2b2t
Logo in use since 2022 | |
| Other names | 2builders2tools |
|---|---|
| Initial release | December 2010[1][2] |
| Founder(s) | Hausemaster[2][3] |
| Platform | Minecraft: Java Edition (version 1.20.4)[4] |
| Size | ~58.2 TB[4] |
| Type | Minecraft server |
| Website |
|
2b2t (2builders2tools) is a Minecraft server founded in December 2010. 2b2t has essentially no rules and players are not permanently banned, known within Minecraft as an "anarchy server".[2] As a result, players commonly engage in the destruction of other players' and groups creations, colloquially called "griefing", as well as hacking using modified software to gain an advantage. 2b2t is the oldest anarchy server in Minecraft, as well as one of the few running 2010 Minecraft servers of any variety. The server is permanently set to hard difficulty and player versus player combat is enabled. It has seen over 780,000 players explore its procedurally generated map, increasing its file size to almost 60 terabytes.[4] 2b2t has been described in news media as the worst Minecraft server due to its toxic playerbase and culture.
History
2010–2016: Founding and early history
The 2b2t Minecraft server was founded in December 2010; it has run consistently without a reset since then.[6][1] The founders are anonymous,[7] choosing to remain unknown or known only via usernames; the most prominent founder is commonly referred to as "Hausemaster".[2][3] The server operates with minimal rules, as an "anarchy server"; except in fixing game-breaking exploits, the server operators are relatively hands-off in administrating the server.[3]
Varying explanations have been given for the origin of the server's rules-free style. One server operator told Vice that the server originated as a regular Minecraft server, before he and his friends "decided to open it up to see how much destruction could be made and started advertising it on various places on the Internet."[7] According to 2b2t player and amateur archivist James Rustles, Hausemaster was given the server by its original founder, who founded it on a principle of maximum player freedom in the tradition of a Garry's Mod server he already owned.[8]
The server was advertised shortly after its creation on online forums such as 4chan, Facepunch Studios, and Reddit, whose users populated the server by the hundreds due to the total freedom it offered.[7] Members from different forums raided each other and their bases on the server.[2] The founders eventually stopped playing Minecraft, though the server remained online due to the large player base that had been formed.[7] A subreddit was created by a player on March 25, 2012.[9] In early 2013, the file size of 2b2t's world map, which is procedurally generated, was reported to be over 500 gigabytes.[5] This increased to almost one terabyte by late 2015,[10] costing US$90 a month to maintain.[7]
2016–present: Player influx
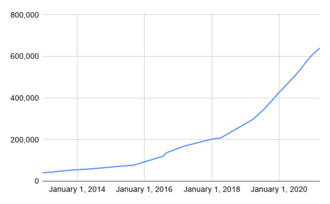
On June 1, 2016, popular YouTuber "TheCampingRusher"[11] uploaded a YouTube video of himself playing on 2b2t. This caused a massive influx of new players from the channel's audience, who were at first mostly tourists, as the video gained over two million views in less than four months from its upload.[2][3] This overwhelmed the server and strained the hardware used to host and run it, bringing together a loose group of older players who banded against these new players.[3]
Although the new players, who were labeled "Rushers", largely outnumbered the older players at the time, the older players had years of experience and resources.[3] Many older players deterred new players by destroying the spawn-in area to make it uninhabitable and extremely challenging to proceed from and repeatedly killing them in-game.[2][3]

Some players built in-game contraptions designed solely to overload the server, with the intent of making it difficult for TheCampingRusher and his fans to play on it. Some placed obscene content around the spawn area and along player-built roads to get TheCampingRusher's YouTube videos taken down for violations of YouTube's terms of service.[3]
The new players, despite having been discouraged to do so by TheCampingRusher, had destroyed bases and monuments on the server that had stood for years, which is partially what had caused such a response from the player base.[3] When Kiberd from Newsweek asked Hausemaster if he disapproved of the massive influx of new players, he responded by saying that "2b2t is definitely not ruined—in my opinion it's how it should be: absolutely chaotic."[2]
In response to the inundated server and hardware, a queue to enter the server was added. Before then, the server would have about ten players online at the same time. However, at the influx peak, the server had thousands of players waiting in queue.[11] The queue gave earlier 2b2t players priority over newer players,[3] although this feature was removed after a year.[12] The regular queue moves slowly and can contain over a thousand players.[2] Waiting in the queue has been described as an onerous task. Players can pay $20 to access a separate "priority" queue for one month.[3]
2018–2021: Nocom exploit

In 2018, a group of players called "Nerds Inc." (a spoof of Monsters, Inc.) discovered a software bug in 2b2t's server software that allowed players to query far-away terrain, which players cannot normally view. The loading of huge areas of terrain puts a heavy workload on the server, which Nerds Inc. used to repeatedly crash the server. This was done with the intent to induce the developers of PaperMC, modified server software used by 2b2t, to create a bug fix for the software,[13] which introduced a vulnerability where the server would now only respond to the querying of far-away terrain if it was already loaded, i.e., proximate to a player. By creating the flawed bug fix, the developers inadvertently gave anyone aware of the vulnerability the ability to test if any given area in the game world contained a player, and to read that area if so. Nerds Inc. was now able to locate all online players and remotely observe the terrain around players in real-time, including valuable storage of in-game items and player-built constructions.[14][15]
Correlating the coinciding timing of player join and disconnect notices and the loading and unloading of locations let Nerds Inc. tell where specific players stood, not just that a player was there.[15] The exploit became more effective with an adaptive tracking system programmed by a member of Nerds Inc.,[14] predicting the paths individual players would take using Monte Carlo localization in response to the server implementing rate-limits preventing less efficient search methods.[16] The data gathered amassed about 2 terabytes during the 3 years of tracking terrain, paths, and base locations.[15]
One group that shared members with Nerds Inc. was supplied with the locations of numerous bases which they raided, looting 200 million in-game items. They kept the exploit secret, creating fake stories behind the destruction of bases and gaslighting. They named the exploit "Nocom", short for "no comment". In 2021, another group called Infinity Incursion independently created a more primitive version of the Nocom exploit and, with their less concealed use of it, other groups started learning about Nocom by June 2021. On July 15, 2021, server admin Hausemaster implemented changes to 2b2t that patched the exploit. Nocom resulted in many bases and in-game item stashes being raided or destroyed, with a total of 15,000 bases being discovered.[15] Rich Stanton of PC Gamer described Nocom as one of the most impactful events in the server's history.[6]
2023: Update to 1.19
On August 14, 2023, 2b2t updated to Minecraft version 1.19, after running on Minecraft 1.12 for years. Several additions to the server became controversial, including resetting established terrain and a "soft item economy reset", which removed and decreased the amounts of certain items in player's inventories and storage, resulting in community backlash.[17]
On August 24, Hausemaster apologized and explained his decisionmaking.[18] The next day he announced that the server would be rolling back to 1.12 temporarily and then updating to 1.19 without the controversial changes, and announcing an option to refund priority status for those who have paid for it and are dissatisfied with the changes.[19][non-primary source needed]
Culture


The culture of 2b2t, as well as Minecraft anarchy servers in general, is inhospitable and nihilistic.[2] Players usually need to hide supplies and be well armed to survive and can expect to be killed several times.[2] This is exacerbated by the server being set to hard difficulty and player versus player combat being enabled, making survival considerably harder.[20] Longtime players are often hostile to new players on the server,[3] whom they often call "newfags".[3][7] The server-wide chat often contains spam, trolling, and trash talking,[3] as well as racial slurs, death threats, and Nazi propaganda.[2][8] Links to obscene content and screamer videos are also common.[3] Players lie to others with the intent of sending them to in-game locations with traps.[3] A common rule among players is to not trust others.[20]
Traps are deliberately placed surrounding the area where players first join the server: pits of lava, areas lit on fire, and portals that lead to lava or enclosed areas of obsidian that force players to disconnect and reconnect, waiting through the long queue again.[2][8] Some players create large obstacles called "lavacasts", in which water and lava are repeatedly poured down staircases of stone, creating mountains of jagged cobblestone.[8] These structures completely surround the spawn area, and many are as tall as the map's height limit.[5]
There have occasionally been events in which dozens of players come together to take control of spawn for a time to build a large base, kill many new players, or destroy other bases, which were referred to as "spawn incursions".[8] Inexperienced players may need many attempts and multiple hours to "escape" the spawn area,[3][8][7] where resources have been consumed or destroyed for thousands of blocks in all directions.[21] The most common cause of death is starvation from being unable to escape the spawn area.[20] A player may last around 1,500 blocks of travel without food before dying of starvation without the help of hacks or glitches.[8] Roisin Kiberd of Newsweek speculated that enduring the challenge may be part of the appeal of 2b2t: since "nobody survives for long, there is a pride in having died there."[2]
Experienced players reside far away from the spawn area in relative safety to play the game and build.[2] The map is less destroyed further away from spawn,[20][7] allowing for trees and animals.[8] Player-built roads called "highways" are used to travel out from spawn.[8][20] The server has no etiquette regarding ownership; anything that is built can be destroyed at any time if found by other players.[3] This destruction, known as griefing, is so commonplace on the server that Brendan Caldwell of Rock, Paper, Shotgun described it as being "just a form of weather". Despite this culture of hostility and destruction, there is an event every April Fools' Day in which the server changes to a different map for a few days and players can come together and cooperate.[8]
Players often make use of modified Minecraft clients incorporating cheats such as X-ray vision, improved bow and sword aim, and radar; these modifications are permitted by 2b2t's (lack of) rules.[2][8] These clients help immensely in allowing the player to navigate the environment and survive.[2][3][8] Players without these clients are at a disadvantage.[8]
Because the server's map is over a decade old, 2b2t has developed an insular subculture with its own history and ethos. Martin Paul Eve, a researcher in digital humanities, found that the wiki documenting the history of 2b2t "refer to the in-game universe as though it were a totality". He liken it to resources documenting the Warez scene; they mingled with the subculture themselves and are difficult to understand without a direct experience.[22]
Reception
Both Robert Guthrie of Kotaku and Andrew Paul of Vice have called 2b2t the worst server in Minecraft.[7][3] Paul called the server a "fantastical world of possibility and horror," and found that it functioned as a kind of virtual "id," representing an "unrestrained stream of populist consciousness".[7] Brendan Caldwell of Rock, Paper, Shotgun described 2b2t as the game's "most obscene server."[8] In June 2012, Craig Pearson of PCGamesN called it Minecraft's most offensive server, noting 2b2t's callousness and obscenity in the form of language, swastikas, and its hostile player base.[20] In 2013, a PCGamesN article by Jeremy Peel reported on Minecraft's newly announced built-in server hosting service, Minecraft Realms, remarking that it would keep children away from 2b2t.[23] In 2014, Tim Edwards wrote in a PCGamesN article addressing Microsoft about their purchase of Minecraft that they should not get "prissy" about player-made creations, stating that "2b2t is still an amazing achievement, with or without the swastikas."[24]
In 2016, in both Newsweek and The Independent, Roisin Kiberd described 2b2t as a malevolent form of Minecraft, a place of beauty and terror. Kiberd called the server "hell", stating that it is "not safe for life", as the server gives "free rein to [players'] darkest impulses."[2] Kiberd concluded that the main appeal of playing on the server comes from learning the possibilities of a server with few limits, as well as enduring its hostile environment.[2][25] Kiberd also noted that there is a so-called "meta-narrative" above 2b2t, involving players using YouTube and Reddit to share analysis and commentary about in-server events.[2] A 2013 IGN article and video listed 2b2t's spawn area as one of the six best things in Minecraft, describing the server as the "end boss" of Minecraft servers, a celebration of destruction and indifference. The article noted 2b2t's propensity towards griefing, the use of hacked clients, and player-built obscenities; and stated that players with thick skin should visit 2b2t at least once.[5]

From September 8, 2018, to February 24, 2019, 2b2t was featured in the Videogames: Design/Play/Disrupt exhibition of the Victoria and Albert Museum in London.[26] The exhibition aimed to explore video games and their designing process, as well as how they captivate players and the social and ethical issues around them. Minecraft was heavily featured in the third section of the exhibition, which focused on games in which players "become creators and designers themselves, often as part of large online communities".[27] 2b2t represented this aspect of Minecraft, which exhibited alongside 15 other video games. The server was described as "littered with archaeological remnants of its history... a palimpsest of a landscape, written over and re-written over by feuds between players, hacks injecting vast structures into the world, and by different waves of Internet communities arriving and rampaging or attempting to settle within it."[26]
In Introduction to Game Design, Prototyping, and Development, published by Pearson Education in August 2017, 2b2t was described as being a "barren hellscape", with its nature being the "ultimate expression of the core mechanic of the game," referring to Minecraft's open-ended sandbox nature.[21] The Ultimate Minecraft Creator, published by Triumph Books in July 2014, stated that despite 2b2t's offensive language and behavior, griefing, and cheating, the server can be a unique and fun experience for players who are willing to put up with its negative aspects.[28]
2b2t also featured in an episode of the Swedish podcast P3 Spel (P3 Games) of Sveriges Radio, which described 2b2t as Minecraft's "most talked-about" server, and how, throughout its history, it has become the "witch's cauldron of chaos" it is today.[9] Master Builder 3.0 Advanced and Ultimate Guide to Mastering Minigames and Servers, published by Triumph Books in April 2015 and April 2016 respectively, both stated that 2b2t "sits among online royalty when it comes to public [Minecraft] servers."[29][30]
Renders
-
A render of 2b2t's spawn region as of late 2017, displaying the various layers of spawn with progressive destruction proceeding inwards toward the center of the world. The render displays the -X (western) axis of the world map from 400 to 3,000 blocks from the map's center.
-
A render from the same perspective as of February 2020, which, in comparison to the render from 2017, shows how the destruction of the spawn area has greatly increased over time
-
A render of 2b2t's spawn region as of June 2019, providing an alternative side view in an isometric projection of the render in the Culture section
References
- ^ a b "2b2t.org". Archived from the original on March 18, 2013. Retrieved January 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Kiberd, Roisin (September 15, 2016). "The Minecraft Server That Will Kill You 1,000 Times". Newsweek. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved September 9, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Guthrie, Robert (September 23, 2016). "The Denizens of Minecraft's 'Worst' Server Are At War With YouTube". Kotaku. Archived from the original on March 29, 2019. Retrieved September 9, 2019.
- ^ a b c "2b2t". Retrieved April 6, 2024.
- ^ a b c d Craig (June 20, 2013). "The 6 Most Amazing Things I've Seen in Minecraft". IGN. Archived from the original on May 28, 2019. Retrieved September 9, 2019.
- ^ a b Stanton, Rich (August 2, 2021). "Minecraft's most anarchic server brought to its knees by griefers". PC Gamer. Archived from the original on April 15, 2022. Retrieved March 10, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Paul, Andrew (October 5, 2015). "The Worst Place in Minecraft". Tech. Vice. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved September 9, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Caldwell, Brendan (February 29, 2016). "Ridealong: The Ruin Of Minecraft's Most Obscene Server". Rock, Paper, Shotgun. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved September 11, 2019.
- ^ a b Norström, Tobias (February 19, 2020). "Dokumentär: Anarki, hat och Minecraft" [DOCUMENTARY: Anarchy, Hatred and Minecraft]. Sveriges Radio (Podcast). Archived from the original on February 25, 2021. Retrieved April 14, 2021.
- ^ "2b2t.org". Archived from the original on September 11, 2015. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- ^ a b Gutelle, Sam (April 27, 2017). "YouTube Millionaires: TheCampingRusher Is "Constantly Thinking About What Video To Make Next"". Tubefilter. Archived from the original on October 17, 2022. Retrieved March 10, 2022.
- ^ "Upcoming changes, website, queue to be reworked and 'pre 1st-june' list to be deleted, and some other information". Reddit. October 12, 2017. Archived from the original on April 19, 2019. Retrieved February 17, 2020.
- ^ "PaperMC patch". GitHub. Archived from the original on July 6, 2022. Retrieved July 6, 2022.
- ^ a b Lowry, Brendan (July 25, 2021). "How the 2B2T Minecraft server was almost toppled by an exploit". Windows Central. Archived from the original on August 11, 2021. Retrieved August 12, 2021.
- ^ a b c d Walker, John (July 30, 2021). "Minecraft's 'Worst' Server Was Exploited So Hard, Griefers Could See The Future". Kotaku. Archived from the original on August 2, 2021. Retrieved August 3, 2021.
- ^ "No Comment Explanation and Information". GitHub. July 24, 2021. Archived from the original on August 11, 2021. Retrieved August 12, 2021.
- ^ Kabra, Akshat (August 22, 2023). "Minecraft's oldest anarchy server, 2b2t, finally receives update after five years, and fans aren't happy". Sportskeeda. Retrieved March 3, 2024.
- ^ "Update on the 1.19 situation - An Apology and Explanation". 2b2t. August 24, 2023. Retrieved March 3, 2024.
- ^ "Server Rollback". 2b2t. August 25, 2023. Retrieved March 3, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f Pearson, Craig (June 3, 2012). "2b2t photodiary: Inside Minecraft's most offensive server". PCGamesN. Archived from the original on June 9, 2012. Retrieved December 26, 2019.
- ^ a b Gibson, Jeremy (August 17, 2017). Introduction to Game Design, Prototyping, and Development: From Concept to Playable Game with Unity and C#. Pearson Education. ISBN 978-0-13-465988-6. Archived from the original on December 6, 2019. Retrieved November 12, 2019.
- ^ Eve, Martin Paul (December 15, 2021). "Original Pirate Material". Warez: The Infrastructure and Aesthetics of Piracy. Brooklyn, NY: Punctum Books. pp. 45–46. doi:10.53288/0339.1.00. hdl:20.500.12657/52029. ISBN 9781685710361. OL 35740478M.
- ^ Peel, Jeremy (March 14, 2013). "Minecraft Realms is a subscription service for families that will "bring in more money than the game itself"". PCGamesN. Archived from the original on July 19, 2016. Retrieved December 2, 2019.
- ^ Edwards, Tim (October 22, 2014). "Dear Microsoft: about that Minecraft deal". PCGamesN. Archived from the original on July 12, 2017. Retrieved May 15, 2020.
- ^ Kiberd, Roisin (September 23, 2016). "There's an alternative Minecraft server without any rules". Indy/Life. The Independent. Archived from the original on October 14, 2019. Retrieved September 20, 2019.
- ^ a b Leith, Sam (August 31, 2018). "Video games at the V&A: is this the most creative artform of the modern age?". Culture. The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on September 5, 2018. Retrieved March 21, 2021.
- ^ Polianskaya, Alina (August 22, 2018). "From Minecraft to arcades and apps: V&A delves into today's video games". Issues. Design Week. Archived from the original on October 30, 2020. Retrieved March 21, 2021.
- ^ The Ultimate Minecraft Creator: The Unofficial Building Guide to Minecraft and Other Games. Triumph Books. July 1, 2014. ISBN 978-1-63319-036-8. Archived from the original on December 6, 2019. Retrieved December 5, 2019.
- ^ Master Builder 3.0 Advanced: Minecraft Secrets and Strategies from the Game's Greatest Players. Triumph Books. April 1, 2015. pp. 43, 49. ISBN 978-1-63319-188-4. Archived from the original on December 11, 2019. Retrieved December 11, 2019.
- ^ Ultimate Guide to Mastering Minigames and Servers: Minecraft Secrets to the World's Best Servers and Minigames. Triumph Books. April 5, 2016. ISBN 978-1-62937-233-4. Archived from the original on December 6, 2019. Retrieved December 5, 2019.



