Porphobilinogen

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-[5-(Aminomethyl)-4-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.970 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Porphobilinogen |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 226.229 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Porphobilinogen (PBG) is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of porphyrins, which include critical substances like hemoglobin and chlorophyll.[1]
The structure of the molecule can be described as molecule of pyrrole with sidechains substituted for hydrogen atoms at positions 2, 3 and 4 in the ring (1 being the nitrogen atom); respectively, an aminomethyl group −CH2−NH2, an acetic acid (carboxymethyl) group −CH2−COOH, and a propionic acid (carboxyethyl) group −CH2−CH2−COOH.
Biosynthesis
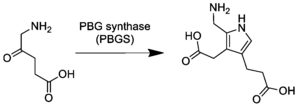
[edit]In the first step of the porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, porphobilinogen is generated from aminolevulinate (ALA) by the enzyme ALA dehydratase.
Metabolism
[edit]In the typical porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, four molecules of porphobilinogen are concatenated by carbons 2 and 5 of the pyrrole ring (adjacent to the nitrogen atom) into hydroxymethyl bilane by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase, also known as hydroxymethylbilane synthase.
Pathologies
[edit]Acute intermittent porphyria causes an increase in urinary porphobilinogen.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). "Hemes in Biology". Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221. ISBN 978-0470048672.
- ^ Aarsand, AK; Petersen PH; Sandberg S (April 2006). "Estimation and application of biological variation of urinary delta-aminolevulinic acid and porphobilinogen in healthy individuals and in patients with acute intermittent porphyria". Clinical Chemistry. 52 (4): 650–656. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2005.060772. PMID 16595824.
