Portal:Central America
The Central America Portal

Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering the United States and the Gulf of Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from southern Mexico to southeastern Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage.
In the pre-Columbian era, Central America was inhabited by the Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica to the north and west and the Isthmo-Colombian peoples to the south and east. Following the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' voyages to the Americas, Spain began to colonize the Americas. From 1609 to 1821, the majority of Central American territories (except for what would become Belize and Panama, and including the modern Mexican state of Chiapas) were governed by the viceroyalty of New Spain from Mexico City as the Captaincy General of Guatemala. On 24 August 1821, Spanish Viceroy Juan de O'Donojú signed the Treaty of Córdoba, which established New Spain's independence from Spain. On 15 September 1821, the Act of Independence of Central America was enacted to announce Central America's separation from the Spanish Empire and provide for the establishment of a new Central American state. Some of New Spain's provinces in the Central American region (i.e. what would become Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua and Costa Rica) were annexed to the First Mexican Empire; however in 1823 they seceded from Mexico to form the Federal Republic of Central America until 1838. (Full article...)
Selected article
Hurricane Gert was a large tropical cyclone that caused extensive flooding and mudslides throughout Central America and Mexico in September 1993. The seventh named storm and third hurricane of the annual hurricane season, Gert originated as a tropical depression from a tropical wave over the southwestern Caribbean Sea on September 14. The next day, the cyclone briefly attained tropical storm strength before moving ashore in Nicaragua and proceeding through Honduras. It reorganized into a tropical storm over the Gulf of Honduras on September 17, but weakened back to a depression upon crossing the Yucatán Peninsula. Once over the warm waters of the Bay of Campeche, Gert quickly strengthened into a Category 2 hurricane by September 20. The hurricane made a final landfall on the Gulf Coast of Mexico near Tuxpan, Veracruz, with peak winds of 100 mph (160 km/h). The rugged terrain disrupted the cyclone's structure; Gert entered the Pacific Ocean as a depression near the state of Nayarit on September 21, where it briefly redeveloped a few strong thunderstorms before dissipating at sea five days later.
Gert's broad wind circulation produced widespread and heavy rainfall across Central America through September 15–17. Combined with saturated soil following Tropical Storm Bret's passage a month earlier, the rain triggered widespread floods and mudslides that isolated thousands of people across numerous communities. In Costa Rica, blustery weather destroyed a national park and led to significant losses in the agricultural and tourism sectors. Much of the Mosquito Coast of Nicaragua and Honduras endured overflowing rivers, engulfing cities, villages, and crops with mud and water. Gert's winds were at their strongest upon landfall in Mexico, yet the worst effects in the country were also due to freshwater flooding after an extreme rainfall event in the Huasteca region resulted in water accumulations as high as 31.41 inches (798 mm). An increasing number of major rivers burst their banks over a period of several days, fully submerging extensive areas of land around the Pánuco basin. Tens of thousands of residents were forced to evacuate as raging floodwaters demolished scores of structures in what was described as the region's worst disaster in 40 years. (Full article...)Did you know...
- ... that Swedish naval officer Axel Lagerbielke was imprisoned in Lima for over a year, held in Callao and eventually escaped from Panama on an English packet boat to Jamaica?
- ... that goalkeeper Daniela Solera had the most touches of any Costa Rican player in their opening match of the 2023 World Cup?
- ... that the Central American government voted for annexation to the First Mexican Empire after a request from Regent Agustín de Iturbide?
- ... that the 7th Macho de Monte Infantry Company of the Panama Defense Forces was named after a tapir?
- ... that Panama cross-banded tree frog males synchronize their mating calls to confuse predators that locate them by sound?
- ... that footballer Alexandra Pinell scored the Costa Rica U20 team's only goal at the FIFA tournament hosted by their country?
- ... that the Adelaide L. T. Douglas House, built for a New York City socialite, housed the United States Olympic Committee before being sold to Guatemala?
- ... that the government of El Salvador, the Catholic Church, and street gangs negotiated a truce to reduce homicides from 2012 to 2014?
Related portals
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Central America-related articles, see WikiProject Central America.
Need help?
Do you have a question about Central America that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
General images
In the news
- 8 September 2024 – 2024 Pasaquina Bell UH-1 crash
- Nine people, including El Salvador's National Civil Police chief Mauricio Arriaza Chicas and a fraud suspect, are killed during a helicopter crash while being en route to San Salvador. The crash is considered to be intentional. All flags on government buildings will be flown half-mast for three days. (BBC)
- 5 September 2024 – Nicaragua–United States relations, Protests against Daniel Ortega
- The United States announces that it has secured the release of 135 political prisoners in Nicaragua, who were jailed by the government of President Daniel Ortega. (Al Jazeera)
- 29 August 2024 –
- Three people are killed and 17 are injured when a car crashes into a group of migrants in Oaxaca, Mexico. (AP)
- 21 August 2024 – 2023–2024 mpox epidemic
- Honduras reports five suspected cases of the new mpox clade. (Prensa Libre)
Subcategories
Topics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus












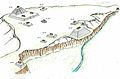
![Image 12Mesoamerica and Central America in the 16th century before Spanish arrival [according to whom?] (from Mesoamerica)](/media/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/06/Mesoam%C3%A9rica_y_Centroamerica_prehispanica_siglo_XVI.svg/120px-Mesoam%C3%A9rica_y_Centroamerica_prehispanica_siglo_XVI.svg.png)