HER2/neu
外观
(重定向自HER2)
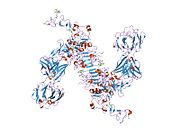
人类表皮生长因子受体2(英语:human epidermal growth factor receptor 2,缩写为HER2,亦称为Neu、ErbB-2、CD340(分化群340)或p185)是一种由ERBB2基因编码的蛋白质。HER2是表皮生长因子受体(EGFR/ErbB)家族的成员。
功能
[编辑]HER2是结合在细胞膜表面的受体酪氨酸激酶,参与导致细胞生长和分化的信号转导途径,由原癌基因HER2/neu编码。一般认为HER2是一个孤受体,表皮生长因子家族的配体都不能激活它。但配体结合ErbB受体时可形成二聚体,且HER2可与ErbB家族的其他成员结合成异二聚体。[7]HER2基因是原癌基因,位于人类17号染色体长臂(17q21-q22)。[8]
与癌症的关系
[编辑]HER-2基因是影响乳癌预后的一个重要因素,大约有25%-30%左右的乳癌患者,受到体内癌细胞HER-2基因过量表现的影响,他们的癌细胞不仅繁殖能力强,对部分化学治疗药物也容易有抗药性,造成病患即使接受手术治疗,癌细胞仍然有较高复发及转移的几率,无法长期存活。
乳癌病患可分为Her-2/neu阳性或Her-2/neu阴性两种截然不同的预后之乳癌。乳癌患者的肿瘤,若HER-2蛋白质出现过量表现,这类的肿瘤生长速度较快且生物行为较为恶性,使得手术后复发率高于其他类型的乳癌。[9]

针对HER2的药物
[编辑]罗氏药厂开发的贺癌平(Herceptin)即是以HER2为标靶的药物,对晚期转移性的乳腺癌颇具效用。
- 重组型人源化单克隆抗体 Trastuzumab (Herceptin®), 是IgG1 monoclonal antibody,可透过结合到乳癌细胞膜上的HER2 receptor的Domain4去抑制下游的hetero- and homodimerization和信号传递。;
- 完全人源化单克隆抗体 Pertuzumab (Perjeta®),和Trastuzumab药理作用位点相似,但Pertuzumab 是结合在HER2的Domain2,去抑制下游路径,而且因为Domain2是属于extracellular receptor dimerization,因此可防止其他的HER family members和HER2进行dimerization,从而抑制了ligand-induced signaling,抑制了细胞生长而进行细胞凋亡,其中HER2/HER3被认为是下游通路激活的最强二聚体;
- 单抗结合型药物 Ado-Trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla®),为新药,是一种Antibody和Drug的conjugate(ADC)。Trastuzumab上述已介绍过他的作用位点,而新药T-DM1则是将Trastuzumab和maytansine 1用thioether键结起来,DM1即derivative of maytansine 1,是一种合成Microtubule 过程中dimerization的抑制剂,将Trastuzumab和cytotoxic agent DM1结合,除了有Trastuzumab本身能够与HER2 receptor Domain4结合,进而停止了癌细胞的生长,DM1透过receptor-mediated进入细胞内作用,并在lysosome内代谢,释放出含DM1的代谢产物,此物质可结合在Microtubule上,导致有丝分裂终止和细胞死亡。[10]
- Neratinib,为口服制剂,irreversible inhibitor,抑制HER2 and EGFR protein tyrosine kinase(TK)。[11]
- 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂 Lapatinib Ditosylate (Tykerb®),口服制剂,和Neratinib相似,一样是EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinase的抑制剂。[11]
- mTOR 抑制剂 Everolimus (Afinitor®)
相互作用
[编辑]参考文献
[编辑]- ^ 與HER2/neu相關的疾病;在維基數據上查看/編輯參考.
- ^ 對人类表皮生长因子受体II起作用的藥物;在維基數據上查看/編輯參考.
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000141736 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000062312 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ Human PubMed Reference:. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Mouse PubMed Reference:. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Olayioye MA. Update on HER-2 as a target for cancer therapy: intracellular signaling pathways of ErbB2/HER-2 and family members. Breast Cancer Res. 2001, 3 (6): 385–389. PMID 11737890. doi:10.1186/bcr327.
- ^ Coussens L. Tyrosine Kinase Receptor with Extensive Homology to EGF Receptor Shares Chromosomal Location with neu Oncogene. Science. 1985, 230: 1132–1139. doi:10.1126/science.2999974.
- ^ HER-2陽性早期乳癌治療的近況. 台湾癌症防治网. 2009年10月16日 [2009-10-06]. (原始内容存档于2011年5月25日).
- ^ Sadeghi, S., Olevsky, O., & Hurvitz, S. A. (2014). Profiling and targeting HER2-positive breast cancer using trastuzumab emtansine. Pharmacogenomics and personalized medicine, 7, 329.
- ^ 11.0 11.1 Goodman, L. S. (1996). Goodman and Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics (Vol. 1549). New York: McGraw-Hill.P.1208
深入阅读
[编辑]- Ross JS, Fletcher JA, Linette GP; et al. The Her-2/neu gene and protein in breast cancer 2003: biomarker and target of therapy. Oncologist. 2003, 8 (4): 307–25. PMID 12897328. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.8-4-307.
- Zhou BP, Hung MC. Dysregulation of cellular signaling by HER2/neu in breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30 (5 Suppl 16): 38–48. PMID 14613025. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2003.08.006.
- Ménard S, Casalini P, Campiglio M; et al. Role of HER2/neu in tumor progression and therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 61 (23): 2965–78. PMID 15583858. doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4277-7.
- Becker JC, Muller-Tidow C, Serve H; et al. Role of receptor tyrosine kinases in gastric cancer: new targets for a selective therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12 (21): 3297–305. PMID 16733844.
- Laudadio J, Quigley DI, Tubbs R, Wolff DJ. HER2 testing: a review of detection methodologies and their clinical performance. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 7 (1): 53–64. PMID 17187484. doi:10.1586/14737159.7.1.53.
- Bianchi F, Tagliabue E, Ménard S, Campiglio M. Fhit expression protects against HER2-driven breast tumor development: unraveling the molecular interconnections. Cell Cycle. 2007, 6 (6): 643–6. PMID 17374991. doi:10.4161/cc.6.6.4033.
- Del Bimbo A., Meoni M., Pala P. Accurate evaluation of HER-2 amplification in FISH images. Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), 2010 IEEE International Conference on. 2010: 407–10. ISBN 978-1-4244-6492-0. doi:10.1109/IST.2010.5548461.
外部链接
[编辑]- ERBB2 expression across human cancerous and healthy tissues[永久失效链接]
- AACR Cancer Concepts Factsheet on HER2
- Her2/neu Vaccine Protects Against Tumor Growth
- Chimeric molecules and Methods of Use
- Breast Friends for Life Network - A South African Breast Cancer Support Forum for HER2 Positive Women
- 医学主题词表(MeSH):Receptor,+erbB-2