Saurichthyiformes
| Saurichthyiformes Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
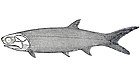
| Life restoration of Saurichthys | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | †Saurichthyiformes Aldinger, 1937 |
| Families | |
| |





Saurichthyiformes is an extinct order of ray-finned fish which existed in Asia, Africa, Australia, Europe and North America, during the late Permian to early Middle Jurassic.[1][2][3][4] Saurichthyiiformes comprise two families, Saurichthyidae and Yelangichthyidae. Yelangichthyidae is monotypic, containing only the genus Yelangichthys. The gar or needlefish-like Saurichthyidae is primarily known from the genus Saurichthys. Additionally, the subgenera Saurorhynchus Costasaurichthys, Eosaurichthys, Lepidosaurichthys, and Sinosaurichthys are frequently used to group species, and are sometimes considered separate genera. Species are known from both marine end freshwater deposits. They had their highest diversity during the Early and Middle Triassic.[5] Their phylogenetic position is uncertain, while they have often been considered members of Chondrostei, and thus related to living sturgeons and paddlefish, phylogenetic analysis of well-preserved remains has considered this relationship equivocal. They may actually belong to the stem-group of Actinopterygii, and thus not closely related to any living group of ray-finned fish.[6]
Systematics
[edit]- Order †Saurichthyiformes Aldinger, 1937 [Saurichthyida Berg, 1937][7][8][9]
- Family †Saurichthyidae Owen 1860 [Saurichthyoidei Bleeker 1859; Belonorhynchidae Woodward 1888; Saurorhynchidae Jordan, 1905]
- Genus †Saurichthys Agassiz, 1834 [Belonorhynchus Bronn 1858; Brevisaurichthys Beltan 1972; Giffonus Costa 1862; Gymnosaurichthys Berg 1940; Ichthyorhynchus Bellotti 1857; Stylorhynchus Martin 1873, non Lesson 1847, non Stein 1848; Systolichthys Beltan 1972]
- †Saurichthys apicalis Agassiz 1834 (type species)
- †Saurichthys breviabdominalis Maxwell et al. 2015[10]
- †Saurichthys curionii (Bellotti 1857)
- †Saurichthys daubreei Firtion 1934
- †Saurichthys dawaziensis Wu et al. 2009
- †Saurichthys dianneae Maxwell et al. 2016
- †Saurichthys dongusensis Minich 1992
- †Saurichthys eximius Minikh 1982
- †Saurichthys gigas (Woodward 1890), non von Quenstedt 1858
- †Saurichthys gracilis (Woodward 1890)
- †Saurichthys grignae Tintori 2013
- †Saurichthys gypsophilus Reis 1892
- †Saurichthys hamiltoni Stensiö 1925
- †Saurichthys hoffmanni Werneburg et al. 2014
- †Saurichthys huanshenensis Chou & Liu 1957
- †Saurichthys irregularis Oertle 1928
- †Saurichthys latifrons Eck 1865
- †Saurichthys lepidosteoides Frech 1903
- †Saurichthys macrocephalus (Deecke 1889)
- †Saurichthys majiashanensis Tintori et al. 2014
- †Saurichthys minimahleri Werneburg et al. 2014
- †Saurichthys nepalensis Beltan & Janvier 1978
- †Saurichthys obrutchevi Minich 1981
- †Saurichthys orientalis Sytchevskaya 1999
- †Saurichthys parvidens Wade 1935
- †Saurichthys piveteaui Beltan 1968
- †Saurichthys proximus Minich 1981
- †Saurichthys rieppeli Maxwell et al. 2015[10]
- †Saurichthys sceltrichensis Renesto et al. 2021[11]
- †Saurichthys seefeldensis Kner 1867
- †Saurichthys spinosa Wu et al. 2018 [12]
- †Saurichthys stensioi Lehman 1952
- †Saurichthys sui Fang & Wu 2022[13]
- †Saurichthys tenuirostris Münster 1839 [14]
- †Saurichthys tertius Minich 1982
- †Saurichthys ultimus Minikh 1992
- †Saurichthys vjuschkovi Minikh 1983
- †Saurichthys yangjuanensis Wu et al. 2015
- †Saurichthys yunnanensis Zhang, Zhou, Lu & Bai 2010
- Subgenus †Costasaurichthys Tintori, 2013[15]
- †Saurichthys (Costasaurichthys) costasquamosus Rieppel 1985 (type species)
- †Saurichthys (Costasaurichthys) paucitrichus Rieppel 1992
- Subgenus †Eosaurichthys Liu & Wei, 1988
- †Saurichthys (Eosaurichthys) chaoi (Liu and Wei 1988) (type species)
- †Saurichthys (Eosaurichthys) madagascariensis Piveteau 1945[16]
- Subgenus †Lepidosaurichthys Tintori, 2013[15]
- †Saurichthys (Lepidosaurichthys) dayi (Raymond 1925) (type species)
- †Saurichthys (Lepidosaurichthys) elongatus Stensiö 1925
- †Saurichthys (Lepidosaurichthys) ornatus Stensiö 1925
- †Saurichthys (Lepidosaurichthys) toxolepis Mutter et al. 2008
- †Saurichthys (Lepidosaurichthys) wimani (Woodward 1912)[17]
- Subgenus †Sinosaurichthys Wu et al., 2010[1]
- †Saurichthys (Sinosaurichthys) longipectoralis Wu et al. 2009 (type species)
- †Saurichthys (Sinosaurichthys) longimedialis Wu et al. 2009
- †Saurichthys (Sinosaurichthys) minuta Wu et al. 2009
- Genus †Saurorhynchus Reis, 1892 [Acidorhynchus Stensiö, 1925][18]
- †Saurichthys (Saurorhynchus) calcaratus Griffith 1977[19]
- †Saurichthys (Saurorhynchus) deperditus (Costa 1862)
- †Saurichthys (Saurorhynchus) striolatus Bronn 1858[19]
- †Saurorhynchus acutus (Agassiz 1844) (type species)
- †Saurorhynchus anningae Maxwell & Stumpf 2017
- †Saurorhynchus brevirostris (Woodward 1895)
- †Saurorhynchus hauffi Maxwell & Stumpf 2017
- Genus †Saurichthys Agassiz, 1834 [Belonorhynchus Bronn 1858; Brevisaurichthys Beltan 1972; Giffonus Costa 1862; Gymnosaurichthys Berg 1940; Ichthyorhynchus Bellotti 1857; Stylorhynchus Martin 1873, non Lesson 1847, non Stein 1848; Systolichthys Beltan 1972]
- Family †Yelangichthyidae Wu et al., 2013
- Genus †Yelangichthys Wu et al., 2013
- †Yelangichthys macrocephalus Wu et al., 2013 (type species)
- Genus †Yelangichthys Wu et al., 2013
- Family †Saurichthyidae Owen 1860 [Saurichthyoidei Bleeker 1859; Belonorhynchidae Woodward 1888; Saurorhynchidae Jordan, 1905]
Phylogeny
[edit]Modified from Maxwell et al.[20] (also see Renesto et al.,[21] Argyriou et al.[6] and Gardiner et al.[22])
| Actinopteri |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Timeline of genera
[edit]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Wu Feixiang; Sun Yuanlin; Xu Guanghui; Hao Weicheng; Jiang Dayong; Sun Zuoyu (2010). "New saurichthyid fishes (Actinopterygii) from the Middle Triassic (Pelsonian, Anisian) of southwestern China" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 56. doi:10.4202/app.2010.0007. S2CID 54877125.
- ^ Stensiö, E. (1925). "Triassic Fishes from Spitzebergen, Part II". Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlinga. 2: 1–126.
- ^ Cartanyà, J., ed. (1999). An overview of the Middle Triassic actinopterygians from Alcover, Mont-ral and El Pinetell (Catalonia, Spain). In: G. Arratia and H. P. Schultze (eds.) Mesozoic Fishes 2—Systematics and Fossil Record: Verlag Dr. F. Pfeil, München. pp. 535–551.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Maxwell, E.E. (2016): First Middle Jurassic record of Saurichthyidae (Actinopterygii). Paläontologische Zeitschrift 90:287-291 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12542-015-0281-5
- ^ Romano C., Kogan I., Jenks J., Jerjen I., Brinkmann W. (2012). "Saurichthys and other fossil fishes from the late Smithian (Early Triassic) of Bear Lake County (Idaho, USA), with a discussion of saurichthyid palaeogeography and evolution" (PDF). Bulletin of Geosciences. 87: 543–570. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1337.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Argyriou, Thodoris; Giles, Sam; Friedman, Matt; Romano, Carlo; Kogan, Ilja; Sánchez-Villagra, Marcelo R. (December 2018). "Internal cranial anatomy of Early Triassic species of †Saurichthys (Actinopterygii: †Saurichthyiformes): implications for the phylogenetic placement of †saurichthyiforms". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 18 (1): 161. Bibcode:2018BMCEE..18..161A. doi:10.1186/s12862-018-1264-4. ISSN 1471-2148. PMC 6211452. PMID 30382811.
- ^ Haaramo, Mikko (2007). "†Saurichthyiformes". Mikko's Phylogeny Archive. Retrieved 30 December 2016.
- ^ Nelson, Joseph S.; Grande, Terry C.; Wilson, Mark V. H. (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118342336.
- ^ van der Laan, Richard (2016). "Family-group names of fossil fishes" (PDF). Retrieved 2023-12-06.
- ^ a b Discovery of two new species of primitive fishes
- ^ Silvio Renesto; Fabio Magnani; Rudolf Stockar (2021). "A new species of Saurichthys (Actinopterygii: Saurichtydae) from the Middle Triassic of Monte San Giorgio". Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 127 (1): 49–71. doi:10.13130/2039-4942/15143.
- ^ Fei-Xiang Wu; Yuan-Lin Sun; Geng-Yu Fang (2018). "A new species of Saurichthys from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of southwestern China". Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 56 (4): 273–294. doi:10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.171023.
- ^ Fang, G., Wu, F.X. (2022). "The predatory fish Saurichthys reflects a complex underwater ecosystem of the Late Triassic Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, China". Historical Biology. 35 (8): 1–11. doi:10.1080/08912963.2022.2098023. S2CID 250567176.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Fossilworks: Saurichthys Agassiz 1843
- ^ a b Tintori, Andrea (2013). "A new species of Saurichthys (Actinopterygii) from the Middle Triassic (early Ladinian) of the northern Grigna Mountain (Lombardy, Italy)". Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 119 (3): 287–302. doi:10.13130/2039-4942/6041.
- ^ Kogan , Romano (2016). "Redescription of Saurichthys madagascariensis Piveteau, 1945 (Actinopterygii, Early Triassic), with implications for the early saurichthyid morphotype". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 36 (4): e1151886. Bibcode:2016JVPal..36E1886K. doi:10.1080/02724634.2016.1151886. S2CID 87234436.
- ^ Kogan, Ilja; Romano, Carlo (2016). "A new postcranium of Saurichthys from the Early Triassic of Spitsbergen" (PDF). Freiberger Forschungshefte C (Paläontologie, Stratigraphie, Fazies 23). 550: 205–221. ISBN 9783860125526.
- ^ Kogan, I. (2016): Acidorhynchus Stensiö, 1925 or Saurorhynchus Reis, 1892: how to call the Jurassic saurichthyid? Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie-Abhandlungen 279:123-126 https://doi.org/10.1127/njgpa/2016/0545
- ^ a b Ilja Kogan; Andrea Tintori; Martin Licht (2020). "Locomotor function of scales and axial skeleton in Middle-Late Triassic species of Saurichthys (Actinopterygii". Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 126 (2): 475–498. doi:10.13130/2039-4942/13551. S2CID 244984857.
- ^ Maxwell, E.E.; Romano, C. & Wu, F.-X. (2021). "Regional disparity in the axial skeleton of Saurichthyidae and implications for axial regionalization in non-teleostean actinopterygians". Journal of Zoology. 315: 29–41. doi:10.1111/jzo.12878. ISSN 0952-8369.
- ^ Silvio Renesto; Fabio Magnani; Rudolf Stockar (2021). "A new species of Saurichthys (Actinopterygii: Saurichtydae) from the Middle Triassic of Monte San Giorgio". Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 127 (1): 49–71. doi:10.13130/2039-4942/15143.
- ^ Gardiner, B.G.; Schaeffer, B. & Masserie, J.A. (2005). "A review of the lower actinopterygian phylogeny". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 144 (4): 511–525. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2005.00181.x.
Additional references
[edit]- Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera". Bulletins of American Paleontology. 364: 560. Retrieved 2011-05-17.