Formamide
| Formamide | |
|---|---|
 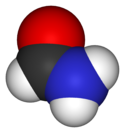
| |
| Chemical name | Methanamide |
| Other names | Carbamaldehyde |
| Chemical formula | CH3NO |
| Molecular mass | 45.04 g/mol |
| CAS number | [75-12-7] |
| Density | 1.133 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | 2-3 °C |
| Boiling point | 210 °C |
| SMILES | C(=O)N |
| Disclaimer and references | |
Formamide, also known as methanamide, is an amide derived from formic acid. It is a clear liquid which is miscible with water and has an ammonia-like odor. It is used primarily for manufacturing sulfa drugs and synthesizing vitamins and as a softener for paper and fiber. In its pure form, it dissolves many ionic compounds that are insoluble in water, so it is also used as a solvent.
Formamide is also a constituent of cryoprotectant vitrification mixtures used for cryopreservation of tissues and organs.
Formamide is also used as an RNA stabiliser in gel electrophoresis by deionizing RNA.
Another use is to add it in sol-gel solutions in order to avoid cracking during sintering.
Production
The reaction of formic acid with ammonia produces ammonium formate, which can then be turned into formamide by heating:
- HCOONH4 → HCONH2 + H2O
Physical data
Vapour density: 1.55 (air = 1)
Vapour pressure: 0.08 mm Hg (11 Pa) at 20 °C
Flash point: 154 °C (open cup)
pKa (DMSO): 23.5 (J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 3095)
External links
