Portal:Phoenicia
THE PHOENICIA PORTAL

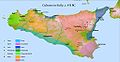
The Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon. They developed a maritime civilization which expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel. The Phoenicians extended their cultural influence through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus, Sicily and Sardinia to the southern coasts of Iberia.
The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions following the decline of most major cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. It is believed that they self-identified as Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, indicating a continuous cultural and geographical association. The name Phoenicia is an ancient Greek exonym that did not correspond precisely to a cohesive culture or society as it would have been understood natively. Therefore, the division between Canaanites and Phoenicians around 1200 BC is regarded as a modern and artificial division.
The Phoenicians, known for their prowess in trade, seafaring and navigation, dominated commerce across classical antiquity and developed an expansive maritime trade network lasting over a millennium. This network facilitated cultural exchanges among major cradles of civilization, such as Greece, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. The Phoenicians established colonies and trading posts across the Mediterranean; Carthage, a settlement in northwest Africa, became a major civilization in its own right in the seventh century BC.
The Phoenicians were organized in city-states, similar to those of ancient Greece, of which the most notable were Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. Each city-state was politically independent, and there is no evidence the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single nationality. While most city-states were governed by some form of kingship, merchant families probably exercised influence through oligarchies. After reaching its zenith in the ninth century BC, the Phoenician civilization in the eastern Mediterranean gradually declined due to external influences and conquests. Yet, their presence persisted in the central and western Mediterranean until the destruction of Carthage in the mid-second century BC. — Read more about Phoenicia, its mythology and language
 Featured article
•
Featured article
•
A Featured article represents some of the best content on Wikipedia

The Temple of Eshmun (Arabic: معبد أشمون) is an ancient place of worship dedicated to Eshmun, the Phoenician god of healing. It is located near the Awali river, 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) northeast of Sidon in southwestern Lebanon. The site was occupied from the 7th century BC to the 8th century AD, suggesting an integrated relationship with the nearby city of Sidon. Although originally constructed by Sidonian king Eshmunazar II in the Achaemenid era (c. 529–333 BC) to celebrate the city's recovered wealth and stature, the temple complex was greatly expanded by Bodashtart, Yatonmilk and later monarchs. Because the continued expansion spanned many centuries of alternating independence and foreign hegemony, the sanctuary features a wealth of different architectural and decorative styles and influences.
The sanctuary consists of an esplanade and a grand court limited by a huge limestone terrace wall that supports a monumental podium which was once topped by Eshmun's Greco-Persian style marble temple. The sanctuary features a series of ritual ablution basins fed by canals channeling water from the Asclepius river (modern Awali) and from the sacred "YDLL" spring; these installations were used for therapeutic and purificatory purposes that characterize the cult of Eshmun. The sanctuary site has yielded many artifacts of value, especially those inscribed with Phoenician texts, such as the Bodashtart inscriptions and the Eshmun inscription, providing valuable insight into the site's history and that of ancient Sidon. (Full article...)
Phoenician mythology •
In early modern scholarship, a cult to a supposed Heliopolitan Triad of Jupiter, Venus and Mercury (or Dionysus) was thought to have originated in ancient Canaanite religion, adopted and adapted firstly by the Greeks, and then by the Romans when they colonised the city of Heliopolis (modern Baalbeck) in the Beqaa Valley of Lebanon. The Canaanite god Baʿal (Hadad) was equated with Jupiter Heliopolitanus as sun-god, Astarte or Atargatis with Venus Heliopolitana as his wife, and Adon, the god of spring, with either Mercury or Dionysus as third member of the triad, son of Heliopolitan Venus and Heliopolitan Jupiter.
The Romans were thought to have built magnificent temples for the Heliopolitan Triad as the ruling deities of Heliopolis, rather in the manner of the colonial temples built to their own Capitoline triad, and for much the same reasons; to foster a Roman identity and co-operation. The take-over of Heliopolis involved the establishment of Roman priesthoods and magistracies; but only two inscriptions at Heliopolis and 4 at Beirut are dedicated to Jupiter, Venus and Mercury. Nearly 30 at Heliopolis and 11 at Beirut are dedicated to Jupiter alone. (Full article...)
Images
 Good article
•
Good article
•
A Good article meets a core set of high editorial standards
The Battle of Leptis Parva was fought in 238 BC between a Carthaginian army of over 30,000 commanded by Hamilcar Barca and Hanno, and approximately 20,000 mutinous Carthaginian soldiers and North African rebels under Matho in the North African province of Byzacium (in modern Tunisia). The battle was the final major conflict of the Mercenary War and resulted in a decisive victory for the Carthaginians.
In 241 BC 20,000 foreign troops who had been employed by Carthage during the First Punic War (264 to 241 BC) mutinied under the leadership of Spendius and Mathos starting the Mercenary War. They were supported by an uprising of Carthage's oppressed African territories and 70,000 local recruits flocked to join them, bringing supplies and finance. War-weary Carthage fared poorly in the initial engagements of the war, especially under the leadership of Hanno. Hamilcar Barca was given supreme command in 239 BC and slowly turned the tide. (Full article...)
Phoenician inscriptions & language •
The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the societies and histories of the ancient Phoenicians, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. The older inscriptions form a Canaanite–Aramaic dialect continuum, exemplified by writings which scholars have struggled to fit into either category, such as the Stele of Zakkur and the Deir Alla Inscription.
The Northwest Semitic languages are a language group that contains the Aramaic language, as well as the Canaanite languages including Phoenician and Hebrew. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) •

- ... that Bochart's 1646 Geographia Sacra seu Phaleg et Canaan was the first full-length book devoted to the Phoenicians?
- ... that archaeological excavations in the historic town of Kharayeb revealed a rural settlement with a complex system of cisterns and a Phoenician temple?
- ... that the discovery of Phoenician metal bowls in 1849 created the entire concept of Phoenician art?
- ... that the sarcophagus of Eshmunazar II, the Phoenician king of Sidon, is one of only three ancient Egyptian sarcophagi unearthed outside Egypt?
- ... that alongside a 7th-century BC Phoenician shipwreck, two additional wrecks from various historical periods were unearthed in Bajo de la Campana, situated off the coast of Cartagena, Spain?
- ... that the earliest-known Phoenician inscriptions were found near Bethlehem?
Related portals
Categories
Wikiproject
Other Wikimedia and Wikiportals
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Parent portal: Lebanon