Synthesizer: Difference between revisions
Popcornfud (talk | contribs) |
Popcornfud (talk | contribs) delete more uncited OR |
||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
| work = Jarrography – The ultimate Jean Michel Jarre discography |
| work = Jarrography – The ultimate Jean Michel Jarre discography |
||
}}</ref> [[Roland Jupiter-8]], [[Oberheim OB-8]], [[Roland SH-101]], [[Sequential Circuits Six-Trak]] and [[Korg Polysix]]. A famous example can be heard on [[Duran Duran]]'s song "[[Rio (song)|Rio]]", in which the arpeggiator on a [[Roland Jupiter-4]] plays a C minor chord in random mode. They fell out of favor by the latter part of the 1980s and early 1990s and were absent from the most popular synthesizers of the period but a resurgence of interest in [[analog synthesizer]]s during the 1990s, and the use of rapid-fire arpeggios in several popular [[dance music|dance]] hits, brought with it a resurgence. |
}}</ref> [[Roland Jupiter-8]], [[Oberheim OB-8]], [[Roland SH-101]], [[Sequential Circuits Six-Trak]] and [[Korg Polysix]]. A famous example can be heard on [[Duran Duran]]'s song "[[Rio (song)|Rio]]", in which the arpeggiator on a [[Roland Jupiter-4]] plays a C minor chord in random mode. They fell out of favor by the latter part of the 1980s and early 1990s and were absent from the most popular synthesizers of the period but a resurgence of interest in [[analog synthesizer]]s during the 1990s, and the use of rapid-fire arpeggios in several popular [[dance music|dance]] hits, brought with it a resurgence. |
||
== Patch == |
|||
{{multiple image |align=right |
|||
|image1=Oberheim 4 voice.jpg|width1=220|caption1=One of the earliest patch memory (bottom left) on [[Oberheim polyphonic|Oberheim Four-voice]] (1975/1976) |
|||
}} |
|||
A synthesizer '''patch''' (some manufacturers chose the term '''program''') is a sound setting. [[Modular synthesizer]]s used cables ("[[patch cord]]s") to connect the different sound modules together. Since these machines had no [[memory (computers)|memory]] to save settings, musicians wrote down the locations of the patch cables and knob positions on a "patch sheet" (which usually showed a diagram of the synthesizer). Ever since, an overall sound setting for any type of synthesizer has been referred to as a patch. |
|||
<!-- ToDo: added description about "preset synthesizer": ARP Soloist in 1970 and Pro Soloist in 1972, ARP String Ensemble by Eminent/Solina in 1974, Moog minitmoog & Satelite, etc. --> |
|||
In mid–late 1970s, patch memory (allowing storage and loading of 'patches' or 'programs') began to appear in synths like the [[Oberheim polyphonic|Oberheim Four-voice]] (1975/1976)<ref name=Oberheim1976Ad> |
|||
{{cite journal |
|||
| title = Oberheim Polyphonic Synthesizer Programmer (ad) |
|||
| url = http://retrosynthads.blogspot.com/2010/02/oberheim-polyphonic-synthesizer.html |
|||
| journal = Contemporary Keyboard Magazine |
|||
| issue = September/October 1976 |
|||
| page = 19 |
|||
| medium = ad |
|||
| date = 15 February 2010 |
|||
}}</ref> <!-- , [[Sequential Circuits]]'s Model 700 Programmer (1977) --> and [[Sequential Circuits Prophet-5]] (1977/1978). After [[MIDI]] was introduced in 1983, more and more synthesizers could import or export patches via MIDI ''SYSEX'' commands. When a synthesizer patch is uploaded to a personal computer that has patch editing software installed, the user can alter the parameters of the patch and download it back to the synthesizer. Because there is no standard patch language, it is rare that a patch generated on one synthesizer can be used on a different model. However, sometimes manufacturers design a family of synthesizers to be compatible. |
|||
== Control interfaces == |
== Control interfaces == |
||
Revision as of 23:44, 15 November 2019
This article possibly contains original research. (December 2018) |

A synthesizer or synthesiser (often abbreviated to synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals that may be converted to sound. Synthesizers may imitate traditional musical instruments such as piano, flute, vocals, or natural sounds such as ocean waves; or generate novel electronic timbres. They are often played with a musical keyboard, but they can be controlled via a variety of other devices, including music sequencers, instrument controllers, fingerboards, guitar synthesizers, wind controllers, and electronic drums. Synthesizers without built-in controllers are often called sound modules, and are controlled via USB, MIDI or CV/gate using a controller device, often a MIDI keyboard or other controller.
Synthesizers use various methods to generate electronic signals (sounds). Among the most popular waveform synthesis techniques are subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis, wavetable synthesis, frequency modulation synthesis, phase distortion synthesis, physical modeling synthesis and sample-based synthesis.
Synthesizers were first used in pop music in the 1960s. In the late 1970s, synths were used in progressive rock, pop and disco. In the 1980s, the invention of the relatively inexpensive Yamaha DX7 synth made digital synthesizers widely available. 1980s pop and dance music often made heavy use of synthesizers. Synthesizers are used in genres such as pop, hip hop, metal, rock, dance, and contemporary classical music.
History
Precursors
As electricity became more widely available, the early 20th century saw the invention of electronic musical instruments including the Telharmonium, Trautonium, Ondes Martenot, and theremin.[1] The Hammond organ, introduced in 1935, was the first electronic instrument to enjoy wide success.[1] In 1948, the Canadian engineer Hugh Le Caine completed the electronic sackbut, a precursor to voltage-controlled synthesizers, with keyboard sensitivity allowing for vibrato, glissando, and attack control.[1]
In 1957, Harry Olson and Herbert Belar completed the RCA Mark II Sound Synthesizer at the RCA laboratories in Princeton, New Jersey. The instrument read punched paper tape that controlled an analog synthesizer containing 750 vacuum tubes. It was acquired by the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center and used almost exclusively by Milton Babbitt, a composer at Princeton University.[1]

1960s – 1970s: Early years
The authors of Analog Days define "the early years of the synthesizer" as between 1964 and the mid-1970s, beginning with the debut of the Moog synthesizer.[2]: 7 Designed by American engineer Robert Moog, the Moog synthesizer was composed of separate modules which created and shaped sounds, connected by patch cords.[3] Whereas previous instruments had created sound from hundreds of vacuum tubes, Moog developed a means of controlling pitch and loudness through voltage, the voltage-controlled oscillator.[4] This, along with devices such as envelopes, noise generators, filters, and sequencers, became standards in the synthesizer market.[5][2]
Around the same period, American engineer Don Buchla created the Buchla Modular Electronic Music System.[6] Instead of a conventional keyboard, Buchla's system used touchplates which transmitted control voltages depending on finger position and force.[2] However, the Moog's keyboard made it more accessible and marketable to musicians, and keyboards became the standard means of controlling synthesizers.[2] In 1970, Moog launched a cheaper, smaller synthesizer, the Minimoog.[7][8] The Minimoog was the first synthesizer sold in music stores,[2] and was more practical for live performance; it standardized the concept of synthesizers as self-contained instruments with built-in keyboards.[9][10]

After retail stores started selling synthesizers in 1971, other synthesizer companies were established, including ARP in the US and EMS in the UK.[2] ARP's products included the ARP 2600, which folded into a carrying case and had built-in speakers, and the Odyssey, a rival to the Minimoog.[2] By the mid-1970s, ARP was the world's largest synthesizer manufacturer.[2] The less expensive EMS synthesizers were used by European art rock and progressive rock acts including Brian Eno and Pink Floyd.[2]
Early synthesizers were monophonic, meaning they could only play one note at a time. Some of the earliest commercial polyphonic synthesizers were created by American engineer Tom Oberheim,[6] such as the OB-X (1979).[2] In 1978, the American company Sequential Circuits released the Prophet-5, first fully programmable polyphonic synthesizer.[5]: 93 The Prophet-5 used microprocessors for patch memory, allowing users to store sounds.[11] This overcame a major difficulty in previous synthesizers, which required users to adjust cables and knobs to change sounds, with no guarantee of exactly recreating a sound.[2] This facilitated a move from synthesizers creating unpredictable sounds to producing "a standard package of familiar sounds".[2]: 385 Along with the Minimoog, the success of the Prophet-5 aided the shift of synthesizers away from large modular units and towards smaller keyboard instruments.[12]
1980s: Market growth and digital technology
The synthesizer market grew dramatically in the 1980s.[5]: 57 1982 saw the introduction of MIDI, a standardized means of synchronizing synthesizers and other electronic instruments; it remains an industry standard.[13]
An influential sampling synthesizer, the Fairlight CMI, was released in 1979 and was widely used throughout the 1980s.[11] The Fairlight had the ability to record and play back samples (prerecorded sounds) at different pitches.[14] Its high price made it inaccessible to amateurs, but it was adopted by high-profile pop musicians including Kate Bush and Peter Gabriel. The success of the Fairlight drove competition, improving sampling technology and lowering prices;[14] early competitors included the E-mu Emulator in 1981[14] and the Akai S-series in 1985.[15]

In 1983, Yamaha released the first commercially successful digital synthesizer, the Yamaha DX7.[16] Based on frequency modulation synthesis, developed by Stanford University engineer John Chowning,[17] the DX7 remains one of the bestselling synthesizers in history[16][18] and was the first synthesizer to earn six-digit sales figures.[5]: 57 It was widely used in 1980s pop music.[19] Compared to the "warm" and "fuzzy" sounds of analog synthesis, digital synthesizers are characterized by their "harsh", "glassy" and "chilly" sounds.[20]
The success of the DX7 led to competing digital synthesizers from companies including Roland, which released the D-50 in 1987 to success. The D-50 blended Roland's linear arithmetic algorithm with samples, and was the first mass-produced synthesizer with built-in effects such as delay, reverb and chorus.[5]: 63 In 1988, the Japanese manufacturer Korg released the M1, a digital workstation featuring sampled transients and loops, built-in effects, and digital synthesis.[21] With over 250,000 units sold, it remains the bestselling synthesizer in history.[21]
Digital synthesizers typically contained preset sounds emulating acoustic instruments, and were more difficult to customize than analog synthesizers, with complex algorithms controlled with menus and buttons.[2] The success of digital synthesizers and samplers led to a downturn in interest in analog synthesizers.[5]: 59
1990s – present: Software synthesizers and analog revival
1997 saw the release of ReBirth by Propellerhead Software and Reality by Seer Systems, the first software synthesizers that could be played in real time via MIDI.[5] In 1999, an update to the music software Cubase allowed users to run software instruments (including synthesizers) as plug-ins, triggering a "torrent" of new software instruments.[22] Propellerhead's Reason, released in 2000, offered users a virtual "rack" of recognisable studio equipment.[22] According to Sound on Sound in 2014, "computer emulations of analog synth architecture are frequently indiscernible from the real thing".[23] Whereas once they had filled rooms, synthesizers now can be embedded on single microchips in any electronic device.[2]
The market for patchable and modular synthesizers rebounded in the late 1990s.[5]: 32 In the 2000s, older analog synthesizers regained popularity, with old equipment sometimes selling for much more than its original price.[23] In the 2010s, new, affordable analog synthesizers were introduced by companies including Moog, Korg, Arturia, and Dave Smith Instruments. Sound on Sound credited the renewed interest to the appeal of imperfect "organic" sounds and simpler interfaces, and to modern surface-mount technology making analog synthesizers cheaper and faster to manufacture.[23]
Impact

When synthesizers emerged in the 1960s, they were viewed as avant-garde, valued by the 1960s psychedelic and counter-cultural scenes for their ability to make new sounds, but with little perceived commercial potential. Switched-On Bach (1968), an bestselling album of Bach compositions arranged for Moog by Wendy Carlos, demonstrated that synthesizers could be more than "random noise machines",[3] taking them to the mainstream.[2] The Moog was adopted by acts including the Doors, the Grateful Dead, the Rolling Stones, the Beatles, and Keith Emerson.[24] Emerson was the first major rock musician to perform with the Moog synthesizer and it became a trademark of his performances, helping take his band Emerson, Lake & Palmer to global stardom; according to Analog Days, the likes of Emerson, with his Moog performances, "did for the keyboard what Jimi Hendrix did for the guitar".[2]: 200
The portable Minimoog (1970), much smaller than the modular synthesizers before it, made synthesizers more common in live performance.[10] The Minimoog took a place in mainstream black music, most notably in the work of Stevie Wonder,[2] and in jazz, such as the work of Sun Ra.[25] It was also used by electronic artists such as Kraftwerk, who used it on their albums Autobahn (1974) and The Man-Machine (1978), and later by Tangerine Dream, Klaus Schulze, and Gary Numan.[25] In the late 1970s and the early 1980s, it was widely used in the emerging disco genre by artists including Abba and Giorgio Moroder.[25]
Early synthesizers could only play one note at a time, making them suitable for basslines, leads and solos.[25] With the rise of polyphonic synthesizers in the 70s and 80s, the "the keyboard in rock once more started to revert to the background, to be used for fills and atmosphere rather than for soloing".[2]: 207 Sampling, introduced with the Fairlight synthesizer in 1979, has influenced all genres of music[4] and had a major influence on the development of electronic and hip hop music.[26][27]
In the 1970s, electronic music composers such as Jean Michel Jarre[28] and Isao Tomita[29][30][31] released successful synthesizer-led instrumental albums. This helped influence the emergence of synthpop, a subgenre of new wave, from the late 1970s to the early 1980s. The work of German krautrock bands such as Kraftwerk[32] and Tangerine Dream, British acts such as John Foxx, Gary Numan and David Bowie, African-American acts such as George Clinton and Zapp, and Japanese electronic acts such as Yellow Magic Orchestra and Kitaro were influential in the development of the genre.[33] Gary Numan's 1979 hits "Are 'Friends' Electric?" and "Cars" made heavy use of synthesizers.[34][35] OMD's "Enola Gay" (1980) used distinctive electronic percussion and a synthesized melody. Soft Cell used a synthesized melody on their 1981 hit "Tainted Love".[33] Nick Rhodes, keyboardist of Duran Duran, used various synthesizers including the Roland Jupiter-4 and Jupiter-8.[36] Chart hits include Depeche Mode's "Just Can't Get Enough" (1981),[33] the Human League's "Don't You Want Me"[37] and works by Ultravox.[33]
In the 1980s, digital synthesizers were widely used in pop music.[19] The Yamaha DX7, released in 1983, became a pop staple, used on songs by A-ha, Kenny Loggins, Kool & the Gang.[20] Its "E PIANO 1" preset became particularly famous,[20] especially for power ballads,[38] and was used by artists including Whitney Houston, Chicago,[38] Prince,[19] Phil Collins, Luther Vandross, Billy Ocean,[20] and Celine Dion.[39] The Roland TB-303 (1981), in conjunction with the Roland TR-808 and TR-909 drum machines, became a foundation of electronic dance music genres such as house and techno when producers acquired cheap second-hand units later in the decade.[40] Korg M1 presets were widely used in 1990s house music, beginning with Madonna's 1990 single "Vogue".[41]
Today, the synthesizer is used in every genre of music.[2]: 7 It is considered by the authors of Analog Days "the only innovation that can stand alongside the electric guitar as a great new instrument of the age of electricity ... Both led to new forms of music, and both had massive popular appeal."[2]: 7 The authors draw a connection to the synthesizer's origins in 1960s psychedelia to the raves and British "second summer of love" of the 1980s and the club scenes of the 1990s and 2000s.[2]: 321 According to Fact in 2016, "The synthesizer is as important, and as ubiquitous, in modern music today as the human voice."[20] It is one of the most important instruments in the music industry.[33]
Film and television
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2019) |
Synthesizers are common in film and television soundtracks.[2]: 273 ARP synthesizers, for example, were used to create sound effects for the 1977 science fiction films Close Encounters of the Third Kind[2]: 9 and Star Wars, including the "voice" of the robot R2-D2.[2]: 273 In the 70s and 80s, synthesizers were used in the scores for thrillers and horror films including A Clockwork Orange (1971), Apocalypse Now (1979), The Fog (1980) and Manhunter (1986).[42] They were also used to create themes for television shows including Knight Rider (1982), Twin Peaks (1990) and Stranger Things (2016).[42]
Jobs
The rise of the synthesizer led to major changes in music industry jobs, comparable to the earlier arrival of sound in film, which put live musicians accompanying silent films out of work.[43] With its ability to imitate instruments such as strings and horns, the synthesizer threatened the jobs of session musicians. For a period, the Moog was banned from use in commercial work, a restriction negotiated by the American Federation of Musicians (AFM).[2] Robert Moog felt that the AFM had not realized that the synthesizer was an instrument to be learnt and mastered like any other, and instead imagined that "all the sounds that musicians could make somehow existed in the Moog — all you had to do was push a button that said 'Jascha Heifetz' and out would come the most fantastic violin player!"[44]
Musician Walter Sear persuaded the AFM that the synthesizer demanded skill, and the category of "synthesizer player" was accepted into the union; however, players were still subject to "suspicion and hostility" for several years.[2]: 149 In 1982, following a tour by Barry Manilow using synthesizers instead of an orchestra, the British Musicians' Union attempted to ban synthesizers, attracting controversy.[45] That decade, a few musicians skilled at programming the popular Yamaha DX7 found employment creating sounds for other acts, creating the "synthesizer programmer" occupation.[46]
Sound synthesis
Additive synthesis builds sounds by combining several waveforms, usually sine waves, into a composite sound.[5]


Subtractive synthesis uses oscillators to generate waveforms, then shapes them with filters to remove or boost specific frequencies.[5]

Frequency modulation (FM) synthesis creates sounds by modulating one waveform with the frequency of another; the resulting complex waveform can, in turn, be used to modulate another, and this another, and so on. FM synthesis can imitate acoustic sounds such as piano, strings and organs.[47]
Phase distortion synthesis is a method implemented on Casio CZ synthesizers. It replaces the traditional analog waveform with a choice of several digital waveforms which are more complex than the standard square, sine, and sawtooth waves. This waveform is routed to a digital filter and digital amplifier, each modulated by an eight-stage envelope. The sound can then be further modified with ring modulation or noise modulation.[48]

Physical modelling synthesis is the synthesis of sound by using a set of equations and algorithms to simulate each sonic characteristic of an instrument, starting with the harmonics that make up the tone itself, then adding the sound of the resonator, the instrument body, etc., until the sound realistically approximates the desired instrument. When an initial set of parameters is run through the physical simulation, the simulated sound is generated. Although physical modeling was not a new concept in acoustics and synthesis, it was not until the development of the Karplus-Strong algorithm and the increase in DSP power in the late 1980s that commercial implementations became feasible. The quality and speed of physical modeling on computers improves with higher processing power.[citation needed]

Linear arithmetic synthesis is a form of synthesis that utilizes PCM samples for the attack of a waveform, and subtractive synthesis for the rest of the envelope. This type of synthesis bridges the gap between the older subtractive synthesis and the newer sample-based synthesis at a time where PCM samples would take up a substantial amount of the memory allotted. The first synthesizer to debut with this form of synthesis was the Roland D-50 in 1987.[citation needed]
Sample-based synthesis involves digitally recording a short snippet of sound from a real instrument or other source and then playing it back at different speeds to produce different pitches. A sample can be played as a one shot, used often for percussion or short duration sounds, or it can be looped, which allows the tone to sustain or repeat as long as the note is held. Samplers usually include a filter, envelope generators, and other controls for further manipulation of the sound. Virtual samplers that store the samples on a hard drive make it possible for the sounds of an entire orchestra, including multiple articulations of each instrument, to be accessed from a sample library.. See also Wavetable synthesis, Vector synthesis.[citation needed]
Analysis/resynthesis is a form of synthesis that uses a series of bandpass filters or Fourier transforms to analyze the harmonic content of a sound. The results are then used to resynthesize the sound using a band of oscillators. The vocoder, linear predictive coding, and some forms of speech synthesis are based on analysis/resynthesis.[citation needed]
Components
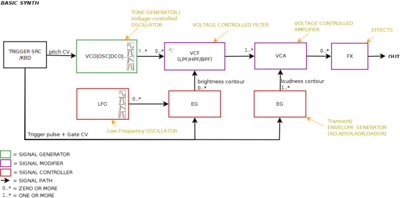
Synthesizers generate sound through various analogue and digital techniques. Early synthesizers were analog hardware based but many modern synthesizers use a combination of DSP software and hardware or else are purely software-based (see softsynth). Digital synthesizers often emulate classic analog designs. Sound is controllable by the operator by means of circuits or virtual stages that may include:
- Oscillators typically produce waveforms (such as sawtooth, sine, or pulse waves) with different timbres.[5]
- Low-frequency oscillators (LFOs) produce waveforms used to modulate parameters, such as the pitch of oscillators (producing vibrato).[5]
- Voltage-controlled filter (VCFs) – "shape" the sound generated by the oscillators in the frequency domain, often under the control of an envelope or LFO. These are essential to subtractive synthesis.
- Envelope generators – provide envelope modulation to "shape" the volume or harmonic content of the produced note in the time domain with the principal parameters being attack, decay, sustain and release. These are used in most forms of synthesis. ADSR control is provided by envelope generators.
- Voltage-controlled amplifiers (VCAs) control the volume or gain of the audio signal. VCAs can be modulated by other components, such as LFOs and envelopes.[5]
- After the signal generated by one (or a mix of more) VCOs has been modified by filters and LFOs, and its waveform has been shaped (contoured) by an ADSR envelope generator, it then passes on to one or more voltage-controlled amplifiers (VCAs). A VCA is a preamp that boosts (amplifies) the electronic signal before passing it on to an external or built-in power amplifier, as well as a means to control its amplitude (volume) using an attenuator. The gain of the VCA is affected by a control voltage (CV), coming from an envelope generator, an LFO, the keyboard or some other source.[49]
Filter
Electronic filters are particularly important in subtractive synthesis, being designed to pass some frequency regions through unattenuated while significantly attenuating ("subtracting") others. The low-pass filter is most frequently used, but band-pass filters, band-reject filters and high-pass filters are also sometimes available.
The filter may be controlled with a second ADSR envelope. An "envelope modulation" ("env mod") parameter on many synthesizers with filter envelopes determines how much the envelope affects the filter. If turned all the way down, the filter produces a flat sound with no envelope. When turned up the envelope becomes more noticeable, expanding the minimum and maximum range of the filter. The envelope applied on the filter helps the sound designer generating long notes or short notes by moving the parameters up and down such as decay, sustain and finally release. For instance by using a short decay with no sustain, the sound generated is commonly known as a stab. Sound designers may prefer shaping the sound with filter instead of volume.
Envelope

Envelopes control how sounds change over time. They may control parameters such as amplitude (volume), filters (frequencies), or pitch. The most common envelope is the ADSR (Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release) envelope:[5]
- Attack time is the time taken for initial run-up of level from nil to peak, beginning when the note is triggered.
- Decay time is the time taken for the subsequent run down from the attack level to the designated sustain level.
- Sustain level is the level during the main sequence of the sound's duration, until the key is released.
- Release time is the time taken for the level to decay from the sustain level to zero after the key is released.
The "attack" and "decay" of a sound have a great effect on the instrument's sonic character.[50]
LFO
A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) generates an electronic signal, usually below 20 Hz. LFO signals create a periodic control signal or sweep, often used in vibrato, tremolo and other effects. In certain genres of electronic music, the LFO signal can control the cutoff frequency of a VCF to make a rhythmic wah-wah sound, or the signature dubstep wobble bass.
Arpeggiator
An arpeggiator (arp) is a feature available on several synthesizers that automatically steps through a sequence of notes based on an input chord, thus creating an arpeggio. The notes can often be transmitted to a MIDI sequencer for recording and further editing. An arpeggiator may have controls for speed, range, and order in which the notes play; upwards, downwards, or in a random order. More advanced arpeggiators allow the user to step through a pre-programmed complex sequence of notes, or play several arpeggios at once. Some allow a pattern sustained after releasing keys: in this way, a sequence of arpeggio patterns may be built up over time by pressing several keys one after the other. Arpeggiators are also commonly found in software sequencers. Some arpeggiators/sequencers expand features into a full phrase sequencer, which allows the user to trigger complex, multi-track blocks of sequenced data from a keyboard or input device, typically synchronized with the tempo of the master clock.
Arpeggiators seem to have grown from the accompaniment system used in electronic organs in the mid-1960s to the mid-1970s.[51] They were also commonly fitted to keyboard instruments through the late 1970s and early 1980s. Notable examples are the RMI Harmonic Synthesizer (1974),[52] Roland Jupiter-8, Oberheim OB-8, Roland SH-101, Sequential Circuits Six-Trak and Korg Polysix. A famous example can be heard on Duran Duran's song "Rio", in which the arpeggiator on a Roland Jupiter-4 plays a C minor chord in random mode. They fell out of favor by the latter part of the 1980s and early 1990s and were absent from the most popular synthesizers of the period but a resurgence of interest in analog synthesizers during the 1990s, and the use of rapid-fire arpeggios in several popular dance hits, brought with it a resurgence.
Control interfaces
Modern synthesizers often look like small pianos, though with many additional knob and button controls. These are integrated controllers, where the sound synthesis electronics are integrated into the same package as the controller. However, many early synthesizers were modular and keyboardless, while most modern synthesizers may be controlled via MIDI, allowing other means of playing such as:
- Fingerboards (ribbon controllers) and touchpads
- Wind controllers
- Guitar-style interfaces
- Drum pads
- Music sequencers
- Non-contact interfaces akin to theremins
- Tangible interfaces like a Reactable, AudioCubes
- Various auxiliary input device including: wheels for pitch bend and modulation, footpedals for expression and sustain, breath controllers, beam controllers, etc.
Fingerboard controller
A ribbon controller or other violin-like user interface may be used to control synthesizer parameters. The idea dates to Léon Theremin's 1922 first concept[53] and his 1932 Fingerboard Theremin and Keyboard Theremin,[54][55] Maurice Martenot's 1928 Ondes Martenot (sliding a metal ring),[56] Friedrich Trautwein's 1929 Trautonium (finger pressure), and was also later utilized by Robert Moog.[57][58][59] The ribbon controller has no moving parts. Instead, a finger pressed down and moved along it creates an electrical contact at some point along a pair of thin, flexible longitudinal strips whose electric potential varies from one end to the other. Older fingerboards used a long wire pressed to a resistive plate. A ribbon controller is similar to a touchpad, but a ribbon controller only registers linear motion. Although it may be used to operate any parameter that is affected by control voltages, a ribbon controller is most commonly associated with pitch bending.
Fingerboard-controlled instruments include the Trautonium (1929), Hellertion (1929) and Heliophon (1936),[60][61][62] Electro-Theremin (Tannerin, late 1950s), Persephone (2004), and the Swarmatron (2004). A ribbon controller is used as an additional controller in the Yamaha CS-80 and CS-60, the Korg Prophecy and Korg Trinity series, the Kurzweil synthesizers, Moog synthesizers, and others.
Rock musician Keith Emerson used it with the Moog modular synthesizer from 1970 onward. In the late 1980s, keyboards in the synth lab at Berklee College of Music were equipped with membrane thin ribbon style controllers that output MIDI. Such ribbon controllers can serve as a main MIDI controller instead of a keyboard, as with the Continuum instrument.
Wind controllers
Wind controllers (and wind synthesizers) are convenient for woodwind and brass players, being designed to imitate those instruments. These are usually either analog or MIDI controllers, and sometimes include their own built-in sound modules (synthesizers). In addition to the follow of key arrangements and fingering, the controllers have breath-operated pressure transducers, and may have gate extractors, velocity sensors, and bite sensors. Saxophone-style controllers have included the Lyricon, and products by Yamaha, Akai, and Casio. The mouthpieces range from alto clarinet to alto saxophone sizes. The Eigenharp, a controller similar in style to a bassoon, was released by Eigenlabs in 2009. Melodica and recorder-style controllers have included the Martinetta (1975)[63] and Variophon (1980),[64] and Josef Zawinul's custom Korg Pepe.[65] A harmonica-style interface was the Millionizer 2000 (c. 1983).[66]
MIDI control
Synthesizers became easier to integrate and synchronize with other electronic instruments and controllers with the introduction of Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) in 1983.[67] First proposed in 1981 by engineer Dave Smith of Sequential Circuits, the MIDI standard was developed by a consortium now known as the MIDI Manufacturers Association.[68] MIDI is an opto-isolated serial interface and communication protocol.[68] It provides for the transmission from one device or instrument to another of real-time performance data. This data includes note events, commands for the selection of instrument presets (i.e. sounds, or programs or patches, previously stored in the instrument's memory), the control of performance-related parameters such as volume, effects levels and the like, as well as synchronization, transport control and other types of data. MIDI interfaces are now almost ubiquitous on music equipment and are commonly available on personal computers (PCs).[68]
The General MIDI (GM) software standard was devised in 1991 to serve as a consistent way of describing a set of over 200 sounds (including percussion) available to a PC for playback of musical scores.[69] For the first time, a given MIDI preset consistently produced a specific instrumental sound on any GM-compatible device. The Standard MIDI File (SMF) format (extension .mid) combined MIDI events with delta times – a form of time-stamping – and became a popular standard for exchanging music scores between computers. In the case of SMF playback using integrated synthesizers (as in computers and cell phones), the hardware component of the MIDI interface design is often unneeded.
Open Sound Control (OSC) is another music data specification designed for online networking. In contrast with MIDI, OSC allows thousands of synthesizers or computers to share music performance data over the Internet in realtime.
Recent trends in synthesizer design, particularly the resurgence of modular systems in eurorack, have allowed for a hybrid of MIDI control and control voltage i/o to be found together in many models. (Examples being the Moog Model D reissue, which was enhanced from its original design to offer both MIDI i/o and CV i/o). In these models of MIDI/CV hybrids, it is often possible to send and receive control voltages to control parameters of equipment at the identical time MIDI messages are being sent and received.
Additional examples of MIDI/CV hybrids include models like the Arturia Minibrute, which is able to receive MIDI messages from an external controller and automatically convert the MIDI signal into gate and pitch notes, which it can then send out as control voltage.
Typical roles
Synth lead
In popular music, a synth lead is generally used for playing the main melody of a song, but it is also often used for creating rhythmic or bass effects. Although most commonly heard in electronic dance music, synth leads have been used extensively in hip-hop music since the 1980s and some types of rock songs since the 1970s. Many post-1980s pop music songs use a synth lead to provide a musical hook to sustain the listener's interest throughout a song.
Synth pad
A synth pad is a sustained chord or tone generated by a synthesizer, often employed for background harmony and atmosphere in much the same fashion that a string section is often used in orchestral music and film scores. Typically, a synth pad is performed using whole notes, which are often tied over bar lines. A synth pad sometimes holds the same note while a lead voice sings or plays an entire musical phrase or section. Often, the sounds used for synth pads have a vaguely organ, string, or vocal timbre. During the late 1970s and 1980s, specialized string synthesizers were made that specialized in creating string sounds using the limited technology of the time. Much popular music in the 1980s employed synth pads, this being the time of polyphonic synthesizers, as did the then-new styles of smooth jazz and new-age music. One of many well-known songs from the era to incorporate a synth pad is "West End Girls" by the Pet Shop Boys, who were noted users of the technique.
The main feature of a synth pad is very long attack and decay time with extended sustains. In some instances pulse-width modulation (PWM) using a square wave oscillator can be added to create a "vibrating" sound.
Synth bass
The bass synthesizer (or "bass synth") is used to create sounds in the bass range, from simulations of the electric bass or double bass to distorted, buzz-saw-like artificial bass sounds, by generating and combining signals of different frequencies. Bass synth patches may incorporate a range of sounds and tones, including wavetable-style, analog, and FM-style bass sounds, delay effects, distortion effects, envelope filters. A modern digital synthesizer uses a frequency synthesizer microprocessor component to generate signals of different frequencies. While most bass synths are controlled by electronic keyboards or pedalboards, some performers use an electric bass with MIDI pickups to trigger a bass synthesizer.
In the 1970s miniaturized solid-state components allowed self-contained, portable instruments such as the Moog Taurus, a 13-note pedal keyboard played by the feet. The Moog Taurus was used in live performances by a range of pop, rock, and blues-rock bands. An early use of bass synthesizer was in 1972, on a solo album by John Entwistle (the bassist for The Who), entitled Whistle Rymes. Genesis bass player Mike Rutherford used a Dewtron "Mister Bassman" for the recording of their album Nursery Cryme in August 1971. Stevie Wonder introduced synth bass to a pop audience in the early 1970s, notably on "Superstition" (1972) and "Boogie On Reggae Woman" (1974). In 1977 Parliament's funk single "Flash Light" used the bass synthesizer. Lou Reed, widely considered a pioneer of electric guitar textures, played bass synthesizer on the song "Families", from his 1979 album The Bells.
Following the availability of programmable music sequencers such as the Synclavier and Roland MC-8 Microcomposer in the late 1970s, bass synths began incorporating sequencers in the early 1980s. The first bass synthesizer with a sequencer was the Firstman SQ-01.[71][72] It was originally released in 1980 by Hillwood/Firstman, a Japanese synthesizer company founded in 1972 by Kazuo Morioka (who later worked for Akai in the early 1980s), and was then released by Multivox for North America in 1981.[73][74][75]
In 1981, Roland released the Roland TB-303 bass synthesizer. Designed to simulate bass guitars, it was a commercial failure; however, cheap second-hand units were adopted by electronic musicians, and its "squelching" sound became a foundation of electronic dance music genres such as house and techno.[76][77]
See also
- Lists
- Various synthesizers
- Related instruments & technologies
- Clavioline (Musitron)
- Electronic keyboard
- Musical instrument
- Music workstation
- Sampler
- Speech synthesis
- Components & technologies
- Music genres
- Notable works
References
- ^ a b c d Chadabe, Joel (14 September 2011). "The Electronic Century Part I: Beginnings". Electronic Musician. Archived from the original on 14 September 2011. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z Pinch, Trevor; Trocco, Frank (2004). Analog Days: The Invention and Impact of the Moog Synthesizer. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01617-0.
- ^ a b Kozinn, Allan. "Robert Moog, Creator of Music Synthesizer, Dies at 71". New York Times. Retrieved 3 December 2018.
- ^ a b McNamee, David (28 September 2009). "Hey, what's that sound: Sampler". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Vail, Mark (2014). The Synthesizer. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195394894.
- ^ a b Lee, Sammy (3 July 2018). "This is the early history of the synthesizer". Red Bull Music. Retrieved 2 November 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Bernstein, Adam (23 August 2005). "Robert Moog Dies; Created Electronic Synthesizer". ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 3 December 2018.
- ^ "Red Bull Music Academy Daily". daily.redbullmusicacademy.com. Retrieved 28 November 2018.
- ^ "Clear Some Space on Your Synth Rack: The Minimoog Returns". WIRED. Retrieved 28 November 2018.
- ^ a b Franklin Crawford (August 23, 2005). "Robert Moog, Ph.D. '64, inventor of the music synthesizer, dies of brain cancer". Cornell University News Service. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
- ^ a b "The 14 most important synths in electronic music history – and the musicians who use them". Fact. 15 September 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ^ "The Prophet 5 and 10", gordonreid.co.uk, archived from the original on 8 August 2002, retrieved 9 January 2014
- ^ "The life and times of Ikutaro Kakehashi, the Roland pioneer modern music owes everything to". FACT Magazine: Music News, New Music. 2 April 2017. Retrieved 6 September 2018.
- ^ a b c Howell, Steve (August 2015). "The Lost Art Of Sampling: Part 1". Sound on Sound. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "A brief history of sampling". MusicRadar. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
- ^ a b Shepard, Brian K. (2013). Refining Sound: A Practical Guide to Synthesis and Synthesizers. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199376681.
The first digital synthesizer to make it into the studios of everyone else, the Yamaha DX7, became one of the most commercially successful synthesizers of all time.
- ^ Holmes, Thom (2008). "Early Computer Music". Electronic and experimental music: technology, music, and culture (3rd ed.). Taylor & Francis. p. 257. ISBN 978-0-415-95781-6. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ^ Holmes, Thom (2008). "Early Computer Music". Electronic and experimental music: technology, music, and culture (3rd ed.). Taylor & Francis. p. 257. ISBN 978-0415957816. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ^ a b c Brøvig-Hanssen, Ragnhild; Danielsen, Anne (19 February 2016). Digital Signatures: The Impact of Digitization on Popular Music Sound. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262034142.
- ^ a b c d e "The 14 most important synths in electronic music history – and the musicians who use them". FACT Magazine: Music News, New Music. 15 September 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2018.
- ^ a b Vail, Mark (February 2002). "Korg M1 (Retrozone)". Sound on Sound. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Tech, Computer Music Specials 2008-10-13T15:29:00 286Z. "A brief history of computer music". MusicRadar. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c "The Analogue Revival". Sound on Sound. March 2014. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Obituary: Dr Robert Moog". BBC News. 22 August 2005. Retrieved 3 December 2018.
- ^ a b c d Weiner, Sophie (20 October 2017). "Minimoog: The First Truly Portable Synthesizer". Red Bull Music Academy. Retrieved 28 November 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Hip-hop's most influential sampler gets a 2017 reboot". Engadget. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- ^ "Meet the unassuming drum machine that changed music forever". Vox. Retrieved 11 May 2018.
- ^ "Jean Michel Jarre | Biography, Albums, Streaming Links | AllMusic". AllMusic. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ Mark Jenkins (2007), Analog synthesizers: from the legacy of Moog to software synthesis, Elsevier, pp. 133–4, ISBN 978-0-240-52072-8, retrieved 27 May 2011
- ^ Tomita at AllMusic. Retrieved 2011-06-04.
- ^ "Snowflakes Are Dancing". Billboard. Retrieved 28 May 2011.
- ^ "Kraftwerk". Discogs. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Borthwick 2004, p. 120
- ^ George-Warren, Holly (2001), The Rolling Stone Encyclopedia of Rock & Roll, Fireside, pp. 707–734, ISBN 0-7432-0120-5
- ^ Robbins, Ira A (1991), The Trouser Press Record Guide, Maxwell Macmillan International, p. 473, ISBN 0-02-036361-3
- ^ Black, Johnny (2003), "The Greatest Songs Ever! Hungry Like the Wolf", Blender Magazine (January/February 2003), archived from the original on 13 October 2007, retrieved 16 April 2008
- ^ Borthwick 2004, p. 130
- ^ a b Simpson, Dave (14 August 2018). "More synthetic bamboo! The greatest preset sounds in pop music". the Guardian. Retrieved 19 October 2018.
- ^ Saxelby, Ruth. "Borne into the 90s [pt.1]". Dummy Mag. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- ^ Beaumont-Thomas, Ben (14 February 2014). "Roland launch new versions of the iconic 808, 909 and 303 instruments". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2 November 2019.
- ^ "A Beginner's Guide To The Synth". Gizmodo Australia. 29 December 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2019.
- ^ a b "A tribute to the synth: how synthesisers revolutionised modern music". BBC. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ From Stage to Studio: Musicians and the Sound Revolution, 1890–1950 (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996).
- ^ Interview with Bob Moog, Plug, Fall 1974,p.2.
- ^ "1981–1990 – The Musicians' Union: A History (1893–2013)". www.muhistory.com.
- ^ Roger T. Dean, ed. (16 September 2009). The Oxford Handbook of Computer Music. Oxford University Press. p. 81. ISBN 9780199887132.
- ^ Crute, Adam (1 July 2019). "Learning the basics of FM synthesis and how it works". MusicTech. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
- ^ "CZ-101 Manual" (PDF). Retrieved 2 January 2019.
- ^
Reid, Gordon (2000). "Synth Secrets, Part 9: An Introduction to VCAs". Sound on Sound (January 2000). Archived from the original on 4 April 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2010.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Charles Dodge, Thomas A. Jerse (1997). Computer Music. New York: Schirmer Books. p. 82.
- ^ US patent 3,358,070, Alan C. Young (Hammond Co.), "Electronic Organ Arpeggio Effect Device", issued 1967-12-12
- ^ "RMI Harmonic Synthesizer". Jarrography – The ultimate Jean Michel Jarre discography.
- ^ Thom Holmes, Thomas B. Holmes (2002), Electronic and experimental music: pioneers in technology and composition, Routledge, p. 59, ISBN 978-0-415-93644-6
- ^
"Radio Squeals Turned to Music for Entire Orchestra", Popular Science (June 1932): 51, June 1932
— the article reported Léon Theremin's new electronic instruments used on his electric orchestra's first public recital at Carnegie Hall, New York City, including Fingerboard Theremin, Keyboard Theremin with fingerboard controller, and Terpsitone (a performance instrument in the style of platform on which a dancer could play a music by the movement of body). - ^
Glinsky, Albert (2000), Theremin: ether music and espionage, University of Illinois Press, p. 145, ISBN 978-0-252-02582-2,
In addition to its 61 keys (five octaves), it had a "fingerboard channel" offering an alternate interface for string players.
- ^ Brend, Mark (2005). Strange sounds: offbeat instruments and sonic experiments in pop. Hal Leonard Corporation. p. 22. ISBN 0-87930-855-9.
- ^ "Moogtonium (1966–1968)". Moog Foundation. 4 March 2010. — Max Brand's version of Mixture Trautonium, built by Robert Moog during 1966–1968.
- ^ Synthesizer technique. Hal Leonard Publishing Corporation. 1984. p. 47. ISBN 0-88188-290-9.
- ^ Pinch, Trevor; Frank Trocco (2004). Analog Days: The Invention and Impact of the Moog Synthesizer. Harvard University Press. p. 62. ISBN 0-674-01617-3.
- ^ "The "Hellertion"(1929) & the "Heliophon"(1936)", 120 Years of Electronic Music, 21 September 2013
- ^ Peter Lertes (1933), Elektrische Musik:ein gemeinverständliche Darstellung ihrer Grundlagen, des heutigen Standes der Technik und ihre Zukunftsmöglickkeiten, (Dresden & Leipzig, 1933)
- ^ J. Marx (1947). "Heliophon, ein neues Musikinstrument". Ömz. ii (1947): 314.
- ^ Christoph Reuter, Martinetta and Variophon, Variophon.de
- ^ Christoph Reuter, Variophon and Martinetta Enthusiasts Page, Variophon.de
- ^ Joseph Pepe Zawinul, Melodicas.com, archived from the original on 20 December 2011 (also another photograph is shown on gallery page)
- ^ Millioniser 2000 Promo Video Rock Erickson London, England 1983, MatrixSynth.com, 21 July 2009
- ^ The Complete MIDI 1.0 Detailed Specification, MIDI Manufacturers Association Inc., retrieved 10 April 2008
- ^ a b c Rothtein, Joseph (1995), MIDI: A Comprehensive Introduction, A-R Editions, pp. 1–11, ISBN 0-89579-309-1, retrieved 30 May 2008
- ^ Webster, Peter Richard; Williams, David Brian (2005), Experiencing Music Technology: Software, Data, and Hardware, Thomson Schirmer, p. 221, ISBN 0-534-17672-0
- ^ Royalty Free Music : Funk – incompetech (mp3). Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com).
- ^ "Firstman SQ-01 Sequence Synthesizer from Multivox" (advertisement). Contemporary Keyboard. Vol. 7, no. June 1981 – November 1981. p. 23.
- ^
"Multivox Firstman SQ-01 Sequencer". Keyboard Report. Contemporary Keyboard. Vol. 7, no. October 1981. pp. 82, 88. ("Keyboard Report, Oct. '81", according to the "Vol.9, 1983".
{{cite magazine}}: Cite magazine requires|magazine=(help)) - ^
"Firstman International". SYNRISE (in German). Archived from the original on 20 April 2003.
FIRSTMAN existiert seit 1972 und hat seinen Ursprung in Japan. Dort ist dieFirma unter dem Markennamen HILLWOOD bekannt. HILLWOOD baute dann auch 1973 den quasi ersten Synthesizer von FIRSTMAN. Die Firma MULTIVOX liess ihre Instrumente von 1976 bis 1980 bei HILLWOOD bauen.","SQ-10 / mon syn kmi ? (1980) / Monophoner Synthesizer mit wahrscheinlich eingebautem Sequenzer. Die Tastatur umfasst 37 Tasten. Die Klangerzeugung beruht auf zwei VCOs.
- ^ Jenkins, Mark (2009). Analog Synthesizers: Understanding, Performing, Buying--From the Legacy of Moog to Software Synthesis. CRC Press. pp. 107–108. ISBN 9781136122781.
- ^ A TALE OF TWO STRING SYNTHS, Sound on Sound, July 2002
- ^ Hamill, Jasper. "The world's most famous electronic instrument is back. Will anyone buy the reissued TB-303?". Forbes. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ Vine, Richard (15 June 2011). "Tadao Kikumoto invents the Roland TB-303". The Guardian. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
Bibliography
- Borthwick, Stuart (2004), Popular Music Genres: An Introduction, Edinburgh University Press, p. 120, ISBN 0-7486-1745-0
{{citation}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Holmes, Thom (2008), Electronic and experimental music: technology, music, and culture (3rd ed.), Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-0-415-95781-6, retrieved 4 June 2011
- Vail, Mark (2000), Vintage Synthesizers: Groundbreaking Instruments and Pioneering Designers of Electronic Music Synthesizers, Backbeat Books, pp. 68–342, ISBN 0-87930-603-3
Further reading
- Gorges, Peter (2005). Programming Synthesizers. Germany, Bremen: Wizoobooks. ISBN 978-3-934903-48-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Schmitz, Reinhard (2005). Analog Synthesis. Germany, Bremen: Wizoobooks. ISBN 978-3-934903-01-2.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Shapiro, Peter (2000). Modulations: A History of Electronic Music: Throbbing Words on Sound. Caipirinha Productions, USA. ISBN 1-891024-06-X.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kuit, Roland (2014). SoundLab I: The Electronic Studio. Publisher's number: 13664. The Netherlands, The Hague: Donemus.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kuit, Roland (2014). SoundLab II: Architectures for Philosophers. Publisher's number: 13665. The Netherlands, The Hague: Donemus.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kuit, Roland (2014). Laboratory of Patching: Illustrated Compendium of Modular Synthesis. Publisher's number: 13662. The Netherlands, The Hague: Donemus.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kuit, Roland (2014). To be On, to be OFF, that's the SWITCH. Publisher's number: 13666. The Netherlands, The Hague: Donemus.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kuit, Roland (2014). Modular strategies in shaping reflections and space. Publisher's number: 13663. The Netherlands, The Hague: Donemus.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)