dihydroorotate to orotate.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ "Entrez Gene: DHODH dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone)".
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Munier-Lehmann H, Vidalain PO, Tangy F, Janin YL (Apr 2013). "On dihydroorotate dehydrogenases and their inhibitors and uses". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 56 (8): 3148–67. doi:10.1021/jm301848w. PMID 23452331.
- ^ Rawls J, Knecht W, Diekert K, Lill R, Löffler M (Apr 2000). "Requirements for the mitochondrial import and localization of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase". European Journal of Biochemistry. 267 (7): 2079–87. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01213.x. PMID 10727948.
- ^ a b c Fang J, Uchiumi T, Yagi M, Matsumoto S, Amamoto R, Takazaki S, et al. (5 February 2013). "Dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase is physically associated with the respiratory complex and its loss leads to mitochondrial dysfunction". Bioscience Reports. 33 (2): e00021. doi:10.1042/BSR20120097. PMC 3564035. PMID 23216091.
- ^ Nagy M, Lacroute F, Thomas D (Oct 1992). "Divergent evolution of pyrimidine biosynthesis between anaerobic and aerobic yeasts". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 89 (19): 8966–70. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.8966N. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.19.8966. PMC 50045. PMID 1409592.
- ^ White RM, Cech J, Ratanasirintrawoot S, Lin CY, Rahl PB, Burke CJ, et al. (Mar 2011). "DHODH modulates transcriptional elongation in the neural crest and melanoma". Nature. 471 (7339): 518–22. Bibcode:2011Natur.471..518W. doi:10.1038/nature09882. PMC 3759979. PMID 21430780.
- ^ a b Liu S, Neidhardt EA, Grossman TH, Ocain T, Clardy J (Jan 2000). "Structures of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in complex with antiproliferative agents". Structure. 8 (1): 25–33. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00077-0. PMID 10673429.
- ^ Hail N, Chen P, Kepa JJ, Bushman LR, Shearn C (Jul 2010). "Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase is required for N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 49 (1): 109–16. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.04.006. PMC 2875309. PMID 20399851.
- ^ Ng SB, Buckingham KJ, Lee C, Bigham AW, Tabor HK, Dent KM, et al. (Jan 2010). "Exome sequencing identifies the cause of a mendelian disorder". Nature Genetics. 42 (1): 30–5. doi:10.1038/ng.499. PMC 2847889. PMID 19915526.
- ^ Fang J, Uchiumi T, Yagi M, Matsumoto S, Amamoto R, Saito T, et al. (Dec 2012). "Protein instability and functional defects caused by mutations of dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase in Miller syndrome patients". Bioscience Reports. 32 (6): 631–9. doi:10.1042/BSR20120046. PMC 3497730. PMID 22967083.
Further reading
[edit]- Rowland P, Björnberg O, Nielsen FS, Jensen KF, Larsen S (Jun 1998). "The crystal structure of Lactococcus lactis dihydroorotate dehydrogenase A complexed with the enzyme reaction product throws light on its enzymatic function". Protein Science. 7 (6): 1269–79. doi:10.1002/pro.5560070601. PMC 2144028. PMID 9655329. Archived from the original on 2008-12-01.
External links
[edit]- dihydroorotate+dehydrogenase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)