VAMP1
Vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (VAMP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAMP1 gene.[5][6]
Function
[edit]Synaptobrevins/VAMPs, syntaxins, and the 25-kD synaptosomal-associated protein SNAP25 are the main components of a protein complex involved in the docking and/or fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. VAMP1 is a member of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)/synaptobrevin family. Multiple alternative splice variants that encode proteins with alternative carboxy ends have been described, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been defined.[6]
Clinical significance
[edit]Homozygous mutations in VAMP1 have been identified in a series of children affected with a form of congenital myasthenic syndrome and similar presynaptic features in these patients and the knock-out VAMP1 mouse have been demonstrated.[7]
VAMP1 expression has been linked to higher survival rates for lung cancer patients.[8]
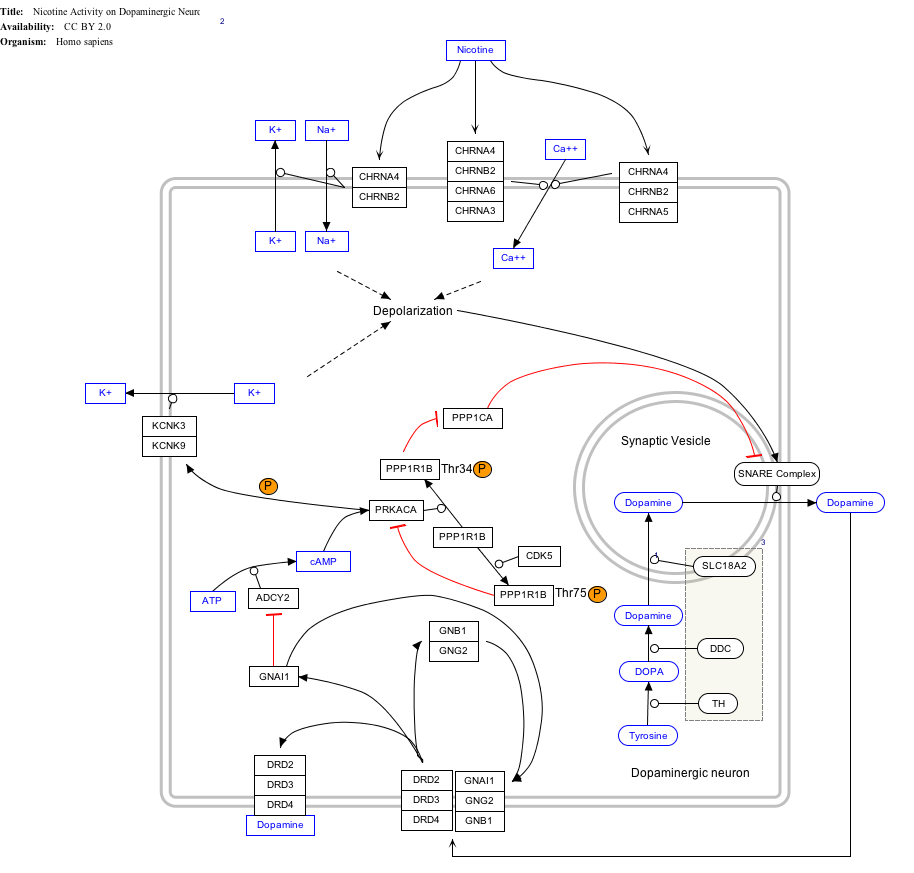
Interactive pathway map
[edit]Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.[§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "NicotineDopaminergic_WP1602".
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000139190 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030337 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Archer BT, Ozçelik T, Jahn R, Francke U, Südhof TC (October 1990). "Structures and chromosomal localizations of two human genes encoding synaptobrevins 1 and 2". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 265 (28): 17267–73. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)44898-8. PMID 1976629.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: VAMP1 vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (synaptobrevin 1)".
- ^ Salpietro V, Lin W, Delle Vedove A, Storbeck M, Liu Y, Efthymiou S, Manole A, Wiethoff S, Ye Q, Saggar A, McElreavey K, Krishnakumar SS, Pitt M, Bello OD, Rothman JE, Basel-Vanagaite L, Hubshman MW, Aharoni S, Manzur AY, Wirth B, Houlden H (April 2017). "Homozygous mutations in VAMP1 cause a presynaptic congenital myasthenic syndrome". Annals of Neurology. 81 (4): 597–603. doi:10.1002/ana.24905. PMC 5413866. PMID 28253535.
- ^ "Research update from the MCM team (March 2023)". World Community Grid. 20 March 2023. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
Further reading
[edit]- Ravichandran V, Chawla A, Roche PA (June 1996). "Identification of a novel syntaxin- and synaptobrevin/VAMP-binding protein, SNAP-23, expressed in non-neuronal tissues". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (23): 13300–3. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.23.13300. PMID 8663154.
- Jagadish MN, Fernandez CS, Hewish DR, Macaulay SL, Gough KH, Grusovin J, Verkuylen A, Cosgrove L, Alafaci A, Frenkel MJ, Ward CW (August 1996). "Insulin-responsive tissues contain the core complex protein SNAP-25 (synaptosomal-associated protein 25) A and B isoforms in addition to syntaxin 4 and synaptobrevins 1 and 2". The Biochemical Journal. 317. 317 ( Pt 3) (3): 945–54. doi:10.1042/bj3170945. PMC 1217577. PMID 8760387.
- Annaert WG, Becker B, Kistner U, Reth M, Jahn R (December 1997). "Export of cellubrevin from the endoplasmic reticulum is controlled by BAP31". The Journal of Cell Biology. 139 (6): 1397–410. doi:10.1083/jcb.139.6.1397. PMC 2132629. PMID 9396746.
- Weir ML, Klip A, Trimble WS (July 1998). "Identification of a human homologue of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)-associated protein of 33 kDa (VAP-33): a broadly expressed protein that binds to VAMP". The Biochemical Journal. 333. 333 ( Pt 2) (2): 247–51. doi:10.1042/bj3330247. PMC 1219579. PMID 9657962.
- Isenmann S, Khew-Goodall Y, Gamble J, Vadas M, Wattenberg BW (July 1998). "A splice-isoform of vesicle-associated membrane protein-1 (VAMP-1) contains a mitochondrial targeting signal". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 9 (7): 1649–60. doi:10.1091/mbc.9.7.1649. PMC 25402. PMID 9658161.
- Nishimura Y, Hayashi M, Inada H, Tanaka T (January 1999). "Molecular cloning and characterization of mammalian homologues of vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated (VAMP-associated) proteins". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 254 (1): 21–6. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9876. PMID 9920726.
- Berglund L, Hoffmann HJ, Dahl R, Petersen TE (November 1999). "VAMP-1 has a highly variable C-terminus generated by alternative splicing". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 264 (3): 777–80. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1588. PMID 10544008.
- Pérez-Brangulí F, Muhaisen A, Blasi J (June 2002). "Munc 18a binding to syntaxin 1A and 1B isoforms defines its localization at the plasma membrane and blocks SNARE assembly in a three-hybrid system assay". Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences. 20 (2): 169–80. doi:10.1006/mcne.2002.1122. PMID 12093152. S2CID 23927545.
- Imabayashi H, Mori T, Gojo S, Kiyono T, Sugiyama T, Irie R, Isogai T, Hata J, Toyama Y, Umezawa A (August 2003). "Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated chondrocytes and chondrogenesis of human bone marrow stromal cells via chondrosphere formation with expression profiling by large-scale cDNA analysis". Experimental Cell Research. 288 (1): 35–50. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00130-7. PMID 12878157.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.